* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Faults - cloudfront.net
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
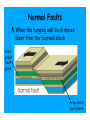
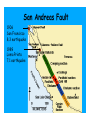
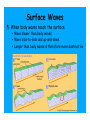
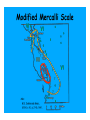
Earth Shattering Quakes Earth Science Earthquake The vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy within the lithosphere. Elastic Rebound Hypothesis Earthquakes are produced when the strength of a rock is exceeded, it breaks, and then causes a sudden release of stored energy called seismic waves. Imperial Fault, CA Elastic Rebound Focus The point within the Earth where an earthquake starts. Located along a fault beneath the surface Epicenter The location on the surface directly above the focus. Faults Fractures in the Earth’s crust where movement has occurred. Normal Faults When the hanging wall block moves lower than the footwall block Area under fault plane Area above fault plane Normal Faults Where is the footwall? Reverse Faults When the hanging wall block moves higher than the footwall block fault plane is between 30-90° Reverse Faults Thrust Faults When the hanging wall block moves higher than the footwall block fault plane is <30° Thrust Faults Strike-Slip Faults When the movement is horizontal and parallel to the fault Strike-Slip San Andreas Fault 1300 km fault in CA Displacement occurs along 100-200 km long segments Each fault segment behaves differently Some segments slowly slip (fault creep) Some segments regularly slip in small earthquakes Some segments stay locked for 100’s of years and produce large earthquakes San Andreas Fault 1906 San Francisco 8.3 earthquake 1989 Loma Prieta 7.1 earthquake Seismic Waves Earthquakes produce body waves and surface waves Body waves travel through Earth’s interior Surface waves travel on the Earth’s surface P Waves Body waves that push (compress) and pull (expand) rock in the direction the waves travel. P Waves S Waves Body waves that shake particles at right angles to the direction the waves travel. S Waves Surface Waves When body waves reach the surface. Move slower than body waves Move side-to-side and up-and-down Larger than body waves & therefore more destructive Surface Waves Raleigh Waves Surface Waves Love Waves Seismograms A record of ground motion produced by a seismograph Richter Scale (old school) Measurement based on the height of the largest seismic wave (P, S, or surface wave) recorded on a seismogram. A tenfold increase in wave height equals and increase of 1 on the Richter Scale For example, a M5.0 earthquake is 10 times greater than a M4.0 earthquake Richter Scale (old school) Moment Magnitude (new school) Measurement based on the amount of displacement that occurs along a fault. The seismogram The amount of movement along the fault The area of surface break The strength of the broken rock Moment Magnitude (new school) Moment Effects Near Epicenter Number Magnitude per Year < 2.0 Not felt >600,000 2.0-2.9 Potentially perceptible >300,000 3.0-3.9 Rarely felt >100,000 4.0-4.9 Can be strongly felt 13,500 5.0-5.9 Can be damaging shocks 1,400 6.0-6.9 Destructive in built-up areas 110 7.0-7.9 Serious damage 12 ≥ 8.0 Destroys communities 0-1 Modified Mercalli Scale Measurement based upon earthquake INTENSITY in terms of the effects at different locations Modified Mercalli Scale • I. Not felt except by a very few under especially favorable conditions. • II. Felt only by a few persons at rest, especially on upper floors of buildings. • III. Felt quite noticeably by persons indoors, especially on upper floors of buildings. Many people do not recognize it as an earthquake. • IV. Felt indoors by many, outdoors by few during the day. At night, some awakened. Dishes, windows, doors disturbed; walls make cracking sound. • V. Felt by nearly everyone; many awakened. Some dishes, windows broken. Unstable objects overturned. • VI. Felt by all, many frightened. Some heavy furniture moved; a few instances of fallen plaster. Damage slight. • VII. Damage negligible in buildings of good design and construction; slight to moderate in well-built ordinary structures; considerable damage in poorly built or badly designed structures; some chimneys broken. • VIII. Damage slight in specially designed structures; considerable damage in ordinary substantial buildings with partial collapse. Damage great in poorly built structures. Fall of chimneys, factory stacks, columns, monuments, walls. • IX. Damage considerable in specially designed structures. Damage great in substantial buildings, with partial collapse. Buildings shifted off foundations. • X. Some well-built wooden structures destroyed; most masonry and frame structures destroyed. Rails bent. • XI. Few, if any (masonry) structures remain standing. Bridges destroyed. Rails bent greatly. • XII. Damage total. Objects thrown into the air. Modified Mercalli Scale Earthquake Triangulation 1. Examine seismograms from 3 different stations 2. Measure the time between P & S waves for each seismogram 3. Use a travel-time graph to determine the distance of each station from the epicenter Earthquake Triangulation 4. Draw circles on a globe to show the possible epicenters (the circle radius is the distance of each station to the epicenter) 5. The point of intersection between the 3 stations is the epicenter Causes of Earthquake Damage Seismic shaking Causes of Earthquake Damage Seismic shaking Liquefaction Causes of Earthquake Damage Seismic shaking Liquefaction Landslides & Mudflows Causes of Earthquake Damage Seismic shaking Liquefaction Landslides & Mudflows Tsunamis