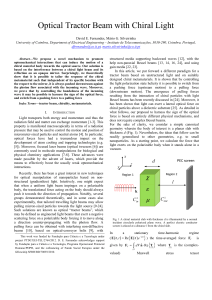
Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
... electric motors which involve the magnetic effect of electric current, and electric generators which involve the electric effect of moving magnets. Hans Christian Oersted (1777–1851) Hans Christian Oersted, one of the leading scientists of the 19th century, played a crucial role in understanding ele ...
... electric motors which involve the magnetic effect of electric current, and electric generators which involve the electric effect of moving magnets. Hans Christian Oersted (1777–1851) Hans Christian Oersted, one of the leading scientists of the 19th century, played a crucial role in understanding ele ...
III - 1 II. Newton`s Laws of Motion Concept Review Warm
... 2. A 3 kg mass is accelerated by a 6 Newton force. Both the mass and force are increased by 3 units (i.e., a 6 kg mass experiences a force of 9 Newtons). The experiment is repeated and the acceleration of the mass is calculated. a. Is the calculated acceleration in the second case different from th ...
... 2. A 3 kg mass is accelerated by a 6 Newton force. Both the mass and force are increased by 3 units (i.e., a 6 kg mass experiences a force of 9 Newtons). The experiment is repeated and the acceleration of the mass is calculated. a. Is the calculated acceleration in the second case different from th ...
Word
... 2. A 3 kg mass is accelerated by a 6 Newton force. Both the mass and force are increased by 3 units (i.e., a 6 kg mass experiences a force of 9 Newtons). The experiment is repeated and the acceleration of the mass is calculated. a. Is the calculated acceleration in the second case different from th ...
... 2. A 3 kg mass is accelerated by a 6 Newton force. Both the mass and force are increased by 3 units (i.e., a 6 kg mass experiences a force of 9 Newtons). The experiment is repeated and the acceleration of the mass is calculated. a. Is the calculated acceleration in the second case different from th ...
DYNAMICS AND RELATIVITY (PART II)
... Work-energy theorem: The work done on an object by the total net force is given by the change of the object’s kinetic energy. ...
... Work-energy theorem: The work done on an object by the total net force is given by the change of the object’s kinetic energy. ...
Chapter 21
... easy movement of charge through it. An insulator does not. • Most metals are good conductors, while most nonmetals are insulators. (See Figure 21.6 at the right.) • Semiconductors are intermediate in their properties between good conductors and good insulators. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education Inc ...
... easy movement of charge through it. An insulator does not. • Most metals are good conductors, while most nonmetals are insulators. (See Figure 21.6 at the right.) • Semiconductors are intermediate in their properties between good conductors and good insulators. Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education Inc ...
Electromagnetic Induction File
... A wire cutting across a magnetic field has an induced EMF (or voltage) Faraday’s Law When the magnetic flux through a loop changes, there is an induced EMF (voltage) The faster the change, the bigger the EMF ...
... A wire cutting across a magnetic field has an induced EMF (or voltage) Faraday’s Law When the magnetic flux through a loop changes, there is an induced EMF (voltage) The faster the change, the bigger the EMF ...
ANISOTROPIC FLUORESCENCE OF POLAR MOLECULES IN
... τf of luminescent molecules and on the relaxation time τ r of their thermal rotational motion. For τf ≤ τr , the emission anisotropy# assumes considerable values as, for example, was observed for a number of trans-stilbene derivatives [4, 5]. For τf » τr, complete fluoroscence depolarization due to ...
... τf of luminescent molecules and on the relaxation time τ r of their thermal rotational motion. For τf ≤ τr , the emission anisotropy# assumes considerable values as, for example, was observed for a number of trans-stilbene derivatives [4, 5]. For τf » τr, complete fluoroscence depolarization due to ...
LAB A7: KINETIC AND STATIC FRICTION
... Read the force of pull for five values of mass (0 to 1 kg in increments of 0.2 kg) placed in the box. Distribute the weight in the box as uniformly as possible. Make a table of the weight of the loaded box (box + added weight) and the corresponding pull force. 2) As you were carrying out the measure ...
... Read the force of pull for five values of mass (0 to 1 kg in increments of 0.2 kg) placed in the box. Distribute the weight in the box as uniformly as possible. Make a table of the weight of the loaded box (box + added weight) and the corresponding pull force. 2) As you were carrying out the measure ...
R - Physics
... The Electric Field. • This concept of “force” field was introduced to explain the counterintuitive concept of action-at-a-distance (two bodies exercise each other a force while they are not in contact). • Consider a charge Q. If we introduce an arbitrary “test” charge q at some distance r from the ...
... The Electric Field. • This concept of “force” field was introduced to explain the counterintuitive concept of action-at-a-distance (two bodies exercise each other a force while they are not in contact). • Consider a charge Q. If we introduce an arbitrary “test” charge q at some distance r from the ...
N - Mr Bernabo at Affton High School
... The earth is also a magnet. It has North and South Magnetic Poles (a little off from geographic poles) ...
... The earth is also a magnet. It has North and South Magnetic Poles (a little off from geographic poles) ...
Chapter -12 Electromagnetism
... 6) If we use end of South Pole of magnet instead of North Pole in the above activity, the deflections are partly reversed. 7) This experiment proves “Whenever there is a continents change of magnetic flux linked with closed coil, a current is generated in coil”. ...
... 6) If we use end of South Pole of magnet instead of North Pole in the above activity, the deflections are partly reversed. 7) This experiment proves “Whenever there is a continents change of magnetic flux linked with closed coil, a current is generated in coil”. ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.