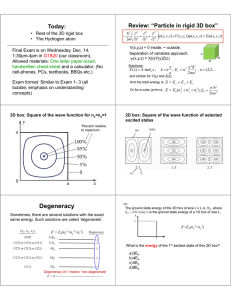
Klicker-questions, chapter 1 1. The figure shows the probability
... 5. The deBroglie wavelength is given by λ=h/p, where p is the momentum of the particle.Which of these statements is correct? a) The deBroglie wavelength of a particle is increasing when the energy of the particle is increasing ...
... 5. The deBroglie wavelength is given by λ=h/p, where p is the momentum of the particle.Which of these statements is correct? a) The deBroglie wavelength of a particle is increasing when the energy of the particle is increasing ...
10: The Expanding Universe
... incredibly strong that anything nearby is pulled in, never to be seen again. Even light can't escape. Black holes are extremely important for several reasons. They demonstrate that matter can be hidden. As we will see later, they may contribute to gravitational waves. But the big whopper is this: Th ...
... incredibly strong that anything nearby is pulled in, never to be seen again. Even light can't escape. Black holes are extremely important for several reasons. They demonstrate that matter can be hidden. As we will see later, they may contribute to gravitational waves. But the big whopper is this: Th ...
Electron Configuration Class Notes
... Postulated that since light shows a “dual nature” – has wave properties as well as particulate properties, then matter should also be able to move - not only as particles - but also as waves! - this property is not observable unless the mass is small enough (like electrons) - may relate wave propert ...
... Postulated that since light shows a “dual nature” – has wave properties as well as particulate properties, then matter should also be able to move - not only as particles - but also as waves! - this property is not observable unless the mass is small enough (like electrons) - may relate wave propert ...
By: 3rd Period Chemistry Actinide Ionization Energy Probability
... Shows interactions between light and electrons occur at specific energies emission ...
... Shows interactions between light and electrons occur at specific energies emission ...
Quantum systems in one-dimension and quantum transport
... IPCMS – Institut de Physique et Chimie des Matériaux de Strasbourg Quantum systems confined to low dimensions, such as spin chains, carbon nanotubes or cold atoms in optical lattices, often behave in a universal way that is efficiently described in terms of simple effective theories. These introduct ...
... IPCMS – Institut de Physique et Chimie des Matériaux de Strasbourg Quantum systems confined to low dimensions, such as spin chains, carbon nanotubes or cold atoms in optical lattices, often behave in a universal way that is efficiently described in terms of simple effective theories. These introduct ...
Physics 2018: Great Ideas in Science: The Physics Module Quantum
... aren’t influenced by its physical environment (e.g., rest mass and charge). ...
... aren’t influenced by its physical environment (e.g., rest mass and charge). ...
It is a commonplace that the non-classical type of rationality
... process rather than the object equal to itself. NB! In classical science the picture of the world must have been the one of the studied object as such; in non-classical science the scientific description includes the instruments and equipment of the research as well as the very act of measuring. In ...
... process rather than the object equal to itself. NB! In classical science the picture of the world must have been the one of the studied object as such; in non-classical science the scientific description includes the instruments and equipment of the research as well as the very act of measuring. In ...
Spin-orbit interaction (or “coupling”)
... … this is known as the Lamb shift of the s level. It was first observed in 1947-1952 and was crucial for the development of QED. Significance of Lamb shift In QED the electromagnetic field is quantised. A quantised field has a zero point energy (analogous to the ground state of the simple harmonic ...
... … this is known as the Lamb shift of the s level. It was first observed in 1947-1952 and was crucial for the development of QED. Significance of Lamb shift In QED the electromagnetic field is quantised. A quantised field has a zero point energy (analogous to the ground state of the simple harmonic ...
Problem set 9
... has mean momentum hpi = ~k0 at t = 0. Write down ψ̃(k, t = 0) and then obtain ψ̃(k, t) in the energy/momentum basis. h3i 2. Find hpi at t > 0. hpi is most easily calculated in the momentum basis. h4i 3. Calculate h x̂i at time t in the above gaussian wave packet. Since ψ̃(k, t) is known, it is good ...
... has mean momentum hpi = ~k0 at t = 0. Write down ψ̃(k, t = 0) and then obtain ψ̃(k, t) in the energy/momentum basis. h3i 2. Find hpi at t > 0. hpi is most easily calculated in the momentum basis. h4i 3. Calculate h x̂i at time t in the above gaussian wave packet. Since ψ̃(k, t) is known, it is good ...
Numerical Methods in Quantum Field Theories
... These two fields give us the foundational tools to describe the interactions of relativistic quantum systems. It should be noted that both equations have solutions with negative energies, which was initially seen as a weakness of the theories. Reinterpretation of those solutions as a particles corre ...
... These two fields give us the foundational tools to describe the interactions of relativistic quantum systems. It should be noted that both equations have solutions with negative energies, which was initially seen as a weakness of the theories. Reinterpretation of those solutions as a particles corre ...
Renormalization

In quantum field theory, the statistical mechanics of fields, and the theory of self-similar geometric structures, renormalization is any of a collection of techniques used to treat infinities arising in calculated quantities.Renormalization specifies relationships between parameters in the theory when the parameters describing large distance scales differ from the parameters describing small distances. Physically, the pileup of contributions from an infinity of scales involved in a problem may then result in infinities. When describing space and time as a continuum, certain statistical and quantum mechanical constructions are ill defined. To define them, this continuum limit, the removal of the ""construction scaffolding"" of lattices at various scales, has to be taken carefully, as detailed below.Renormalization was first developed in quantum electrodynamics (QED) to make sense of infinite integrals in perturbation theory. Initially viewed as a suspect provisional procedure even by some of its originators, renormalization eventually was embraced as an important and self-consistent actual mechanism of scale physics in several fields of physics and mathematics. Today, the point of view has shifted: on the basis of the breakthrough renormalization group insights of Kenneth Wilson, the focus is on variation of physical quantities across contiguous scales, while distant scales are related to each other through ""effective"" descriptions. All scales are linked in a broadly systematic way, and the actual physics pertinent to each is extracted with the suitable specific computational techniques appropriate for each.