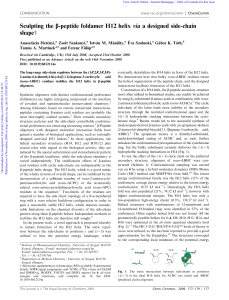
Structure, catalytic activity and evolutionary relationships of 1
... Key words: 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase, ethylene synthesis Both ethylene and the enzymes of ethylene synthesis are subjects of intensive scientific investigation. The present review discusses structure, catalytic activity and evolutionary relationships of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxy ...
... Key words: 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase, ethylene synthesis Both ethylene and the enzymes of ethylene synthesis are subjects of intensive scientific investigation. The present review discusses structure, catalytic activity and evolutionary relationships of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxy ...
PDB format description
... (ii) If a HET group is composed of more than one distinct part, then the formulas for these parts will occur on separate FORMUL cards, each with the same component number and HET identifier. All except the last of these records will be terminated with a period. (iii) Solvent molecules and certain ot ...
... (ii) If a HET group is composed of more than one distinct part, then the formulas for these parts will occur on separate FORMUL cards, each with the same component number and HET identifier. All except the last of these records will be terminated with a period. (iii) Solvent molecules and certain ot ...
Sculpting the b-peptide foldamer H12 helix via a designed side
... secondary structure, oligomers of trans-ABHC were constructed (Scheme 1). Conformational sampling was carried out on 4 by using a hybrid molecular dynamics (MD)–Monte Carlo (MC) method and MMFF94x force field.10 The lowest energy conformational family was the H12 helix (32% of the conformers, average ...
... secondary structure, oligomers of trans-ABHC were constructed (Scheme 1). Conformational sampling was carried out on 4 by using a hybrid molecular dynamics (MD)–Monte Carlo (MC) method and MMFF94x force field.10 The lowest energy conformational family was the H12 helix (32% of the conformers, average ...
amino acids M
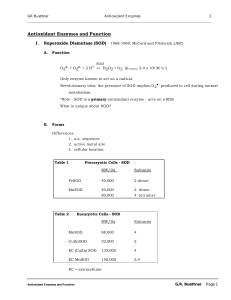
... 2o : Local structures which include, folds, turns, helices and b -sheets held in place by hydrogen bonds. 3o : 3-D arrangement of all atoms in a single polypeptide chain. 4o : Arrangement of polypeptide chains into a functional protein, eg. hemoglobin. ...
... 2o : Local structures which include, folds, turns, helices and b -sheets held in place by hydrogen bonds. 3o : 3-D arrangement of all atoms in a single polypeptide chain. 4o : Arrangement of polypeptide chains into a functional protein, eg. hemoglobin. ...
Essentiality of Histidine in Ruminant and Other Animals Including
... (steers), it was similarly demonstrated that the first, second and third limiting amino acids of rumen microbial proteins for these animals were methionine, lysine and threonine, respectively, based on their experimental results obtained after feeding the animals with pure diets containing urea as a ...
... (steers), it was similarly demonstrated that the first, second and third limiting amino acids of rumen microbial proteins for these animals were methionine, lysine and threonine, respectively, based on their experimental results obtained after feeding the animals with pure diets containing urea as a ...
the significance of hydrogen bonding
... catalyze the cleavage of RNA, including specific acids and bases, metal ions and their complexes not to mention naturally occurring enzymes.2-4 Nature has optimized the structure of the active sites of RNA-cleaving enzymes and ribozymes to achieve selective and efficient phosphodiester hydrolysis. M ...
... catalyze the cleavage of RNA, including specific acids and bases, metal ions and their complexes not to mention naturally occurring enzymes.2-4 Nature has optimized the structure of the active sites of RNA-cleaving enzymes and ribozymes to achieve selective and efficient phosphodiester hydrolysis. M ...
INTERMEDIARY METABOLISM
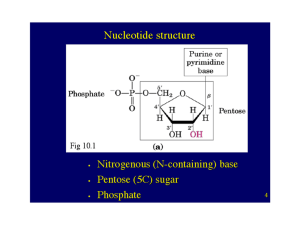
... In addition to these major bases, a number of other purine and pyrimidine derivatives have been isolated in small amount from various nucleic acids. The transfer RNAs (t-RNAs) contain several unusual bases, such as methylated or dimethylated derivatives of adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil. Othe ...
... In addition to these major bases, a number of other purine and pyrimidine derivatives have been isolated in small amount from various nucleic acids. The transfer RNAs (t-RNAs) contain several unusual bases, such as methylated or dimethylated derivatives of adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil. Othe ...
Mechanistic Studies of Two Selected Flavin
... Choline oxidase catalyzes the flavin-dependent, two-step oxidation of choline to glycine betaine via the formation of an aldehyde intermediate. The oxidation of choline includes two reductive half-reactions followed by oxidative half-reactions. In the first oxidation reaction, the alcohol substrate ...
... Choline oxidase catalyzes the flavin-dependent, two-step oxidation of choline to glycine betaine via the formation of an aldehyde intermediate. The oxidation of choline includes two reductive half-reactions followed by oxidative half-reactions. In the first oxidation reaction, the alcohol substrate ...
Strain in Protein Structures as Viewed Through Nonrotameric Side
... larger protein structure set and observed that a significant fraction (up to 30%) of particular side-chain types could not be assigned to a rotameric state based on the criterion that rotameric side chains can deviate in each of the 1 and 2 angles by no more than 20° from the closest associated ro ...
... larger protein structure set and observed that a significant fraction (up to 30%) of particular side-chain types could not be assigned to a rotameric state based on the criterion that rotameric side chains can deviate in each of the 1 and 2 angles by no more than 20° from the closest associated ro ...
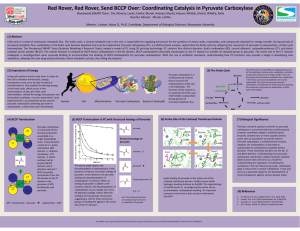
Poster
... Cells exist in a state of continuous metabolic flux. The Krebs cycle, a central metabolic hub in the cell, is responsible for supplying precursors for the synthesis of amino acids, nucleotides, and compounds required for energy transfer. During periods of increased metabolic flux, metabolites in the ...
... Cells exist in a state of continuous metabolic flux. The Krebs cycle, a central metabolic hub in the cell, is responsible for supplying precursors for the synthesis of amino acids, nucleotides, and compounds required for energy transfer. During periods of increased metabolic flux, metabolites in the ...
Accurate Prediction of Contact Numbers for Multi
... of residues in the protein for computing the oligomeric contact number. All nonprotein molecules were removed before computing the contact numbers. Nonprotein molecules such as coenzymes, ligands, and internal waters play important roles in the function of membrane proteins. However, the biochemical ...
... of residues in the protein for computing the oligomeric contact number. All nonprotein molecules were removed before computing the contact numbers. Nonprotein molecules such as coenzymes, ligands, and internal waters play important roles in the function of membrane proteins. However, the biochemical ...
Ars Pharmaceutica - Facultad de Farmacia
... flour in order to be used as a non-conventional ingredient in the formulation and preparation of diets for fish is very important. The traditional method for the amino acid composition analysis of proteins is separation by ion-exchange chromatography and post-column derivatization with ninhydrin as ...
... flour in order to be used as a non-conventional ingredient in the formulation and preparation of diets for fish is very important. The traditional method for the amino acid composition analysis of proteins is separation by ion-exchange chromatography and post-column derivatization with ninhydrin as ...
2.2.56. amino acid analysis
... by a rinse with HPLC grade methanol, dried overnight in an oven, and stored covered until use. Alternatively, pyrolysis of clean glassware at 500 °C for 4 h may also be used to eliminate contamination from hydrolysis tubes. Adequate disposable laboratory material can also be used. Acid hydrolysis is ...
... by a rinse with HPLC grade methanol, dried overnight in an oven, and stored covered until use. Alternatively, pyrolysis of clean glassware at 500 °C for 4 h may also be used to eliminate contamination from hydrolysis tubes. Adequate disposable laboratory material can also be used. Acid hydrolysis is ...
Purine metabolism - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... It is strongly inhibited by the end products IMP, AMP, and GMP. This type of inhibition is called FEEDBACK INHIBITION. ...
... It is strongly inhibited by the end products IMP, AMP, and GMP. This type of inhibition is called FEEDBACK INHIBITION. ...
Catalytic triad

A catalytic triad refers to the three amino acid residues that function together at the centre of the active site of some hydrolase and transferase enzymes (e.g. proteases, amidases, esterases, acylases, lipases and β-lactamases). An Acid-Base-Nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine amino acid, but occasionally threonine. Because enzymes fold into complex three-dimensional structures, the residues of a catalytic triad can be far from each other along the amino-acid sequence (primary structure), however, they are brought close together in the final fold.As well as divergent evolution of function (and even the triad's nucleophile), catalytic triads show some of the best examples of convergent evolution. Chemical constraints on catalysis have led to the same catalytic solution independently evolving in at least 23 separate superfamilies. Their mechanism of action is consequently one of the best studied in biochemistry.