principles of genetics
... Linkage and crossing over, Cytological basis of crossing over, Molecular mechanisms of crossing over, Recombination frequency as a measure of linkage intensity, Two factor and three factor crosses, Interference and coincidence, Somatic cell hybridization. Unit 3: Mutations ...
... Linkage and crossing over, Cytological basis of crossing over, Molecular mechanisms of crossing over, Recombination frequency as a measure of linkage intensity, Two factor and three factor crosses, Interference and coincidence, Somatic cell hybridization. Unit 3: Mutations ...
DNA
... alteration. Tumor-Suppressor Genes : inhibit expression of tumor phenotype. When are inactivated or lost abnormal proliferation Oncogenes :Genes which can potentially induce neoplastic transformation. They include genes for growth factors, growth factor receptors, protein ...
... alteration. Tumor-Suppressor Genes : inhibit expression of tumor phenotype. When are inactivated or lost abnormal proliferation Oncogenes :Genes which can potentially induce neoplastic transformation. They include genes for growth factors, growth factor receptors, protein ...
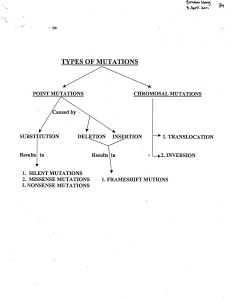
CHROMOSAL MUTATIONS SUBSTITUTION
... • Some mutations in the genome lead to the developme nt of diseases that may be inherited. Example: Cystic Fibrosis disease is an example of Negative (deleteriou s) Side Effect. Mutations in the Cystic Fibrosis Transmem brane Regulator (CFTR) gene that res~lt in Cystic Fibrosis can be passed on from ...
... • Some mutations in the genome lead to the developme nt of diseases that may be inherited. Example: Cystic Fibrosis disease is an example of Negative (deleteriou s) Side Effect. Mutations in the Cystic Fibrosis Transmem brane Regulator (CFTR) gene that res~lt in Cystic Fibrosis can be passed on from ...
Mutations Foldable
... Color the segment of DNA that has been deleted; next to the picture write: Deletions occur when a segment of DNA has been removed Color the segment of DNA that has been inverted; next to the picture write: Inversions occur when a segment of DNA has been flipped Color the segment of DNA that has been ...
... Color the segment of DNA that has been deleted; next to the picture write: Deletions occur when a segment of DNA has been removed Color the segment of DNA that has been inverted; next to the picture write: Inversions occur when a segment of DNA has been flipped Color the segment of DNA that has been ...
Life 101 - findyourtao2011
... Definition: The rate of the “movement” or flow of an organism within a group of organisms and between different groups. The immigration and emigration of organisms and its genes. Gene Flow depends on the organism. Corn, for example, have a low rate of gene flow because it is stationary and is wind p ...
... Definition: The rate of the “movement” or flow of an organism within a group of organisms and between different groups. The immigration and emigration of organisms and its genes. Gene Flow depends on the organism. Corn, for example, have a low rate of gene flow because it is stationary and is wind p ...
Spineless Fish and Dark Flies Prove Gene Regulation Crucial
... activity of a gene called ebony. abstract/science.1182213), two The new work narrows down teams not only independently the cause to an enhancer upstream report that changes in regulatory Color coordinated. In Africa, lowland fruit flies are light-colored, whereas those of the gene. By dissecting the ...
... activity of a gene called ebony. abstract/science.1182213), two The new work narrows down teams not only independently the cause to an enhancer upstream report that changes in regulatory Color coordinated. In Africa, lowland fruit flies are light-colored, whereas those of the gene. By dissecting the ...
The Modern Synthesis: Evolution and Genetics
... – Eg: human populations that eat a lot of starch have two copies of genes for starch proteins, make double the protein ...
... – Eg: human populations that eat a lot of starch have two copies of genes for starch proteins, make double the protein ...
OUTLINE OF GENETICS LECTURE #1 A. TERMS PHENOTYPE
... nitrous acid. Treatment of cells results in oxidative deamination of cytosine, which then resembles uracil, which will base pair with a T. This change will cause a mutation to occur during DNA replication whereby a C-G base pair is converted T-A. Alklyating agents such as ethyl methane sulfonate whi ...
... nitrous acid. Treatment of cells results in oxidative deamination of cytosine, which then resembles uracil, which will base pair with a T. This change will cause a mutation to occur during DNA replication whereby a C-G base pair is converted T-A. Alklyating agents such as ethyl methane sulfonate whi ...
PGS: 454 – 458
... individuals survive in their environment and reproduce. Some mutations do not help an organism survive. Other mutations have no effect. b. If a mutation (change) occurs in the DNA of sex cells (gametes) of the parent(s), then those changes could be inherited by the offspring (next generation). c. In ...
... individuals survive in their environment and reproduce. Some mutations do not help an organism survive. Other mutations have no effect. b. If a mutation (change) occurs in the DNA of sex cells (gametes) of the parent(s), then those changes could be inherited by the offspring (next generation). c. In ...
Genetic Mutations
... • Red blood cells form an abnormal crescent shape • Hemoglobin (protein) is abnormally shaped • don't move easily through your blood vessels • form clumps and get stuck in the blood vessels ...
... • Red blood cells form an abnormal crescent shape • Hemoglobin (protein) is abnormally shaped • don't move easily through your blood vessels • form clumps and get stuck in the blood vessels ...
Double helix- a double twist
... We get half our DNA from mom and half from Dad. Get a mixture of their genes which code the same proteins and traits that they have. ...
... We get half our DNA from mom and half from Dad. Get a mixture of their genes which code the same proteins and traits that they have. ...
Mutations File
... c. Rewrite the amino acid sequence with the mutated strand. d. Is this considered a “silent” mutation (a mutation that causes no changes) or is it an “expressed” mutation (a mutation that causes a change in the amino acid sequence, and therefore a change in the protein?) 5. What are two sources of m ...
... c. Rewrite the amino acid sequence with the mutated strand. d. Is this considered a “silent” mutation (a mutation that causes no changes) or is it an “expressed” mutation (a mutation that causes a change in the amino acid sequence, and therefore a change in the protein?) 5. What are two sources of m ...
Effects of DNA Mutations in Sex Cells… Genetic Disease or Birth
... may be webbing gene OR between it may fingers occur asand a spontaneous toes. Bones in hands mutation and(which feet become meansfused it’s not resulting linked to in heredity. less flexibility and function. ...
... may be webbing gene OR between it may fingers occur asand a spontaneous toes. Bones in hands mutation and(which feet become meansfused it’s not resulting linked to in heredity. less flexibility and function. ...
File
... • Chemical mutagens associated with one or more forms of cancer • Cancer is uncontrolled cell division • The result of somatic cells that disrupt the expression of genes involved in regulation of the cell cycle ...
... • Chemical mutagens associated with one or more forms of cancer • Cancer is uncontrolled cell division • The result of somatic cells that disrupt the expression of genes involved in regulation of the cell cycle ...
No Slide Title
... Figure 2. Occurrence of somatic mutation in one DNA strand in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Somatic mutation was induced in BL2 cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Single cells were either analyzed for mutations in the V4-39 gene after 90 min of stimulation or isolated in single wells and l ...
... Figure 2. Occurrence of somatic mutation in one DNA strand in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Somatic mutation was induced in BL2 cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Single cells were either analyzed for mutations in the V4-39 gene after 90 min of stimulation or isolated in single wells and l ...
Mutations and Metabolic Pathways
... In the above diagram, the enzymes are shown in red. Discuss why patients with Porphyria may have different causes of the disorder, and how two parents with Porphyria could give birth to children who do not have it. In your answer you should consider: ...
... In the above diagram, the enzymes are shown in red. Discuss why patients with Porphyria may have different causes of the disorder, and how two parents with Porphyria could give birth to children who do not have it. In your answer you should consider: ...
The role of positive selection in molecular evolution
... evolution postulates that random genetic drift, not selection, is the major driving force behind evolution at the molecular level. Here, we address this question within a Poisson Random Field framework, based on aligned DNA sequence data from two closely related species. We investigate heavy-tailed ...
... evolution postulates that random genetic drift, not selection, is the major driving force behind evolution at the molecular level. Here, we address this question within a Poisson Random Field framework, based on aligned DNA sequence data from two closely related species. We investigate heavy-tailed ...
iiiliiiltiiliiiitii lilliitlii$itttit ffffli|tiiiiiiHii.
... interfere with DNA replication and lead to mutation. Whenever a cell copiesits DNA, there is a small chance it may misread the sequenceand add the wrong nucleotide. Our cells have proofreading proteins that can fix most of these errors, but they sometimes let mistakesslip bv. Mutations alter DNA in ...
... interfere with DNA replication and lead to mutation. Whenever a cell copiesits DNA, there is a small chance it may misread the sequenceand add the wrong nucleotide. Our cells have proofreading proteins that can fix most of these errors, but they sometimes let mistakesslip bv. Mutations alter DNA in ...
5.6 Mutations
... Usually occurs between two nonhomologous chromosomes. Result is a fusion protein with an altered function ...
... Usually occurs between two nonhomologous chromosomes. Result is a fusion protein with an altered function ...
Molecular Biology (Ms. Lucky Juneja)
... Most mutations affect only one base pair in a given location and therefore are called point mutations. There are several types of point mutations: 1.Silent mutation: If a mutation is an alteration of the nucleotide sequence of DNA, mutations can occur and have no visible effect because of code dege ...
... Most mutations affect only one base pair in a given location and therefore are called point mutations. There are several types of point mutations: 1.Silent mutation: If a mutation is an alteration of the nucleotide sequence of DNA, mutations can occur and have no visible effect because of code dege ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.