* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt
Yagi–Uda antenna wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
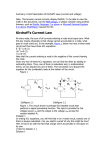
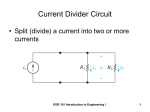
ENGS2613 Intro Electrical Science Week 3 Dr. George Scheets Read Problems 2.17, 20, 22, 23, 26, & 27 Quiz #2, 3 February 2.5, 3.1, & 3.2 Analyze a circuit using either KVL or KCL equations Quiz #1 Available for pickup in ES016 Quiz 1A Scores have been bumped by 1 point Up to a max score of 10 Using Kirchhoff's Current Law Draw & label current thru every element Label voltage drops for each element Node = wire at single voltage. Boundary is set by any circuit element. Write Current Equations, mostly using KCL & Ohm's Law Passive device (Resistor): MUST follow current directions Current into + voltage side, Current out on – voltage side Active device (Voltage or Current source): Generally Assume Current exits + side & enters – side Label voltages at each node Arbitrary direction Hit each circuit element once (& only once) Same current? Use same label KCL: Sum of currents entering node = sum of currents exiting Solve Equations DC Circuit with Resistors Pause. Look at circuit. Mark known voltages Mark known currents Is it possible to simplify? Worth doing so? Can you use Ohm's Law? Have 2 of 3 (V, I, or R)? Can you use KCL? Know I's thru a node, except one? Formally use KCL or KVL KCL: Write current equations based on Node Current I/O KVL: Write voltage add/drop equations (ΔV's) based on Current Loops Noted Problem Areas Ohm's Law: V = IR Voltage Drop across a device = Current thru the device * Device's Resistance Might Help to think of it as ΔV = IR KVL Loop Currents = Actual current thru a device if only 1 Loop Current More than one Loop Current? Actual current = sum of the Loop Currents Power Active device: P = VI Passive device (Resistor): P = VI = I2R = V2/R Transistors Source: learn.mikroe.com & hothardware.com Intel's i7 processor has over 1.3 billion transitors.