Document
... It is well known fact that the theory of radiation reaction in electrodynamics as worked out by Lorentz [1] (actually by Lorentz, Abraham and Dirac) has solutions, which exhibits a runaway nature and/or non-causal preacceleration. In fact the non-causal pre-acceleration without runaway makes more se ...
... It is well known fact that the theory of radiation reaction in electrodynamics as worked out by Lorentz [1] (actually by Lorentz, Abraham and Dirac) has solutions, which exhibits a runaway nature and/or non-causal preacceleration. In fact the non-causal pre-acceleration without runaway makes more se ...
L01_5342_Sp02
... • Compton showed Dp = hkinitial - hkfinal, so an photon (wave) is particle-like • DeBroglie hypothesized a particle could be wave-like, l = h/p • Davisson and Germer demonstrated wave-like interference phenomena for electrons to complete the duality model L1 January 15 ...
... • Compton showed Dp = hkinitial - hkfinal, so an photon (wave) is particle-like • DeBroglie hypothesized a particle could be wave-like, l = h/p • Davisson and Germer demonstrated wave-like interference phenomena for electrons to complete the duality model L1 January 15 ...
Atomic Structure
... 1. The Bohr model of the atom was the first quantum mechanical model of the atom. a. Bohr postulated that a hydrogen atom could only exist without radiating in one of a set of stationary states. Explain what is meant by this postulate. b. Bohr related his postulate to the classical picture of a hydr ...
... 1. The Bohr model of the atom was the first quantum mechanical model of the atom. a. Bohr postulated that a hydrogen atom could only exist without radiating in one of a set of stationary states. Explain what is meant by this postulate. b. Bohr related his postulate to the classical picture of a hydr ...
Exercises in Statistical Mechanics
... Exercises in Statistical Mechanics Based on course by Doron Cohen, has to be proofed Department of Physics, Ben-Gurion University, Beer-Sheva 84105, Israel This exercises pool is intended for a graduate course in “statistical mechanics”. Some of the problems are original, while other were assembled ...
... Exercises in Statistical Mechanics Based on course by Doron Cohen, has to be proofed Department of Physics, Ben-Gurion University, Beer-Sheva 84105, Israel This exercises pool is intended for a graduate course in “statistical mechanics”. Some of the problems are original, while other were assembled ...
Why quantum gravity? - University of Oxford
... general theory of relativity which accurately describes many phenomena occuring at very different distance scales: from the gravitational red-shift of light observed in the laboratory experiment of Pound and Rebka; through the precession of the perihelion of Mercury; to the evolution of the universe ...
... general theory of relativity which accurately describes many phenomena occuring at very different distance scales: from the gravitational red-shift of light observed in the laboratory experiment of Pound and Rebka; through the precession of the perihelion of Mercury; to the evolution of the universe ...
File - Chemistry 11 Enriched
... Each element has a specific electron configuration defining where the electrons are located. In order to understand the location of electrons, we must now look at the atom in three dimensions rather than the planetary early model of the atom. The orbitals are not two dimensional tracks like railroad ...
... Each element has a specific electron configuration defining where the electrons are located. In order to understand the location of electrons, we must now look at the atom in three dimensions rather than the planetary early model of the atom. The orbitals are not two dimensional tracks like railroad ...
Part 7 – Quantum physics Useful weblinks Fermilab Inquiring Minds
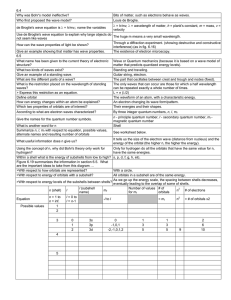
... atomic and molecular orbitals. http://chemed.chem.purdue.edu/genchem/topicreview/bp/ch6/quantum.html Quantum Numbers This website is from the University of Colorado. It gives a solid non-mathematical explanation of quantum numbers and how they work in atomic physics, including spin. http://www.color ...
... atomic and molecular orbitals. http://chemed.chem.purdue.edu/genchem/topicreview/bp/ch6/quantum.html Quantum Numbers This website is from the University of Colorado. It gives a solid non-mathematical explanation of quantum numbers and how they work in atomic physics, including spin. http://www.color ...
Renormalization

In quantum field theory, the statistical mechanics of fields, and the theory of self-similar geometric structures, renormalization is any of a collection of techniques used to treat infinities arising in calculated quantities.Renormalization specifies relationships between parameters in the theory when the parameters describing large distance scales differ from the parameters describing small distances. Physically, the pileup of contributions from an infinity of scales involved in a problem may then result in infinities. When describing space and time as a continuum, certain statistical and quantum mechanical constructions are ill defined. To define them, this continuum limit, the removal of the ""construction scaffolding"" of lattices at various scales, has to be taken carefully, as detailed below.Renormalization was first developed in quantum electrodynamics (QED) to make sense of infinite integrals in perturbation theory. Initially viewed as a suspect provisional procedure even by some of its originators, renormalization eventually was embraced as an important and self-consistent actual mechanism of scale physics in several fields of physics and mathematics. Today, the point of view has shifted: on the basis of the breakthrough renormalization group insights of Kenneth Wilson, the focus is on variation of physical quantities across contiguous scales, while distant scales are related to each other through ""effective"" descriptions. All scales are linked in a broadly systematic way, and the actual physics pertinent to each is extracted with the suitable specific computational techniques appropriate for each.