* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerPoint - Science A 2 Z
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
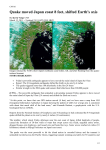
By Candy Olson Fault lines = relief of stress Subduction: normal faulting reverse faulting strikeslip transform http://www.iris.edu/gifs/animations/faults.htm tsunami http:/www.pbs.org/wnet/savageearth/animations/tsu nami/main.html Danger -Getting knocked about by debris -Being pulled out to sea Observed phenomena Gas clouds-can be irritating, fatal, eclipse the sky Lightning Haze –before, during and after a quake Water/steam geiser Sand, coal or other mineral geiser Land splits, drops, or raises seismograph Measurements 1st in China@135 C.E. Han dynasty-invented by Chang Heng 1st modern day seismograph in 1875 by Cecchi in Italy – used a suspended pendulum Work was done in 1880’s in Japan that continued to improve on Cecchi’s work http://earthquake.usgs.gov/learning/kids/kidsLearnin gLinks.php Types of measurement Richter scale: measures movement of suspended pen (seismograph) during a quake Seismic moment: measures how much and how far the Earth’s crust moves during a quake Types of earthquakes Benioff zone- focus is deep in subduction zone Surface- focus is at or near the surface of the Earth’s crust http://www.pbs.org/wnet/savageearth/animations/eart hquakes/index.html How do scientists know where the focus is? One station recording a quake gives a circle of possibilites. Two stations give two possibilities. Three stations finds the location of the epicenter. Four stations finds the depth/ focus. Scientific advancement from studying earthquakes: Have learned that entire plates can shake in a great quake; Are learning what the interior of the Earth is made of/how it’s arranged. Are learning the geological history of the Earth. Lab activity http://web.ics.purdue.edu/~braile/edumod/slinky/sli nky.htm