* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2 Earth as a System
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
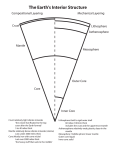
CHAPTER 2 EARTH AS A SYSTEM 2.1 EARTH: A UNIQUE PLANET Only known planet that: Has liquid water on its surface. Has an atmosphere that contains Oxygen gas Supports life Formed 4.6 billion years ago Not a perfect circle. Oblate sphere. Pg 27 Equatorial Circumference 40,074 km 2.1 COMPOSITIONAL ZONES OF EARTH’S INTERIOR Crust- the thin, solid, outermost zone of Earth. Continental Crust- 15 to 80 km thick Oceanic Crust- 5-10 km thick Mantle- layer that underlies the crust. Denser than the crust. 2,900 km thick- makes up 2/3 of Earth’s mass Core- The center of Earth Sphere shaped 3,500 km thick Composed of Iron and Nickel 2.1 STRUCTURAL ZONES OF EARTH’S INTERIOR Lithosphere- The solid, outer layer of Earth that consists of the crust and the rigid upper part of the mantle. 15-300 km thick Asthenosphere- The solid, plastic layer of the mantle beneath the lithosphere; made of mantle rock that flows very slowly, which allows tectonic plates to move on top of it. 200-250 km thick. Mesosphere- literally, the ‘middle sphere”’ the strong, lower part of the mantle between the asthenosphere and the outer core. Outer Core-Dense liquid underneath the Mesosphere 2,900 km down Inner Core- Dense, rigid solid. Center of the Earth. 5,150 km down. 2.1 EARTH AS A MAGNETIC Earth has a North and South Pole Pg 29 Figure 3 Earth’s magnetic field extends beyond the Earth’s Atmosphere and affects a region of space called the magnetosphere. Source of Magnetic Field may be the liquid iron in Earth’s outer core. Motions within the core produce electric currents that in turn create Earth’s magnetic field. Recent studies indicate that the sun and moon also have magnetic fields. Research in this field can help understand how we have our magnetic field. 2.1 EARTH’S GRAVITY Gravity is the force of attraction that exists between all matter in the universe. Newton’s Law of Gravitation states that, “the force of attraction between any two objects depends on the masses of the objects and the distance between the objects” The larger and closer the objects are, the greater the force of gravity is. 2.2 ENERGY IN THE EARTH SYSTEM System-An organized group of related object or components that interact to create a whole They can be closed or open systems 2.2 ENERGY IN THE EARTH SYSTEM Matter vs Energy Matter- Anything that has mass and takes up space. Energy-the ability to do work Made of atoms and/or molecules Transforms into heat, light, vibrations, or waves Both can be transferred (or moved) into a system or out of a system 2.1 SYSTEMS Closed System: A system in which energy, but not matter is exchanged with the surroundings Open System: A system in which both energy and matter can be exchanged with the surroundings. Pg 32 Closed Jar- Energy in the form of light and heat can be exchanged through the sides. Because the jar is closed no matter can be exchanged with a closed container. Open Jar, lake, Earth is considered a system-A closed system because matter exchange is limited. FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS Law of Conservation of Matter: States “Matter cannot be created or destroyed.” It instead, transforms or changes. Example: As a chemical breaks down from a reaction it releases energy in the form of heat. PG 33-35 OUTLINE NOTES EARTH’S FOUR SYSTEMS The Atmosphere 78% Nitrogen, 21% Oxygen, 1% other The Hydrosphere 71% of earth covered in water Only 3% is fresh water The Geosphere Largest solid part of earth The Biosphere Composed of all the forms of life/organic matter EARTH’S ENERGY BUDGET First Law of Thermodynamics Conservation of energy and matter Second Law of Thermodynamics “When energy transfer takes place, matter becomes less organized with time” Universe’s energy is spread out more and more uniformly over time INTERNAL SOURCES OF ENERGY Pg 35 “The Earth’s interior was headed by radioactive decay and gravitational contraction” What does this mean? The Idea of convection Warm things rise…..why??? Why is it important….well this process drives the plate motions in the surface layers of the geosphere that create mountain ranges and ocean basins. EXTERNAL ENERGY SOURCES The Sun Solar radiation warms Earth’s atmosphere and surface Convection of air masses causes winds and ocean currents Gravitational Energy From moon and sun cause tides/currents CYCLES OF THE EARTH SYSTEM Nitrogen Cycle Pg 36 Carbon Cycle Pg 37 Builds protein that builds cells Essential substances in the fuels used for life processes. Phosphorus Cycle Pg 37 Part of some molecules that organism need to build cells Phosphorus was discovered from extracting it from urine. Water Cycle Pg 38 2.3 ECOLOGY ECOLOGY The study of the complex relationships between living things and their nonliving, or abiotic environment. ECOSYSTEMS A community of organisms and the environment that the organisms inhabit is called an ecosystem. As large as an ocean or as small as a rotting log. Largest ecosystem is the biosphere Energy flows through these ecosystems producers, consumers, decomposers (food webs) Any examples? BALANCING FORCES IN ECOSYSTEMS Organisms in an ecosystem use matter and energy. Amounts of matter and energy are limited The largest population that an environment can support at any given time is called the carrying capacity. ENERGY TRANSFER Starts with the Sun and photosynthesis Photosynthesis captures energy that then flows through ecosystems from the plants, to the animals that feed on the plants, and finally to the decomposers of animals and plant remains. Food Webs Pg 41 What is an Energy Pyramid? Let’s talk about efficiently of a food web. CREATE YOUR OWN FOOD WEB Create your own food web using the different animals either in the movie “The Lion King” How does the song “The Cycle of Life” related to this food web?