Poster - MSOE Center for BioMolecular Modeling
... cell. Tissue factor can be found on most cells in the human body. The tissue factor serves as a cofactor with factor VII to promote the activation of factor X. Factor X activates prothrombin, which then activates thrombin in a reaction that requires Factor V. Thrombin converts soluble fibrinogen int ...
... cell. Tissue factor can be found on most cells in the human body. The tissue factor serves as a cofactor with factor VII to promote the activation of factor X. Factor X activates prothrombin, which then activates thrombin in a reaction that requires Factor V. Thrombin converts soluble fibrinogen int ...
Metabolism & Enzymes - T.R. Robinson High School
... Too much activation energy for life Activation energy amount of energy needed to destabilize the bonds of a molecule moves the reaction over an “energy hill” ...
... Too much activation energy for life Activation energy amount of energy needed to destabilize the bonds of a molecule moves the reaction over an “energy hill” ...
ppt - 3.LF UK 2015
... The figure is found at: http://fig.cox.miami.edu/~cmallery/255/255enz/enzymology.htm (December 2006) ...
... The figure is found at: http://fig.cox.miami.edu/~cmallery/255/255enz/enzymology.htm (December 2006) ...
end of semester main examination - UR-CST
... 2. Answer Question ONE in Section A, and any TWO out of questions in Section B 3. No written materials allowed into the examination room. 4. Write all answers in the booklet provided. 5. Do not forget to write your Registration Number. 6. All Questions carry a maximum of 20 Marks each ...
... 2. Answer Question ONE in Section A, and any TWO out of questions in Section B 3. No written materials allowed into the examination room. 4. Write all answers in the booklet provided. 5. Do not forget to write your Registration Number. 6. All Questions carry a maximum of 20 Marks each ...
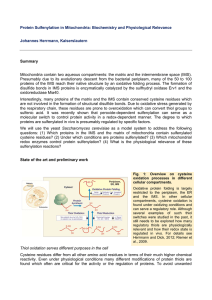
Protein Sulfenylation in Mitochondria: Biochemistry and
... In some cellular compartments such as in the bacterial periplasm, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the intermembrane space of mitochondria (IMS), dedicated machineries exist which introduce stable disulfide bonds into newly synthesized proteins. In this case, thiol oxidation can significantly cont ...
... In some cellular compartments such as in the bacterial periplasm, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the intermembrane space of mitochondria (IMS), dedicated machineries exist which introduce stable disulfide bonds into newly synthesized proteins. In this case, thiol oxidation can significantly cont ...
WrkSht4-AAroles-Mutations
... a completely different direction; the Calpha of the N‑ cap residue is where that abrupt change takes place. Ser, Thr, Asn, and Asp are all very common in N‑ cap positions, usually making an H-bond from the side-chain oxygen to a free backbone NH group in the first turn of the helix, as in this case ...
... a completely different direction; the Calpha of the N‑ cap residue is where that abrupt change takes place. Ser, Thr, Asn, and Asp are all very common in N‑ cap positions, usually making an H-bond from the side-chain oxygen to a free backbone NH group in the first turn of the helix, as in this case ...
... the submitted sequence could be assigned. The gene coding for this putative anti-sigma factor is located adjacent to a predicted σECF gene (BDI_1680) and a CSS receptor gene (BDI_1682), which strongly suggests that the resulting protein is, like FoxR, part of a CSS system. Indeed, although FoxR and ...
PT2009-1 Overcoming Peptide Problems by Design.indd
... unique with regard to its chemical and physical properties. While some peptides are difcult to synthesize, many peptides are relatively straightforward to synthesize but may still be difcult to purify after synthesis. A common problem with many peptides is insolubility in aqueous solution. For pur ...
... unique with regard to its chemical and physical properties. While some peptides are difcult to synthesize, many peptides are relatively straightforward to synthesize but may still be difcult to purify after synthesis. A common problem with many peptides is insolubility in aqueous solution. For pur ...
Enzymes with Molecular Tunnels - Department of Biochemistry | UW
... active site of the large subunit, and is lined, for the most part, with unreactive side chains and backbone atoms. The portion of the tunnel lying between the two active sites of the large subunit is somewhat less hydrophobic. In support of the molecular tunnel, many of the residues lining the pathw ...
... active site of the large subunit, and is lined, for the most part, with unreactive side chains and backbone atoms. The portion of the tunnel lying between the two active sites of the large subunit is somewhat less hydrophobic. In support of the molecular tunnel, many of the residues lining the pathw ...
... Amino acid 2. Only the protonated form of histidine can participate acid in protein in electrostatic interactions, therefore any effects Energy HA A A HA on the deprotonated form can be ignored. 3. The negative charge on the aspartic acid residue will stabilize the + charge on the histidine side cha ...
Microbial fermentation (Enzymology,metabolic pathways and
... Enzymes. Enzymes equilibrium state. Factors effects enzymes catalytic activity. Natural mechanisms for regulating enzyme activity. Enzymes activators. Classification of enzymes. ...
... Enzymes. Enzymes equilibrium state. Factors effects enzymes catalytic activity. Natural mechanisms for regulating enzyme activity. Enzymes activators. Classification of enzymes. ...
Novel Specific Halogenating Enzymes from Bacteria
... (van Pée et al., 1987; Wiesner et al., 1988). Some of these non-heme haloperoxidases were identified as chloroperoxidases and they seemed to have some substrate specificity with regard to the chlorination reaction, as they did not chlorinate all the substrates they could brominate (Bongs & van Pée, ...
... (van Pée et al., 1987; Wiesner et al., 1988). Some of these non-heme haloperoxidases were identified as chloroperoxidases and they seemed to have some substrate specificity with regard to the chlorination reaction, as they did not chlorinate all the substrates they could brominate (Bongs & van Pée, ...
slides
... In general, large superfamilies are more diverse, and the relationships within them are harder to discover . Thus, unnormalized coverage is typically less than the linearly normalized coverage, which in turn is less than quadratically normalized coverage. One important point of comparison for search ...
... In general, large superfamilies are more diverse, and the relationships within them are harder to discover . Thus, unnormalized coverage is typically less than the linearly normalized coverage, which in turn is less than quadratically normalized coverage. One important point of comparison for search ...
Enzymes
... When instructed to do so, each lab table will place a piece of candy in the beaker of water and each student will place a piece of candy in their cheek. Do not suck on the candy. The candy will be left in place for 15 minutes. 1. Predict the difference in mass between the candy in the water and the ...
... When instructed to do so, each lab table will place a piece of candy in the beaker of water and each student will place a piece of candy in their cheek. Do not suck on the candy. The candy will be left in place for 15 minutes. 1. Predict the difference in mass between the candy in the water and the ...
Primary structure: the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
... polypeptide chain; read from the N-terminal amino acid to the C-terminal amino acid • Secondary structure: conformations of amino acids in localized regions of a polypeptide chain; examples are -helix, b-pleated sheet, and random coil Tertiary structure: the overall conformation of a polypeptide ch ...
... polypeptide chain; read from the N-terminal amino acid to the C-terminal amino acid • Secondary structure: conformations of amino acids in localized regions of a polypeptide chain; examples are -helix, b-pleated sheet, and random coil Tertiary structure: the overall conformation of a polypeptide ch ...
Document
... 1. Determine the amino acids present and their relative ratios 2. Cleave the peptide or protein into smaller peptide fragments and determine their sequences 3. Cleave the peptide or protein by another method and determine their sequences. Align the sequences of the peptide fragments from the two met ...
... 1. Determine the amino acids present and their relative ratios 2. Cleave the peptide or protein into smaller peptide fragments and determine their sequences 3. Cleave the peptide or protein by another method and determine their sequences. Align the sequences of the peptide fragments from the two met ...
Catalytic triad

A catalytic triad refers to the three amino acid residues that function together at the centre of the active site of some hydrolase and transferase enzymes (e.g. proteases, amidases, esterases, acylases, lipases and β-lactamases). An Acid-Base-Nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine amino acid, but occasionally threonine. Because enzymes fold into complex three-dimensional structures, the residues of a catalytic triad can be far from each other along the amino-acid sequence (primary structure), however, they are brought close together in the final fold.As well as divergent evolution of function (and even the triad's nucleophile), catalytic triads show some of the best examples of convergent evolution. Chemical constraints on catalysis have led to the same catalytic solution independently evolving in at least 23 separate superfamilies. Their mechanism of action is consequently one of the best studied in biochemistry.