* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nodal Analysis 1
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Topology (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
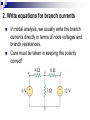
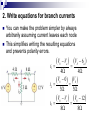
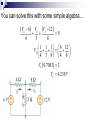
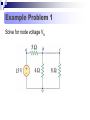
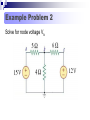
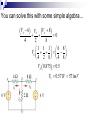
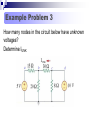
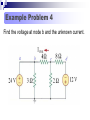
Lesson 7: Nodal Analysis I Learning Objectives Apply Ohm’s Law using nodal voltages. Apply the Nodal Analysis method to determine an unknown node voltage and branch currents in a simple DC circuit Nodal analysis Based on a systematic application of KCL, nodal analysis allows us to obtain a set of simultaneous equations to solve for voltages and current in any linear circuit. Nodal analysis steps In nodal analysis we are interested in finding node voltages. Given a circuit with n nodes, 1. Select a reference node. Assign voltages va, vb, vc …. to the remaining nodes. 2. Apply KCL to each node expressing branch currents in terms of node voltages. 3. Solve the resulting simultaneous equations to obtain unknown node voltages. 1. Identify the nodes What are the voltages of the three nodes a,b,c below? Va 6V Vb unknown Vc 12V 2. Write equations for branch currents In nodal analysis, we usually write the branch currents directly in terms of node voltages and branch resistances. Care must be taken in keeping the polarity correct! 2. Write equations for branch currents You can make the problem simpler by always arbitrarily assuming current leaves each node This simplifies writing the resulting equations and prevents polarity errors. i1 i2 i3 Vb Va Vb 6a 4 Vb 0 3 Vb Vc 8 4 Vb 3 Vb 12 8 3. Substitute into KCL and solve for the unknowns Vb 6 4 current out = current in i1 i2 i3 0 Vb Vb 12 0 3 8 You can solve this with some simple algebra… Vb 6 4 Vb Vb 12 0 8 3 1 1 1 6 12 Vb 4 3 8 4 8 Vb 0.7083 3 Vb 4.235V Example Problem 1 Solve for node voltage Vb Example Problem 2 Solve for node voltage Vb Making it tougher… The polarity of the voltage supplies changes how you write the equations Notice the inverted supply on the right and how you write the equation i1 i2 i3 Vb Va Vb 6a 4 Vb 0 2 Vb Vc 8 4 Vb 2 Vb 8 8 Vb 8 8 You can solve this with some simple algebra… Vb 6 4 Vb Vb 8 0 2 8 1 1 1 6 8 Vb 4 2 8 4 8 Vb 0.875 0.5 Vb 0.571V 571mV Example Problem 3 How many nodes in the circuit below have unknown voltages? Determine IUNK Example Problem 4 Find the voltage at node b and the unknown current.