Glossary - The Birman Cat Club
... Chromosome: Contains the main information carrying single piece of double stranded DNA Codon: a nucleotide triplet Congenital: existing at birth, not inherited Congenital disorder: may be the result of genetic abnormalities, the inter-uterine environment, errors of development, infection during preg ...
... Chromosome: Contains the main information carrying single piece of double stranded DNA Codon: a nucleotide triplet Congenital: existing at birth, not inherited Congenital disorder: may be the result of genetic abnormalities, the inter-uterine environment, errors of development, infection during preg ...
Robust systems persist in response to mutations
... one binding site. Payne and Wagner found that the more sites a transcription factor can bind to—and the more one can "hop" from one compatible site to the next through single mutations—the more robust the transcription factor's function. What's more, that robustness makes it easier for a population ...
... one binding site. Payne and Wagner found that the more sites a transcription factor can bind to—and the more one can "hop" from one compatible site to the next through single mutations—the more robust the transcription factor's function. What's more, that robustness makes it easier for a population ...
Genetics Factsheet - Cystic Fibrosis Ireland
... up of a large number of tissuespecific cells. 2. In each cell there is a nucleus which controls the cell – the “brain” of the cell. 3. The nucleus is made up of 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. 4. Each chromosome contains hundreds of genes. 5. Genes are formed by 2 strands of DNA linking to form a ...
... up of a large number of tissuespecific cells. 2. In each cell there is a nucleus which controls the cell – the “brain” of the cell. 3. The nucleus is made up of 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. 4. Each chromosome contains hundreds of genes. 5. Genes are formed by 2 strands of DNA linking to form a ...
Unit 4: DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Tier 3 Vocabulary = words and language specific to the content area. Please remember that in order to develop strong content reading and writing, Tier 2 words must be continually developed. Sample Materials & Resources = just some of the resources that can be used. Please recall that students bring ...
... Tier 3 Vocabulary = words and language specific to the content area. Please remember that in order to develop strong content reading and writing, Tier 2 words must be continually developed. Sample Materials & Resources = just some of the resources that can be used. Please recall that students bring ...
ADVANCES IN COCHLEAR IMPLANTATION
... mutation from each parent in both copies of a particular gene and develops a health condition. If the child inherits only one copy of the gene with the mutation, he/she will be a carrier of the condition but will not develop it. When 2 parents are carriers of the same mutation, their children have a ...
... mutation from each parent in both copies of a particular gene and develops a health condition. If the child inherits only one copy of the gene with the mutation, he/she will be a carrier of the condition but will not develop it. When 2 parents are carriers of the same mutation, their children have a ...
Mutations and Selective Advantage
... Mutations Can Provide an Advantage Mutations that were once no advantage, or perhaps were even a disadvantage, may become favourable in a changing environment. In this situation, the mutation provides a selective advantage – a genetic advantage of one organism over its competitors. Over time, a sel ...
... Mutations Can Provide an Advantage Mutations that were once no advantage, or perhaps were even a disadvantage, may become favourable in a changing environment. In this situation, the mutation provides a selective advantage – a genetic advantage of one organism over its competitors. Over time, a sel ...
1. Which of the following genotype below shows a pure dominant
... 14. cDNA can be cloned into vectors to create a cDNA library. In analyzing cDNA clones. It is often difficult to find clones that are full length, that is, extend to the 5’ end of the mRNA. Why is this so? 15. Acridine dyes induce frames shift mutations. Is such a mutation likely to be more detrimen ...
... 14. cDNA can be cloned into vectors to create a cDNA library. In analyzing cDNA clones. It is often difficult to find clones that are full length, that is, extend to the 5’ end of the mRNA. Why is this so? 15. Acridine dyes induce frames shift mutations. Is such a mutation likely to be more detrimen ...
What do Genes Look Like - Effingham County Schools
... Syndrome) B. ____________________________– affect other cells- not inherited by offspring (many cancers caused by somatic mutations) Two Types of DNA mutations ...
... Syndrome) B. ____________________________– affect other cells- not inherited by offspring (many cancers caused by somatic mutations) Two Types of DNA mutations ...
Protein Synthesis-Part Two - Halton District School Board
... 4. Inversion: The order of the genes is changed. • The new sequence may not produce a viable organism, depending on which genes are reversed. • Advantageous characteristics from this mutation are also possible ...
... 4. Inversion: The order of the genes is changed. • The new sequence may not produce a viable organism, depending on which genes are reversed. • Advantageous characteristics from this mutation are also possible ...
BIOL 221-GENETICS
... 2. epistasis II. Genes on Chromosomes A. Evidence for genes on chromosomes 1. history of the question 2. white-eyed flies and sex determination B. Chromosomal results of mitosis and meiosis 1. events of mitosis and meiosis 2. meiosis and Mendelism C. Linkage and recombination 1. crossing over 2. det ...
... 2. epistasis II. Genes on Chromosomes A. Evidence for genes on chromosomes 1. history of the question 2. white-eyed flies and sex determination B. Chromosomal results of mitosis and meiosis 1. events of mitosis and meiosis 2. meiosis and Mendelism C. Linkage and recombination 1. crossing over 2. det ...
mutation as a source of variation
... Genetic variation is essential for Darwin’s theory of natural selection and all genetic variation must come, ultimately, from mutations. A mutation is any hereditary change in the DNA sequence or in chromosome number, form or structure. Most mutations arise from errors during DNA replication that fa ...
... Genetic variation is essential for Darwin’s theory of natural selection and all genetic variation must come, ultimately, from mutations. A mutation is any hereditary change in the DNA sequence or in chromosome number, form or structure. Most mutations arise from errors during DNA replication that fa ...
Genes and CHI
... are many genes in the body and put together, they form the genetic code. Mutations are ‘spelling mistakes’ or ‘faults’ in these genetic codes. There are several genes in the body that help in controlling how insulin is made and pushed out. ‘Spelling mistakes’ in these genes can cause CHI. The two mo ...
... are many genes in the body and put together, they form the genetic code. Mutations are ‘spelling mistakes’ or ‘faults’ in these genetic codes. There are several genes in the body that help in controlling how insulin is made and pushed out. ‘Spelling mistakes’ in these genes can cause CHI. The two mo ...
MUTATIONS - MsWalshMosher
... There are two ways in which DNA can become mutated: Mutations can be inherited. Parent to child ...
... There are two ways in which DNA can become mutated: Mutations can be inherited. Parent to child ...
genetic continuity
... ALTER THE GENETIC INSTRUCTIONS OF AN ORGANISM BY SUBSTITUTING DNA MOLECULES ...
... ALTER THE GENETIC INSTRUCTIONS OF AN ORGANISM BY SUBSTITUTING DNA MOLECULES ...
mutations
... coli. Mutations that confer RifR in E. coli and M. tuberculosis are indicated directly above (for E. coli) or below (for M. tuberculosis) as follows: D for deletions, V for insertions, and colored dots for amino acid substitutions (substitutions at each position are indicated in single amino acid co ...
... coli. Mutations that confer RifR in E. coli and M. tuberculosis are indicated directly above (for E. coli) or below (for M. tuberculosis) as follows: D for deletions, V for insertions, and colored dots for amino acid substitutions (substitutions at each position are indicated in single amino acid co ...
Evolution_3
... • General Theory of Evolution or “Macroevolution” is the theory that all the living forms in the world have arisen from a single source which itself came from an inorganic form. • Problem with “macroevolution” is that it goes against what we have observed in nature, in that it does not recognize the ...
... • General Theory of Evolution or “Macroevolution” is the theory that all the living forms in the world have arisen from a single source which itself came from an inorganic form. • Problem with “macroevolution” is that it goes against what we have observed in nature, in that it does not recognize the ...
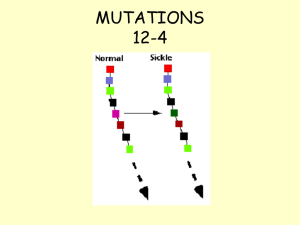
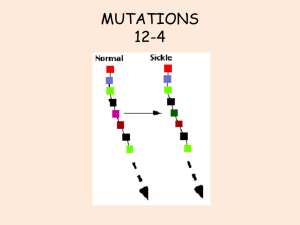
MUTATIONS 12-4 - Somers Public School District
... http://www.biology-online.org/2/8_mutations.htm ...
... http://www.biology-online.org/2/8_mutations.htm ...
Document
... a. Alternative RNA splicing allows multiple proteins to be made from a gene (19.8) b. mRNA lifespan determines how much translation can occur i. lifespan may depend on the 3’UTR sequence (19.5) ii. lifespan may depend on miRNA action (19.9) II. Gene Expression in Diploid, Multi-Cellular Organisms A. ...
... a. Alternative RNA splicing allows multiple proteins to be made from a gene (19.8) b. mRNA lifespan determines how much translation can occur i. lifespan may depend on the 3’UTR sequence (19.5) ii. lifespan may depend on miRNA action (19.9) II. Gene Expression in Diploid, Multi-Cellular Organisms A. ...
Regulation & Mutations
... Results of Mutations • Some cause death or diseases or malfunctions • Some are not noticed at all • Some lead to abnormalities that assist the organism and make them better suited for their environment ...
... Results of Mutations • Some cause death or diseases or malfunctions • Some are not noticed at all • Some lead to abnormalities that assist the organism and make them better suited for their environment ...
Mutation in Mitosis and Meiosis
... Mutations can be: positive – have a good effect on the organism negative – be detrimental or fatal neutral – have no effect (repetition of triplet code) If a mutation occurs in a gamete or during meiosis, the mutation is passed on to the offspring. Mutations during DNA replication 1. base pair subst ...
... Mutations can be: positive – have a good effect on the organism negative – be detrimental or fatal neutral – have no effect (repetition of triplet code) If a mutation occurs in a gamete or during meiosis, the mutation is passed on to the offspring. Mutations during DNA replication 1. base pair subst ...
Class Presentation Questions 12
... carry ___________________________ & half carry _______________________________. This ensures that just about half of the zygotes will be _______________ & half will be ____________. 7. A human female inherits ________ copy (copies) of every gene located on each of the X chromosomes. 8. Describe six ...
... carry ___________________________ & half carry _______________________________. This ensures that just about half of the zygotes will be _______________ & half will be ____________. 7. A human female inherits ________ copy (copies) of every gene located on each of the X chromosomes. 8. Describe six ...
13.3 Mutations File
... affect zero, one or many amino acids Insertion or deletion: a base is either inserted or deleted from the DNA sequence This results in a frameshift mutation: the entire reading frame following that point is thrown off This is much more severe than a substitution, because many amino acids will be alt ...
... affect zero, one or many amino acids Insertion or deletion: a base is either inserted or deleted from the DNA sequence This results in a frameshift mutation: the entire reading frame following that point is thrown off This is much more severe than a substitution, because many amino acids will be alt ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.