* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Classification of Matter
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Liquid–liquid extraction wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Distillation wikipedia , lookup
Spinodal decomposition wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Water pollution wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Continuous distillation wikipedia , lookup
Colloidal crystal wikipedia , lookup
Crystallization wikipedia , lookup
Photopolymer wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Particle-size distribution wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
Vapor–liquid equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Sol–gel process wikipedia , lookup
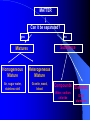
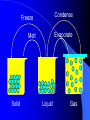
Classification of Matter Chapter 15 Composition of Matter – Sec. 1 Pure Substances – Same composition throughout – Either an element or compound Element – All one type of atom – Everything made of atoms Compound – Atoms of two or more elements chemically bonded together Composition of Matter Mixtures – Made of two or more substances that can be easily separated by physical means Heterogeneous Mixture – Different materials can be seen easily – Granite, concrete, vegetable soup Homogeneous Mixture (Solution) – Blended evenly throughout – Vinegar, Kool-aid MATTER Can it be separated? no yes Substance Mixtures Homogeneous Mixture Heterogeneous Mixture Air, sugar water, stainless stell Granite, wood, blood Compounds Elements Water, sodium chloride Gold, aluminum Mixtures Colloid ~ heterogeneous – Particles larger than solution but not heavy enough to settle out – Milk, paint, fog and smoke Detecting Colloids – Pass a beam of light through it Colloid – See beam Solution – Cannot see beam – Particles big enough to scatter light – Tyndall Effect Mixtures Suspension ~ heterogeneous – Not solution, not colloid – Muddy pond water – Heterogeneous mixture with a liquid and visible particles that settle Properties of Matter Section 2 Physical Properties Def: characteristic observed without changing the identity of the material – Ex: color, shape, size, density Appearance Behavior – Magnetic, malleable, flow of liquid Separating Mixtures Sand and Rock mixture? – Filter or sift Iron filings and Aluminum mixture? – Magnet Physical Change Change in size, shape or state of matter and identity is same – Solid to a liquid? – Yes Condense Freeze Evaporate Melt Solid Liquid Gas Physical Change How to get pure water from salt water? – Distillation – evaporate liquid and then recondense it Chemical Properties and Changes Chemical Property – can be observed only by changing the substance – Flammability, reactivity, decomposition Chemical Change – change where a NEW substance is formed Weathering – Physical or Chemical Change? – Both! Law of Conservation of Mass Matter is neither created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction Mass of all substances before = mass of all substances after change