Hydrolysis of a Series of Synthetic Peptide Substrates by the Human
... Briefly, the 3C proteins were purified from the soluble extract of induced cells using a two-stage high pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) procedure on a cation-exchange column (TSK SP5PW) and a gel permeation column (TSK G3000SW). The HRV-14 3C proteins were homogeneous, as judged by SDS-PAGE, i ...
... Briefly, the 3C proteins were purified from the soluble extract of induced cells using a two-stage high pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) procedure on a cation-exchange column (TSK SP5PW) and a gel permeation column (TSK G3000SW). The HRV-14 3C proteins were homogeneous, as judged by SDS-PAGE, i ...
NMR studies of the methionine methyl groups in calmodulin
... residues in apo-CaM are in a different environment from those in calcium-CaM. Binding of a target peptide to the two hydrophobic regions causes a large dist~.'ibution of chemical shifts, indicating that the Met residues are experiencing even more widely different environments in this state; this was ...
... residues in apo-CaM are in a different environment from those in calcium-CaM. Binding of a target peptide to the two hydrophobic regions causes a large dist~.'ibution of chemical shifts, indicating that the Met residues are experiencing even more widely different environments in this state; this was ...
Bio 226: Cell and Molecular Biology
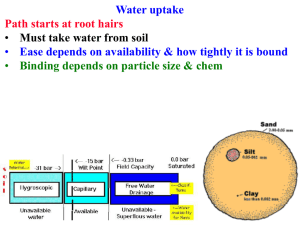
... • others take up tetra- & penta-peptides by H+ symport Also have ABC transporters that import peptides N is vital! NO3- & NH4+ are main forms ...
... • others take up tetra- & penta-peptides by H+ symport Also have ABC transporters that import peptides N is vital! NO3- & NH4+ are main forms ...
Amino Acids and Protein Digestibility and Metabolizable Energy
... critical in the poultry industry. Estimation of chemical energy in feedstuff is relatively easy; however, this estimation in birds is not precise and measurement of metabolizable energy is common (Scott et al., 1998). To improve dietary efficiency, it is necessary to elucidate the exact amino acid r ...
... critical in the poultry industry. Estimation of chemical energy in feedstuff is relatively easy; however, this estimation in birds is not precise and measurement of metabolizable energy is common (Scott et al., 1998). To improve dietary efficiency, it is necessary to elucidate the exact amino acid r ...
Introduction Milk is the exclusive nutrient source for the neonate. ... practices and availability of highly selected sows have allowed for...
... acids. Several other amino acids showed inhibitory effects on valine (Table 1). Valine was inhibited by alanine (a short chain neutral amino acid), methionine (a sulfur containing short chain amino acid), glutamine (an amide derivative of an acidic amino acid), cyclo-leucine (a non-protein amino aci ...
... acids. Several other amino acids showed inhibitory effects on valine (Table 1). Valine was inhibited by alanine (a short chain neutral amino acid), methionine (a sulfur containing short chain amino acid), glutamine (an amide derivative of an acidic amino acid), cyclo-leucine (a non-protein amino aci ...
Comparison of the Functional Differences for the Homologous Residues within... Carboxy Phosphate and Carbamate Domains of Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase
... Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase (CPS) from Escherichia coli catalyzes the formation of carbamoyl phosphate from two molecules of MgATP, bicarbonate, and glutamine. It has been previously shown that the amino- and carboxy-terminal halves of the large subunit of this protein are homologous. A working m ...
... Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase (CPS) from Escherichia coli catalyzes the formation of carbamoyl phosphate from two molecules of MgATP, bicarbonate, and glutamine. It has been previously shown that the amino- and carboxy-terminal halves of the large subunit of this protein are homologous. A working m ...
(a) (b)
... dodecahedron core with a diameter of about 25 nm. E2 has three domains: the amino-terminal lipoyl domain; the central E1- and E3-binding domain; and the inner-core acyltransferase domain. The active site of E1 and E3 has bound TPP and FAD, respectively. The attachment of lipoate to E2 produces a lon ...
... dodecahedron core with a diameter of about 25 nm. E2 has three domains: the amino-terminal lipoyl domain; the central E1- and E3-binding domain; and the inner-core acyltransferase domain. The active site of E1 and E3 has bound TPP and FAD, respectively. The attachment of lipoate to E2 produces a lon ...
Hydrolysis of Bradykinin by Angiotensin
... (HEPES) was purchased from Calbiochem. The dipeptides, serylproline (Ser-Pro), phenylalanylarginine (PheArg), and Gly-Phe, were purchased from Fox Chemical Company. The concentrations of standard solutions of the peptides were determined by amino acid analysis following acid hydrolysis. The syntheti ...
... (HEPES) was purchased from Calbiochem. The dipeptides, serylproline (Ser-Pro), phenylalanylarginine (PheArg), and Gly-Phe, were purchased from Fox Chemical Company. The concentrations of standard solutions of the peptides were determined by amino acid analysis following acid hydrolysis. The syntheti ...
What is a Multiple Alignment?
... – Pairs of conserved hydrophobic amino acids separated by pairs of unconserved or hydrophilic residues suggests an α-helix with one face packed in the protein core. Similarly, an i, i+3, i+4, i+7 pattern of conserved residues.” ...
... – Pairs of conserved hydrophobic amino acids separated by pairs of unconserved or hydrophilic residues suggests an α-helix with one face packed in the protein core. Similarly, an i, i+3, i+4, i+7 pattern of conserved residues.” ...
glycogen metabolism
... of Several Enzymes • Four enzyme activities: – one to degrade glycogen, – two to remodel glycogen so that it remains a substrate for degradation – one to convert the product of glycogen breakdown into a form suitable for further metabolism. ...
... of Several Enzymes • Four enzyme activities: – one to degrade glycogen, – two to remodel glycogen so that it remains a substrate for degradation – one to convert the product of glycogen breakdown into a form suitable for further metabolism. ...
Document
... successive amino acids is known as a peptide bond The C-N bond between the first amino acid’s carbonyl carbon and the second amino acid’s amine nitrogen has some double bond ...
... successive amino acids is known as a peptide bond The C-N bond between the first amino acid’s carbonyl carbon and the second amino acid’s amine nitrogen has some double bond ...
Intersubunit contacts are often facilitated by specificity
... Intersubunit contacts are often facilitated by specificity-determining positions Computational identification of protein positions that possibly account for precise recognition of the interaction partner ...
... Intersubunit contacts are often facilitated by specificity-determining positions Computational identification of protein positions that possibly account for precise recognition of the interaction partner ...
Ube2W conjugates ubiquitin to α-amino groups of protein N
... where the ubiquitin is first adenylated, then covalently linked via a thioester bond to a cysteine residue in an E1 enzyme (ubiquitin-activating enzyme). The ubiquitin is then transferred via a second thioester bond on to an E2 enzyme (ubiquitinconjugating enzyme). In human cells there are almost 40 ...
... where the ubiquitin is first adenylated, then covalently linked via a thioester bond to a cysteine residue in an E1 enzyme (ubiquitin-activating enzyme). The ubiquitin is then transferred via a second thioester bond on to an E2 enzyme (ubiquitinconjugating enzyme). In human cells there are almost 40 ...
Analysis of amino acids and peptide primary structure determination
... • Amino acids are covalently bonded to one another by amide linkages (bonds) between the carboxylic acid group of one amino acid and the amino group of the next amino acid. • Amide bonds are strong and are resistant to hydrolysis, but there are enzymes that catalyze their hydrolysis (to the amino ac ...
... • Amino acids are covalently bonded to one another by amide linkages (bonds) between the carboxylic acid group of one amino acid and the amino group of the next amino acid. • Amide bonds are strong and are resistant to hydrolysis, but there are enzymes that catalyze their hydrolysis (to the amino ac ...
T03 growth2013
... electron donor. For example an aerobic bacterium growing by oxidising sugar to CO2 for ATP generation will also use the same sugar as a starting material for biomass synthesis. The sugar may be partly degraded via glycolysis to pyruvate or even to Acetyl-CoA to use parts of the TCA cycle for biomass ...
... electron donor. For example an aerobic bacterium growing by oxidising sugar to CO2 for ATP generation will also use the same sugar as a starting material for biomass synthesis. The sugar may be partly degraded via glycolysis to pyruvate or even to Acetyl-CoA to use parts of the TCA cycle for biomass ...
METBIONET GUIDELINES FOR AMINO ACID ANALYSIS.
... and deproteinisation is essential for accurate measurement of (free) sulphur containing amino acids. Total homocysteine can be measured as an alternative to free homocystine, although specimens still require prompt separation. Notes: · Serum should not be used because blood needs to clot at room tem ...
... and deproteinisation is essential for accurate measurement of (free) sulphur containing amino acids. Total homocysteine can be measured as an alternative to free homocystine, although specimens still require prompt separation. Notes: · Serum should not be used because blood needs to clot at room tem ...
Reasons for the occurrence of the twenty coded protein amino acids
... amino acid from proteins would be its suitability or unsuitability for protein structure and function. An example would be the ability to form ordered secondary and tertiary structures. Unfortunately, there is insufficient information on the relationship between structure and function to deal adequa ...
... amino acid from proteins would be its suitability or unsuitability for protein structure and function. An example would be the ability to form ordered secondary and tertiary structures. Unfortunately, there is insufficient information on the relationship between structure and function to deal adequa ...
Catalytic triad

A catalytic triad refers to the three amino acid residues that function together at the centre of the active site of some hydrolase and transferase enzymes (e.g. proteases, amidases, esterases, acylases, lipases and β-lactamases). An Acid-Base-Nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine amino acid, but occasionally threonine. Because enzymes fold into complex three-dimensional structures, the residues of a catalytic triad can be far from each other along the amino-acid sequence (primary structure), however, they are brought close together in the final fold.As well as divergent evolution of function (and even the triad's nucleophile), catalytic triads show some of the best examples of convergent evolution. Chemical constraints on catalysis have led to the same catalytic solution independently evolving in at least 23 separate superfamilies. Their mechanism of action is consequently one of the best studied in biochemistry.