Combinatorial mutagenesis to restrict amino acid usage in an
... by KSC (K ⫽ G ⫹ T); the Leu and Val codons were replaced by STG; the Ile codons were replaced by VTC or VTT (V ⫽ A ⫹ C ⫹ G); the Met codons were replaced by VTG; the Lys codons were replaced by ARA or ARG; the Glu codons were replaced by GAW (W ⫽ A ⫹ T) or GAS; the Asn codons were replaced by RAC or ...
... by KSC (K ⫽ G ⫹ T); the Leu and Val codons were replaced by STG; the Ile codons were replaced by VTC or VTT (V ⫽ A ⫹ C ⫹ G); the Met codons were replaced by VTG; the Lys codons were replaced by ARA or ARG; the Glu codons were replaced by GAW (W ⫽ A ⫹ T) or GAS; the Asn codons were replaced by RAC or ...
Proteinases as catalysts in peptide synthesis
... while performing the synthesis in essentially water-free organic solvent. SUBTILISIN AND OTHER SERINE PROTEINASES Serine proteinases are especially suitable for kinetically controlled peptide synthesis so far as the rate of acyl-enzyme formation and its further interaction with an amino component by ...
... while performing the synthesis in essentially water-free organic solvent. SUBTILISIN AND OTHER SERINE PROTEINASES Serine proteinases are especially suitable for kinetically controlled peptide synthesis so far as the rate of acyl-enzyme formation and its further interaction with an amino component by ...
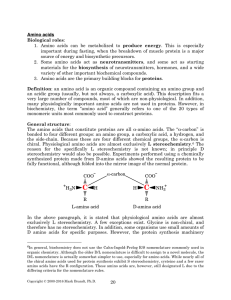
Amino Acids - Rose
... 1. The structures of all twenty standard amino acids. 2. The three and one letter codes for these amino acids. 3. The general properties of these compounds, such as size, charge, polar or nonpolar character. Acid-base chemistry of amino acids At pH >> pKa, the ionizable group will be deprotonated. F ...
... 1. The structures of all twenty standard amino acids. 2. The three and one letter codes for these amino acids. 3. The general properties of these compounds, such as size, charge, polar or nonpolar character. Acid-base chemistry of amino acids At pH >> pKa, the ionizable group will be deprotonated. F ...
FREE Sample Here
... Gly-Ser-Ala-His-Phe-Pro-Asn-Ala-Val-Glu-Cys-Ala-Ser A) chymotrypsin and thrombin B) trypsin and chymotrypsin C) thermolysin and chymotrypsin D) trypsin and thermolysin E) none of the above Answer: C Difficulty: 2 ...
... Gly-Ser-Ala-His-Phe-Pro-Asn-Ala-Val-Glu-Cys-Ala-Ser A) chymotrypsin and thrombin B) trypsin and chymotrypsin C) thermolysin and chymotrypsin D) trypsin and thermolysin E) none of the above Answer: C Difficulty: 2 ...
Higher Human Biology unit 1 section 5 ENZYMES
... • Made of protein, enzymes possess a region called the active site where the reaction occurs. It has a specific shape that is complementary to the shape of its substrate. • The enzyme’s active site changes shape very slightly as the substrate enters it, making the fit even more precise. This is kn ...
... • Made of protein, enzymes possess a region called the active site where the reaction occurs. It has a specific shape that is complementary to the shape of its substrate. • The enzyme’s active site changes shape very slightly as the substrate enters it, making the fit even more precise. This is kn ...
Metabolism & Enzymes - San Juan Unified School District
... each enzyme works with a specific substrate chemical fit between active site & substrate H bonds & ionic bonds ...
... each enzyme works with a specific substrate chemical fit between active site & substrate H bonds & ionic bonds ...
The Family of Berberine Bridge Enzyme-like
... This project would not have been realized without the help of various collaboration partners. Therefore I thank Prof. Christoph W. Sensen and B.Sc. Andreea M. Grecu for their support in the elaboration of the phylogenetics of the BBE-like protein family. The support of Prof. Bernd Nidetzky and Dr. A ...
... This project would not have been realized without the help of various collaboration partners. Therefore I thank Prof. Christoph W. Sensen and B.Sc. Andreea M. Grecu for their support in the elaboration of the phylogenetics of the BBE-like protein family. The support of Prof. Bernd Nidetzky and Dr. A ...
Mechanistic Role of an NS4A Peptide Cofactor with the Truncated
... the intermolecular consensus sequence site2 D/E-X-X-X-XC*-A/S differs from the intramolecular cleavage site by substitution of Thr for Cys at the P1 position (Grakoui et al., 1993a; Pizzi et al., 1994). A body of experimental evidence demonstrated that the 70 kDa NS3 protein is composed of two domai ...
... the intermolecular consensus sequence site2 D/E-X-X-X-XC*-A/S differs from the intramolecular cleavage site by substitution of Thr for Cys at the P1 position (Grakoui et al., 1993a; Pizzi et al., 1994). A body of experimental evidence demonstrated that the 70 kDa NS3 protein is composed of two domai ...
Amino Acids
... Acidic such as Glutamine, Asparagine etc… Basic such as Lysine and Histidine etc… ...
... Acidic such as Glutamine, Asparagine etc… Basic such as Lysine and Histidine etc… ...
Nutritional Requirements and Biosynthetic
... Metabolic studies of the Trypanosomidae have in general been confined to studies of catabolism and there is little known about the pathways of biosynthesis in these organisms. The development of a simple chemically defined growth medium for the parasitic flagellate Strigomonas (Herpetomonas) oncopel ...
... Metabolic studies of the Trypanosomidae have in general been confined to studies of catabolism and there is little known about the pathways of biosynthesis in these organisms. The development of a simple chemically defined growth medium for the parasitic flagellate Strigomonas (Herpetomonas) oncopel ...
Nutritional Requirements and Biosynthetic
... Metabolic studies of the Trypanosomidae have in general been confined to studies of catabolism and there is little known about the pathways of biosynthesis in these organisms. The development of a simple chemically defined growth medium for the parasitic flagellate Strigomonas (Herpetomonas) oncopel ...
... Metabolic studies of the Trypanosomidae have in general been confined to studies of catabolism and there is little known about the pathways of biosynthesis in these organisms. The development of a simple chemically defined growth medium for the parasitic flagellate Strigomonas (Herpetomonas) oncopel ...
CaoSpr10
... two mutants (H302A and E303A), with the wild-type ProRS activity set at 100%. The enzyme concentrations used were 1 M (BioRad concentration). Values reported are the average of two or three experiments with < 20 % difference between trials. ...
... two mutants (H302A and E303A), with the wild-type ProRS activity set at 100%. The enzyme concentrations used were 1 M (BioRad concentration). Values reported are the average of two or three experiments with < 20 % difference between trials. ...
medicinal-chemistry-lect-3-n-17-acid-base
... When the PH=PKa , the compound is 50% ionized (or 50% unionized). When the PKa =PH , the molar concentration of the acid equals to molar concentration of its conjugate base. When log ⌊conjugate base⌋/[acid] =1 ...
... When the PH=PKa , the compound is 50% ionized (or 50% unionized). When the PKa =PH , the molar concentration of the acid equals to molar concentration of its conjugate base. When log ⌊conjugate base⌋/[acid] =1 ...
Poster
... diseases (2). In this project, a number of putative sEH inhibitors were designed. Work was based on previous drug design efforts as well as on the threedimensional structure of the human enzyme (3). sEH crystal structures exhibit two domains with distinct activities—the C-terminal domain catalyzes t ...
... diseases (2). In this project, a number of putative sEH inhibitors were designed. Work was based on previous drug design efforts as well as on the threedimensional structure of the human enzyme (3). sEH crystal structures exhibit two domains with distinct activities—the C-terminal domain catalyzes t ...
Document
... of intermediates), and conformational changes that limit the rate of product release. 3. The value of kcat/KM defines the apparent second-order rate constant for substrate binding and sets a lower limit on the second-order rate constant for substrate binding. The term kcat/KM is less than the true r ...
... of intermediates), and conformational changes that limit the rate of product release. 3. The value of kcat/KM defines the apparent second-order rate constant for substrate binding and sets a lower limit on the second-order rate constant for substrate binding. The term kcat/KM is less than the true r ...
Non-homologous Recombination of Deoxyribonucleoside Kinases
... phosphorylates pyrimidine and purine deoxyribonucleosides, as well as several NAs. DmdNK has been the subject of both rational and random mutagenesis approaches to probe its substrate specificity.6,7 In contrast with DmdNK, the less studied hTK2 is ∼30 to 80-fold less efficient at phosphorylating py ...
... phosphorylates pyrimidine and purine deoxyribonucleosides, as well as several NAs. DmdNK has been the subject of both rational and random mutagenesis approaches to probe its substrate specificity.6,7 In contrast with DmdNK, the less studied hTK2 is ∼30 to 80-fold less efficient at phosphorylating py ...
Catalytic triad

A catalytic triad refers to the three amino acid residues that function together at the centre of the active site of some hydrolase and transferase enzymes (e.g. proteases, amidases, esterases, acylases, lipases and β-lactamases). An Acid-Base-Nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine amino acid, but occasionally threonine. Because enzymes fold into complex three-dimensional structures, the residues of a catalytic triad can be far from each other along the amino-acid sequence (primary structure), however, they are brought close together in the final fold.As well as divergent evolution of function (and even the triad's nucleophile), catalytic triads show some of the best examples of convergent evolution. Chemical constraints on catalysis have led to the same catalytic solution independently evolving in at least 23 separate superfamilies. Their mechanism of action is consequently one of the best studied in biochemistry.