* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download p(O 2 )
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
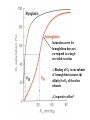
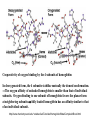
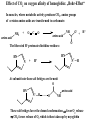
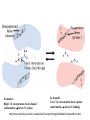
Oxygen binding by myoglobin (Mb) Since O2 is a gas, we can replace the concentration [O2] by partial pressure p(O2) [ Mb] p(O2 ) Kd [ MbO2 ] p(O2 ) Y [ K d p(O2 )] Exercise 1 Calculate the saturation curve for oxygen binding to myoglobin. Disociation constant of the MbO2 complex at 37 °C, pH = 7, p = 760 Torr: Kd = 2.8 Torr. p(O2) [Torr] 0.5 1 2 3 5 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 Y [%] Y [%] 15.2 26.3 41.7 51.7 64.1 78.1 87.7 91.5 93.5 94.7 95.5 96.2 96.6 97.0 100 80 60 Exercise 2: Calculate the slope of the saturation curve at p(O2) = 0. Plot the slope dY/d[p(O2)] as a function of p(O2) 40 20 0 0 30 60 p(O2) [Torr] 90 p(O2 ) Y [ K d p(O2 )] Kd dY 1 p(O2 ) dp(O2 ) [ K d p(O2 )] [ K d p(O2 )]2 [ K d p(O2 )]2 At p(O2) = 0 dY 1 dp(O2 ) K d Čím silnější afinita mezi Mb a O2, tím strmější křivka v bodě 0;0 -1 dY/dp(O ) [Torr ] 2 0.30 0.25 0.20 0.15 0.10 0.05 0.00 0 20 40 60 p(O2) [Torr] 80 Slope of the saturation curve decreases with p(O2) 100 Saturation curve for hemoglobinu does not correspond to a single reversible reaction Binding of O2 to one subunit of hemoglobin increases the affinity for O2 of the other subunits „Cooperative effect“ Cooperativity of oxygen binding by the 4 subunits of hemoglobin: In deoxygenated form, the 4 subunits stabilize mutually the domed conformation. The oxygen affinity of unloaded hemoglobin is smaller than that of individual subunits. Oxygen binding to one subunit of hemoglobin favors the planar form at neighboring subunits fully loaded hemoglobin has an affinity similar to that of an individual subunit. http://www.chemistry.wustl.edu/~edudev/LabTutorials/Hemoglobin/MetalComplexinBlood.html Effect of CO2 on oxygen afinity of hemoglobin: „Bohr-Effect“ In muscles, where metabolic activity produces CO2, amino groups of certains amino acids are transformed to carbamate: NH2 + O C O amino acid amino acid HN N + H+ + H+ O The liberated H+ protonates histidine residues: HN O- NH N+ H At subunit interfaces salt bridges are formed: O HN N+ amino acid H O- NH These salt bridges favor the domed conformation favor O2 release CO2 favors release of O2 which is then taken up by myoglobin In muscles: High CO2 concentration favors domed conformation favors O2 release In bronchi: Low CO2 concentration favors planar conformation favors O2 binding http://www.chemistry.wustl.edu/~edudev/LabTutorials/Hemoglobin/MetalComplexinBlood.html