dummy variables - bryongaskin.net
... function as well as the conditional mean function. We can interpret the resulting coefficients as the effect of one-unit changes in the independent variable on the probability that the dependent variable equals one. Predicted values from the linear probability model One potential problem with the li ...
... function as well as the conditional mean function. We can interpret the resulting coefficients as the effect of one-unit changes in the independent variable on the probability that the dependent variable equals one. Predicted values from the linear probability model One potential problem with the li ...
part a (for mm students only)
... We should use relatively more labour if we learn that the marginal product per dollar of labour expenditures is less than a marginal product per dollar of capital ...
... We should use relatively more labour if we learn that the marginal product per dollar of labour expenditures is less than a marginal product per dollar of capital ...
ECONOMETRICS LECTURE: HECKMAN’s SAMPLE SELECTION MODEL
... two groups of people (i) industrious; (ii) lazy. Industrious people get higher wages and have jobs, lazy people do not. In effect we are doing the regression in this simplified example on the industrious part of the labour force. The returns to education will be estimated on them alone not the whole ...
... two groups of people (i) industrious; (ii) lazy. Industrious people get higher wages and have jobs, lazy people do not. In effect we are doing the regression in this simplified example on the industrious part of the labour force. The returns to education will be estimated on them alone not the whole ...
Supplementary Material
... performed according to the following reliability criteria (default values): B sites), N/B ...
... performed according to the following reliability criteria (default values): B sites), N/B ...
Presentation
... - count data -depending on chosen parameters positively skewed - generalisation of poisson ...
... - count data -depending on chosen parameters positively skewed - generalisation of poisson ...
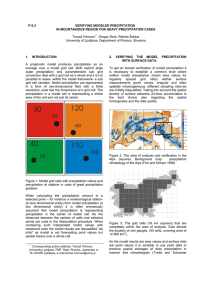
P 8.3 VERIFYING MODELED PRECIPITATION IN MOUNTANIOUS
... heights averaged over grid cell size as an auxiliary variable. With climatological precipitation (Kastelec, 1999) we get a significant increase of the maximum with the smallest grid cells, (from 158 mm to 204 mm) and a slight increase in variability compared to ordinary kriging, while mean is conser ...
... heights averaged over grid cell size as an auxiliary variable. With climatological precipitation (Kastelec, 1999) we get a significant increase of the maximum with the smallest grid cells, (from 158 mm to 204 mm) and a slight increase in variability compared to ordinary kriging, while mean is conser ...
to read the entire article
... fog to very clear air. Observator and its Obsermet solution are a frequent choice for windfarm projects, with measurements of windspeed direction, temperature, humidity, barometric pressure, cloud base and visibility as well as wave height. Dutch and overseas harbour authorities also use Obsermet sy ...
... fog to very clear air. Observator and its Obsermet solution are a frequent choice for windfarm projects, with measurements of windspeed direction, temperature, humidity, barometric pressure, cloud base and visibility as well as wave height. Dutch and overseas harbour authorities also use Obsermet sy ...
Easy Methods to Investigate Large Datasets Using
... we also see that this variable has a maximum value of 208, suggesting the existence of outliers. The probability plot clearly shows several outliers beyond 50 that would need to be investigated before this variable were used in any analysis. This sort of information would be difficult to gather from ...
... we also see that this variable has a maximum value of 208, suggesting the existence of outliers. The probability plot clearly shows several outliers beyond 50 that would need to be investigated before this variable were used in any analysis. This sort of information would be difficult to gather from ...
Introduction to Spatial Data Mining
... Patterns usually have to be defined in the spatial attribute subspace and not in the complete attribute space Longitude and latitude (or other coordinate systems) are the glue that link different data collections together People are used to maps in GIS; therefore, data mining results have to be summ ...
... Patterns usually have to be defined in the spatial attribute subspace and not in the complete attribute space Longitude and latitude (or other coordinate systems) are the glue that link different data collections together People are used to maps in GIS; therefore, data mining results have to be summ ...