Chapter 12 guided Notes 2
... To understand genetics, biologists had to learn the chemical makeup of a gene. Scientists discovered that genes are made up of DNA. Scientist also found that DNA stores and transmits the genetic information from one generation to the next. Scientists began studying DNA structure to find out how it c ...
... To understand genetics, biologists had to learn the chemical makeup of a gene. Scientists discovered that genes are made up of DNA. Scientist also found that DNA stores and transmits the genetic information from one generation to the next. Scientists began studying DNA structure to find out how it c ...
File
... Produces a chromosome that is totally different from the original chromosomes of both parents Takes place during Meiosis Two chromosomes intertwine and exchange one end of the chromosome with the other ...
... Produces a chromosome that is totally different from the original chromosomes of both parents Takes place during Meiosis Two chromosomes intertwine and exchange one end of the chromosome with the other ...
Chromosomes and Inertitance
... Somatic-cell mutation – mutations that occur in organisms body cells ...
... Somatic-cell mutation – mutations that occur in organisms body cells ...
Epigenetic Clock and Biological Age Steve Horvath, Professor of
... Steve Horvath, Professor of Human Genetics and Biostatistics, University of California, Los Angeles The DNA methylation based biomarker of aging known as the "epigenetic clock" can be used to measure the DNA methylation (DNAm) age of any human (or chimpanzee) tissue, cell type, or fluid that contain ...
... Steve Horvath, Professor of Human Genetics and Biostatistics, University of California, Los Angeles The DNA methylation based biomarker of aging known as the "epigenetic clock" can be used to measure the DNA methylation (DNAm) age of any human (or chimpanzee) tissue, cell type, or fluid that contain ...
Genetic Principles
... • The probability of a fit this good by chance is .00007 • Possible that Mendel’s sample size was larger than he reported. ...
... • The probability of a fit this good by chance is .00007 • Possible that Mendel’s sample size was larger than he reported. ...
Advances in Genetics
... Inbreeding • Inbreeding involves crossing two individuals that have similar characteristics • Inbred organisms have alleles very similar to their parents • This increases the chance of a genetic disorder showing in the offspring ...
... Inbreeding • Inbreeding involves crossing two individuals that have similar characteristics • Inbred organisms have alleles very similar to their parents • This increases the chance of a genetic disorder showing in the offspring ...
Intro to Genetics Webquest
... 18) The passing of traits from parents to a child is the basis of ...
... 18) The passing of traits from parents to a child is the basis of ...
part - MOCKSTER.NET!
... one trait is more favorable, so is favored Overproduction these come about from mutations and may or may not be helpful Variation over time, one species may become several Adaptations there is naturally variety among individuals in a population Selection all species tend to produce more offspring th ...
... one trait is more favorable, so is favored Overproduction these come about from mutations and may or may not be helpful Variation over time, one species may become several Adaptations there is naturally variety among individuals in a population Selection all species tend to produce more offspring th ...
Exploring Mutant Organisms Teacher Extended Background
... originated from the same population and had spread out over numerous islands. Some birds developed physical traits, specifically distinct beak shapes, which gave them an advantage in their new habitats and made it easier for them to access food. Darwin suggested that these advantageous traits were p ...
... originated from the same population and had spread out over numerous islands. Some birds developed physical traits, specifically distinct beak shapes, which gave them an advantage in their new habitats and made it easier for them to access food. Darwin suggested that these advantageous traits were p ...
genetics Study Guide(fall 2016) - new book)
... what is a dihybrid cross? how is it similar and different than single gene inheritance? the law of independent assortment solve dihybrid cross problems using two methods - a 16 square (dihybrid) Punnett square and also mathematically, using the Law of Products more terms used in genetics (mutation, ...
... what is a dihybrid cross? how is it similar and different than single gene inheritance? the law of independent assortment solve dihybrid cross problems using two methods - a 16 square (dihybrid) Punnett square and also mathematically, using the Law of Products more terms used in genetics (mutation, ...
mutated
... Causes of Mutations Spontaneous mutations Damage may occur at any time in any cell. Errors during chromosome replication happen only about once in 100,000 bases. Given that the human genome has about 6 billion bases, this means each replication cycle will have 60,000 errors associated with it. Cell ...
... Causes of Mutations Spontaneous mutations Damage may occur at any time in any cell. Errors during chromosome replication happen only about once in 100,000 bases. Given that the human genome has about 6 billion bases, this means each replication cycle will have 60,000 errors associated with it. Cell ...
Mutations 1
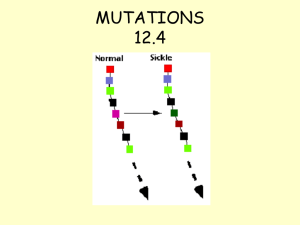
... strand of the gene, after replication daughter DNA molecules with mutations in coding strand will appear in the next population of organisms. Types of mutations 1-Base-substitution mutations Single base changes (point mutations) may be transitions or transversions. In transition mutation, pyrimi ...
... strand of the gene, after replication daughter DNA molecules with mutations in coding strand will appear in the next population of organisms. Types of mutations 1-Base-substitution mutations Single base changes (point mutations) may be transitions or transversions. In transition mutation, pyrimi ...
BIOL290
... A. Understand the changes that can occur in chromosomes, such as translocation, inversion, deletion, duplication, and loss/gain of genetic material. B. Review the terms euploidy and aneuploidy and be able to recognize examples of each. C. Understand the correlation between chromosome sets and size o ...
... A. Understand the changes that can occur in chromosomes, such as translocation, inversion, deletion, duplication, and loss/gain of genetic material. B. Review the terms euploidy and aneuploidy and be able to recognize examples of each. C. Understand the correlation between chromosome sets and size o ...
study guide - cloudfront.net
... 5. What are the differences between mitosis and meiosisII? (notes) 6. How many and what type of cells are produced in meiosis? (p.276) 7. What cells and where in the body does mitosis occur (hint: somatic or sex cells)?(notes) 8. What cells and where in the body does meiosis occur? (use the hint fro ...
... 5. What are the differences between mitosis and meiosisII? (notes) 6. How many and what type of cells are produced in meiosis? (p.276) 7. What cells and where in the body does mitosis occur (hint: somatic or sex cells)?(notes) 8. What cells and where in the body does meiosis occur? (use the hint fro ...
File
... Mutations can arise in a number of ways. Errors during DNA replication or recombination can lead to nucleotide-pair substitutions, insertions, or deletions, as well as to mutations affecting longer stretches of DNA. If an incorrect nucleotide is added to a growing chain during replication, for exampl ...
... Mutations can arise in a number of ways. Errors during DNA replication or recombination can lead to nucleotide-pair substitutions, insertions, or deletions, as well as to mutations affecting longer stretches of DNA. If an incorrect nucleotide is added to a growing chain during replication, for exampl ...
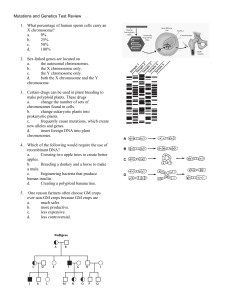
Mutations and Genetics Test Review 1. What percentage of human
... Mutations and Genetics Test Review 1. What percentage of human sperm cells carry an X chromosome? a. ...
... Mutations and Genetics Test Review 1. What percentage of human sperm cells carry an X chromosome? a. ...
Name____________________________ DNA Investigation
... 5) Other than providing the instructions for building a hemoglobin molecule, what are two other examples provided in the slideshow of traits that are controlled by genes? C) At the top of the web-page, click on “What is a Chromosome?” and watch the slideshow. 6) Look at the set of human chromosomes ...
... 5) Other than providing the instructions for building a hemoglobin molecule, what are two other examples provided in the slideshow of traits that are controlled by genes? C) At the top of the web-page, click on “What is a Chromosome?” and watch the slideshow. 6) Look at the set of human chromosomes ...
8.7 Mutations
... D. Chromosomal mutations affect many genes. 2. 2 types of chromosomal mutations. 1. Gene duplication results from unequal crossing over 2. Translocation results from the exchange of DNA segments between nonhomologous chromosomes. 3. Chromosomal mutations tend to have a bigger affect on the individua ...
... D. Chromosomal mutations affect many genes. 2. 2 types of chromosomal mutations. 1. Gene duplication results from unequal crossing over 2. Translocation results from the exchange of DNA segments between nonhomologous chromosomes. 3. Chromosomal mutations tend to have a bigger affect on the individua ...
Gene Technology
... An average adult male liger can weigh over 900 pounds. An adult male Siberian tiger can grow to an average weight of 500 pounds, An adult African lion can average 450 pounds. The reproductive process that creates a liger leaves out the growth inhibitor gene present in the male lion and the female ti ...
... An average adult male liger can weigh over 900 pounds. An adult male Siberian tiger can grow to an average weight of 500 pounds, An adult African lion can average 450 pounds. The reproductive process that creates a liger leaves out the growth inhibitor gene present in the male lion and the female ti ...
Characteristics of Living Things (Essay
... CELL DIVISION & GENETICS 2. Mitosis & Meiosis & the Cell Cycle Diploid vs. haploid Somatic vs. germ cell Importance of each process Stages. What happens? When? Spermatogenesis & Oogenesis 2. DNA in different forms DNA basic structure. Remember nucleotides? Drawings? What is a gene? Cen ...
... CELL DIVISION & GENETICS 2. Mitosis & Meiosis & the Cell Cycle Diploid vs. haploid Somatic vs. germ cell Importance of each process Stages. What happens? When? Spermatogenesis & Oogenesis 2. DNA in different forms DNA basic structure. Remember nucleotides? Drawings? What is a gene? Cen ...
Slide 1
... • Not all mutations are bad – some make bacteria ANTI-BIOTIC RESISTANT. Good for the bacteria, not-so-good for you! • Some mutations result in no change ...
... • Not all mutations are bad – some make bacteria ANTI-BIOTIC RESISTANT. Good for the bacteria, not-so-good for you! • Some mutations result in no change ...
Biology 218 Microbial Metabolism and Genetics Chapter Six
... Prokaryotic Genetics Review Vocabulary Phenotype: physical traits Genotype: genetic make-up Mutations: replication errors, single base pairs Recombination: rearranging or acquiring genes ...
... Prokaryotic Genetics Review Vocabulary Phenotype: physical traits Genotype: genetic make-up Mutations: replication errors, single base pairs Recombination: rearranging or acquiring genes ...
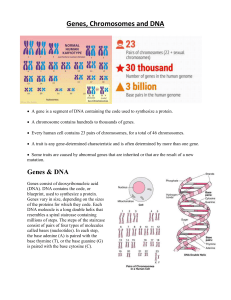
Genes Chromosomes and DNA
... A trait is any gene-determined characteristic and is often determined by more than one gene. Some traits are caused by abnormal genes that are inherited or that are the result of a new mutation. ...
... A trait is any gene-determined characteristic and is often determined by more than one gene. Some traits are caused by abnormal genes that are inherited or that are the result of a new mutation. ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.