Part 3 - Alexander Local Schools
... I can… describe how DNA becomes the traits using RNA I can… define mutations and give 3 types I can… describe some harmful mutations in humans I can… explain the three possible outcomes of mutations. ...
... I can… describe how DNA becomes the traits using RNA I can… define mutations and give 3 types I can… describe some harmful mutations in humans I can… explain the three possible outcomes of mutations. ...
Mutations
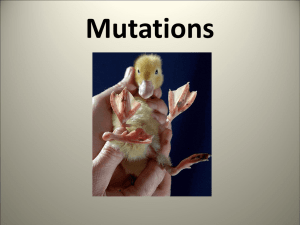
... Types of mutations (either germ or somatic): 1. Chromosomal mutations: -entire chromosomes is affected therefore many genes are involved resulting in the most severe forms of mutations. -Example: Down Syndrome Edwards Syndrome ...
... Types of mutations (either germ or somatic): 1. Chromosomal mutations: -entire chromosomes is affected therefore many genes are involved resulting in the most severe forms of mutations. -Example: Down Syndrome Edwards Syndrome ...
12.4 Mutations
... • Changes in the genetic material • Mistake in copying, carcinogens • Single gene = gene mutation • Entire chromosome = chromosomal mutation ...
... • Changes in the genetic material • Mistake in copying, carcinogens • Single gene = gene mutation • Entire chromosome = chromosomal mutation ...
25L-Mutations - Doral Academy Preparatory
... character or trait. In humans when parents pass their genes down to their children, an average of 60 errors is introduced to the genetic code. Out of the 6 billion letters of DNA (3 billion base pairs) there are on average one new mutation in every 100 million letters of DNA. A mutation can be harmf ...
... character or trait. In humans when parents pass their genes down to their children, an average of 60 errors is introduced to the genetic code. Out of the 6 billion letters of DNA (3 billion base pairs) there are on average one new mutation in every 100 million letters of DNA. A mutation can be harmf ...
MUTATIONS • Mutations are errors made in the DNA sequence that
... deletions (one or more nucleotides are removed from the DNA sequence (see Fig.1, p.260) If a frameshift mutation happens to insert one or two nucleotides, it can have devastating effects because every amino acid in the polypeptide chain If a frameshift mutation inserts three nucleotides, it will ...
... deletions (one or more nucleotides are removed from the DNA sequence (see Fig.1, p.260) If a frameshift mutation happens to insert one or two nucleotides, it can have devastating effects because every amino acid in the polypeptide chain If a frameshift mutation inserts three nucleotides, it will ...
Key ideas age 321 ivaniaa
... 2. List the kinds of mutations? mutations as change in DNA point mutation A. Insertion or deletion. B. Mutations as changes in results of gene. C. Silent mutation. D. Messene mutation. E. Frameshipft mutation. F. Nonsense mutation. G. More or fewer amino acids. H. Chromosomal mutation. I. Detection. ...
... 2. List the kinds of mutations? mutations as change in DNA point mutation A. Insertion or deletion. B. Mutations as changes in results of gene. C. Silent mutation. D. Messene mutation. E. Frameshipft mutation. F. Nonsense mutation. G. More or fewer amino acids. H. Chromosomal mutation. I. Detection. ...
Genetic changes - Southington Public Schools
... Mutations in gametes will be passed to the offspring. Types of mutations 1. Point mutations—a change in a single base of a DNA chain. This results in a different “message.” Example: normal sequence THE DOG BIT THE CAT mutation THE DOG BIT THE CAR Sense mutation: the changed codon makes a differe ...
... Mutations in gametes will be passed to the offspring. Types of mutations 1. Point mutations—a change in a single base of a DNA chain. This results in a different “message.” Example: normal sequence THE DOG BIT THE CAT mutation THE DOG BIT THE CAR Sense mutation: the changed codon makes a differe ...
Guided Notes - Boone County Schools
... our parents ○ Half of our DNA comes from mom ○ the other half comes from dad ● Some genes parents pass down are recessive, while some are dominant. ○ anytime a _____________ trait is partnered with recessive trait the dominant train will always win over the recessive in an organism’s ph ...
... our parents ○ Half of our DNA comes from mom ○ the other half comes from dad ● Some genes parents pass down are recessive, while some are dominant. ○ anytime a _____________ trait is partnered with recessive trait the dominant train will always win over the recessive in an organism’s ph ...
12-4 Mutations - Lincoln Park High School
... 5. Frameshift Mutations- a type of insertion or deletion a)The addition or deletion of a nucleotide causes a shift in the grouping of codons b)Can change every amino acid that follows the point of the mutation c) can change a protein so much that it does not work normally ...
... 5. Frameshift Mutations- a type of insertion or deletion a)The addition or deletion of a nucleotide causes a shift in the grouping of codons b)Can change every amino acid that follows the point of the mutation c) can change a protein so much that it does not work normally ...
Mathematical Tools for Understanding Genome Rearrangements
... Wednesday September 19, 2012 12:10 - 12:50 p.m. *CETL (OL 1142)* The diversity of life is a direct result of inaccuracy in DNA replication. At some point in the past, humans and mice had a common ancestor, and many "mistakes" later, we have two apparently very different species. At the level of DNA, ...
... Wednesday September 19, 2012 12:10 - 12:50 p.m. *CETL (OL 1142)* The diversity of life is a direct result of inaccuracy in DNA replication. At some point in the past, humans and mice had a common ancestor, and many "mistakes" later, we have two apparently very different species. At the level of DNA, ...
Unit 3- Section 2
... Most of the code is useless Useful code=genes Genes code for proteins b. EX: Melanin a. ...
... Most of the code is useless Useful code=genes Genes code for proteins b. EX: Melanin a. ...
mutations
... SOMATIC MUTATIONS TAKE PLACE IN BODY CELLS AND ARE PASSED ON TO THE DAUGHTER CELLS THROUGH MITOSIS. ...
... SOMATIC MUTATIONS TAKE PLACE IN BODY CELLS AND ARE PASSED ON TO THE DAUGHTER CELLS THROUGH MITOSIS. ...
Mutations
... 1. Chromosomal mutations: -entire chromosomes is affected therefore many genes are involved resulting in the most severe forms of mutations. A baby can be born with an extra chromosome or missing one chromosome. -Example: Down Syndrome Turner Syndrome ...
... 1. Chromosomal mutations: -entire chromosomes is affected therefore many genes are involved resulting in the most severe forms of mutations. A baby can be born with an extra chromosome or missing one chromosome. -Example: Down Syndrome Turner Syndrome ...
MUTATIONS
... - alters codon changing it to a STOP codon and only part of the protein is translated - lead to non-functional proteins ...
... - alters codon changing it to a STOP codon and only part of the protein is translated - lead to non-functional proteins ...
14.4 Gene Mutations
... If this occurs in somatic (body) cells, the change cannot be inherited. Only mutations in the DNA within gametes can be passed on to the next generation. ...
... If this occurs in somatic (body) cells, the change cannot be inherited. Only mutations in the DNA within gametes can be passed on to the next generation. ...
Document
... hemoglobin distorts cell shape causing them to stick together and disrupt circulation B. Insertions and deletions – the addition or removal of an extra base causes a frame shift mutation C. Transposable elements: DNA segments move spontaneously on chromosome which may inactivate the gene where it in ...
... hemoglobin distorts cell shape causing them to stick together and disrupt circulation B. Insertions and deletions – the addition or removal of an extra base causes a frame shift mutation C. Transposable elements: DNA segments move spontaneously on chromosome which may inactivate the gene where it in ...
DNA Mutations
... • External factors can also cause mutations. • These mistakes could be good or bad. ...
... • External factors can also cause mutations. • These mistakes could be good or bad. ...
Mutations - Lakeland Regional High School / Overview
... • Do NOT affect the organism but are passed on to offspring ...
... • Do NOT affect the organism but are passed on to offspring ...
Mutation

In biology, a mutation is a permanent change of the nucleotide sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA or other genetic elements. Mutations result from damage to DNA which is not repaired or to RNA genomes (typically caused by radiation or chemical mutagens), errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity.Mutation can result in several different types of change in sequences. Mutations in genes can either have no effect, alter the product of a gene, or prevent the gene from functioning properly or completely. Mutations can also occur in nongenic regions. One study on genetic variations between different species of Drosophila suggests that, if a mutation changes a protein produced by a gene, the result is likely to be harmful, with an estimated 70 percent of amino acid polymorphisms that have damaging effects, and the remainder being either neutral or weakly beneficial. Due to the damaging effects that mutations can have on genes, organisms have mechanisms such as DNA repair to prevent or correct mutations by reverting the mutated sequence back to its original state.