End-product control of enzymes of branched
... for that amino acid become very high. This is due to loss of end-product control of expression of genes encoding the biosynthetic enzymes when the internal level of the amino acid becomes insufficient for end-product control. We have carried out similar experiments with auxotrophs of S. coelicolor, ...
... for that amino acid become very high. This is due to loss of end-product control of expression of genes encoding the biosynthetic enzymes when the internal level of the amino acid becomes insufficient for end-product control. We have carried out similar experiments with auxotrophs of S. coelicolor, ...
IOSR Journal of Agriculture and Veterinary Science (IOSR-JAVS)
... cassava peels at a mixing ratio of 1:1 had significant effect in increasing average cumulative biogas yield. They posited that substrates with very high C/N ratio would produce very low biogas (Table 4). However, when codigested with materials with a low C/N ratio, stabilize the ratio to an optimal ...
... cassava peels at a mixing ratio of 1:1 had significant effect in increasing average cumulative biogas yield. They posited that substrates with very high C/N ratio would produce very low biogas (Table 4). However, when codigested with materials with a low C/N ratio, stabilize the ratio to an optimal ...
Bioretrosynthetic Construction of a Non
... Nannemann, an alumnus of the Bachmann research group, on the biochemical characterization of phosphopentomutase prior to me joining the lab which allowed me to start directly with assay development and mutagenesis. The structural and mechanistic insights gained through their work on phosphopentomuta ...
... Nannemann, an alumnus of the Bachmann research group, on the biochemical characterization of phosphopentomutase prior to me joining the lab which allowed me to start directly with assay development and mutagenesis. The structural and mechanistic insights gained through their work on phosphopentomuta ...
Substrate Specificity of Tonin from Rat Submaxillary Gland
... through ionic interaction with a negatively charged moiety of the enzyme or through formation of a hydrogen bond. Alternatively, it is also conceivable that this residue stabilizes a particular conformation of the peptide, thereby rendering it a better substrate for fast hydrolysis. In this context ...
... through ionic interaction with a negatively charged moiety of the enzyme or through formation of a hydrogen bond. Alternatively, it is also conceivable that this residue stabilizes a particular conformation of the peptide, thereby rendering it a better substrate for fast hydrolysis. In this context ...
Staphylococcus haemolyticus lipase
... In our cloning experiment, E. coli XL1 Blue strain transformed with the plasmid (pSHL) carrying the lipase L62 whole gene showed low lipase activity. This low lipase activity in the recombinant E. coli strain in comparison with the original staphylococcal strain (L62) was possibly caused by a low ex ...
... In our cloning experiment, E. coli XL1 Blue strain transformed with the plasmid (pSHL) carrying the lipase L62 whole gene showed low lipase activity. This low lipase activity in the recombinant E. coli strain in comparison with the original staphylococcal strain (L62) was possibly caused by a low ex ...
Amino acid fluxes to and from seawater in axenic veliger larvae of a
... with time were determined by reverse-phase HPLC analysis. The techniques used were based on the ophthaldialdehyde (OPA) derivatization of primary amines (Lindroth & Mopper 1979) a n d the subsequent separation of the fluorescent derivatives on C-18 columns using the sodium acetate buffer system of J ...
... with time were determined by reverse-phase HPLC analysis. The techniques used were based on the ophthaldialdehyde (OPA) derivatization of primary amines (Lindroth & Mopper 1979) a n d the subsequent separation of the fluorescent derivatives on C-18 columns using the sodium acetate buffer system of J ...
Chapter 25 Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... a) The COOH group does not readily undergo nucleophilic acyl substitution because the OH group is not a good leaving group. By converting the COOH group into an activated ester, the compound can now undergo nucleophilic acyl substitution because it has a good leaving group. b) The nitro group stabil ...
... a) The COOH group does not readily undergo nucleophilic acyl substitution because the OH group is not a good leaving group. By converting the COOH group into an activated ester, the compound can now undergo nucleophilic acyl substitution because it has a good leaving group. b) The nitro group stabil ...
[7] Semisynthesis of Proteins Containing Selenocysteine
... selenocysteine insertion is present in its gene. To produce TR, a gene fusion was created that placed a bacterial selenocysteine insertion sequence (SECIS) element immediately downstream of the UGA stop codon. There, the SECIS element allowed decoding of the UGA codon as one for selenocysteine. This ...
... selenocysteine insertion is present in its gene. To produce TR, a gene fusion was created that placed a bacterial selenocysteine insertion sequence (SECIS) element immediately downstream of the UGA stop codon. There, the SECIS element allowed decoding of the UGA codon as one for selenocysteine. This ...
Karbohidrat Metabolizması
... PEP Carboxykinase catalyzes GTP-dependent oxaloacetate PEP. It is thought to proceed in 2 steps: Oxaloacetate is first decarboxylated to yield a pyruvate enolate anion intermediate. This is phosphorylated by phosphate transfer from GTP. A metal ion such as Mn++ is required, in addition to Mg++ ass ...
... PEP Carboxykinase catalyzes GTP-dependent oxaloacetate PEP. It is thought to proceed in 2 steps: Oxaloacetate is first decarboxylated to yield a pyruvate enolate anion intermediate. This is phosphorylated by phosphate transfer from GTP. A metal ion such as Mn++ is required, in addition to Mg++ ass ...
Nucleoside Phosphoramidate Monoesters: Potential
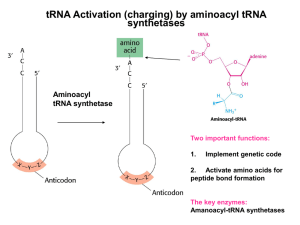
... The accuracy of protein synthesis depends on correct charging of tRNAs with amino acids 1. tRNA synthetases must link tRNAs with their correct amino acids. 2. tRNA synthetases recognize correct amino acids by specific binding to the active site and proofreading. 3. tRNA synthetases recognize correc ...
... The accuracy of protein synthesis depends on correct charging of tRNAs with amino acids 1. tRNA synthetases must link tRNAs with their correct amino acids. 2. tRNA synthetases recognize correct amino acids by specific binding to the active site and proofreading. 3. tRNA synthetases recognize correc ...
Bio1A - Lec 9 slides File
... Cofactors, Coenzymes & Prosthetic groups are REQUIRED portions of the enzyme. • often required for proper protein folding • typically required at the active site -For bonding -Supplies electrons or functional groups for the reaction -Temporarily for E-S transient complexes ...
... Cofactors, Coenzymes & Prosthetic groups are REQUIRED portions of the enzyme. • often required for proper protein folding • typically required at the active site -For bonding -Supplies electrons or functional groups for the reaction -Temporarily for E-S transient complexes ...
A Survey of Left-handed Helices in Protein Structures
... Schellman motifs.10 To our knowledge, there are currently only three protein structure entries in the PDB that have a lefthanded helix assigned. Two of these are four residues long and they are found in thermolysin (PDB code 8tln)11 and neutral protease (1npc).12 The third one is a three-residue lon ...
... Schellman motifs.10 To our knowledge, there are currently only three protein structure entries in the PDB that have a lefthanded helix assigned. Two of these are four residues long and they are found in thermolysin (PDB code 8tln)11 and neutral protease (1npc).12 The third one is a three-residue lon ...
eg1
... multiple forms (Knowles et al. 1987, Kubicek 1992). V. volvacea produces a cellulolytic system that includes multiple forms of all three classes when grown on crystalline cellulose (Cai et al. 1994, 1999). In addition to EG1, four other CMC-hydrolysing proteins were separated in lower yields from cu ...
... multiple forms (Knowles et al. 1987, Kubicek 1992). V. volvacea produces a cellulolytic system that includes multiple forms of all three classes when grown on crystalline cellulose (Cai et al. 1994, 1999). In addition to EG1, four other CMC-hydrolysing proteins were separated in lower yields from cu ...
Applied and Environmental Microbiology
... nitrogen fixation ability of A. amazonense at high concentrations. In contrast, A. brasiliense strains did not grow as well on glutamate and serine as did A. lipoferum and A. amazonense. A. brasiliense could not grow on histidine as the sole carbon and nitrogen source (Table 1). Nitrogen fixation wa ...
... nitrogen fixation ability of A. amazonense at high concentrations. In contrast, A. brasiliense strains did not grow as well on glutamate and serine as did A. lipoferum and A. amazonense. A. brasiliense could not grow on histidine as the sole carbon and nitrogen source (Table 1). Nitrogen fixation wa ...
amino-acids - ChemConnections
... When formed by amino acids, each amide group is called a peptide bond. Peptides are formed by condensation of the -COOH group of one amino acid and the NH group of another amino acid. The acid forming the peptide bond is named first. Example: if a dipeptide is formed from alanine and glycine so that ...
... When formed by amino acids, each amide group is called a peptide bond. Peptides are formed by condensation of the -COOH group of one amino acid and the NH group of another amino acid. The acid forming the peptide bond is named first. Example: if a dipeptide is formed from alanine and glycine so that ...
26. oxidation of amino acids
... to glutamate and NH4+. Glutamine is, thus, a major transport form of ammonia. It is normally present in blood in much higher concentrations than other amino acids. D. Transport of Ammonia from Muscle to Liver Through Alanine (= Glucose—Alanine Cycle) Alanine also plays a special role in transporting ...
... to glutamate and NH4+. Glutamine is, thus, a major transport form of ammonia. It is normally present in blood in much higher concentrations than other amino acids. D. Transport of Ammonia from Muscle to Liver Through Alanine (= Glucose—Alanine Cycle) Alanine also plays a special role in transporting ...
E. coli
... deprotonation of NH4+ by an Asp causes a flap (324-328) to close over active site ammonia attacks glutamyl-g-P forming tetrahedral intermediate Pi and a proton are lost The flap opens and glutamine leaves ...
... deprotonation of NH4+ by an Asp causes a flap (324-328) to close over active site ammonia attacks glutamyl-g-P forming tetrahedral intermediate Pi and a proton are lost The flap opens and glutamine leaves ...
Catalytic triad

A catalytic triad refers to the three amino acid residues that function together at the centre of the active site of some hydrolase and transferase enzymes (e.g. proteases, amidases, esterases, acylases, lipases and β-lactamases). An Acid-Base-Nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine amino acid, but occasionally threonine. Because enzymes fold into complex three-dimensional structures, the residues of a catalytic triad can be far from each other along the amino-acid sequence (primary structure), however, they are brought close together in the final fold.As well as divergent evolution of function (and even the triad's nucleophile), catalytic triads show some of the best examples of convergent evolution. Chemical constraints on catalysis have led to the same catalytic solution independently evolving in at least 23 separate superfamilies. Their mechanism of action is consequently one of the best studied in biochemistry.







![[7] Semisynthesis of Proteins Containing Selenocysteine](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004768810_1-d08ecd7536246bbf8b4baa16bb630c93-300x300.png)