A rotating coil - Collins.co.uk.
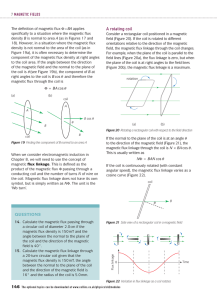
... The definition of magnetic flux Φ = BA applies specifically to a situation where the magnetic flux density B is normal to area A (as in Figures 17 and 18). However, in a situation where the magnetic flux density is not normal to the area of the coil (as in Figure 19a), it is often necessary to deter ...
... The definition of magnetic flux Φ = BA applies specifically to a situation where the magnetic flux density B is normal to area A (as in Figures 17 and 18). However, in a situation where the magnetic flux density is not normal to the area of the coil (as in Figure 19a), it is often necessary to deter ...
the integral form of ampere`s law
... a) Make sure your power supply is turned OFF. Open “Ampere’s Law.cmbl, in your Lab 8 experiment folder; there is no need to Collect data. You should see a small window in the lower-left hand corner of the window, labeled “Magnetic Field” (B). Take the magnetic field probe (long pen-like sensor conne ...
... a) Make sure your power supply is turned OFF. Open “Ampere’s Law.cmbl, in your Lab 8 experiment folder; there is no need to Collect data. You should see a small window in the lower-left hand corner of the window, labeled “Magnetic Field” (B). Take the magnetic field probe (long pen-like sensor conne ...
Electric Field: Sheet of Charge
... The electric field of a point charge Q can be obtained by a straightforward application of Gauss' law. Considering a Gaussian surface in the form of a sphere at radius r, the electric field has the same magnitude at every point of the sphere and is directed outward. The electric flux is then just th ...
... The electric field of a point charge Q can be obtained by a straightforward application of Gauss' law. Considering a Gaussian surface in the form of a sphere at radius r, the electric field has the same magnitude at every point of the sphere and is directed outward. The electric flux is then just th ...
CH27-revision-lecture - University of Southampton
... • The direction of the induced emf and current is described by the minus sign in Faraday’s law. • But it’s easier to get the direction from conservation of energy. • The direction of the induced current must be such as to oppose that change that gives rise to it. • This is known as Lenz’s law. • Oth ...
... • The direction of the induced emf and current is described by the minus sign in Faraday’s law. • But it’s easier to get the direction from conservation of energy. • The direction of the induced current must be such as to oppose that change that gives rise to it. • This is known as Lenz’s law. • Oth ...
Tuesday, June 20, 2006 - UTA HEP WWW Home Page
... can be obtained in terms of initial From momentum m1 v1i v1 f m2 v2i v2 f speeds as conservation above m m2 2m2 v1i v2i v1 f 1 m1 m2 m1 m2 Tuesday, June 20, 2006 ...
... can be obtained in terms of initial From momentum m1 v1i v1 f m2 v2i v2 f speeds as conservation above m m2 2m2 v1i v2i v1 f 1 m1 m2 m1 m2 Tuesday, June 20, 2006 ...
Influence of Impurity Spin Dynamics on Quantum Transport in Epitaxial Graphene
... process (b) always leads to the decoherence of electrons, process (a) leads only to additional scattering phases for a fixed spin configuration of impurities (relative to the electron spin). These phases would in general be the same for the two reversed sequences of visited scatterers; hence, they w ...
... process (b) always leads to the decoherence of electrons, process (a) leads only to additional scattering phases for a fixed spin configuration of impurities (relative to the electron spin). These phases would in general be the same for the two reversed sequences of visited scatterers; hence, they w ...
Gel Electrophoresis
... independently of other macroion properties ● Since it is very difficult to determine the effective charge Qeff of a macromolecule in solution we will only be concerned with the idealized case of only 2 forces acting on the ...
... independently of other macroion properties ● Since it is very difficult to determine the effective charge Qeff of a macromolecule in solution we will only be concerned with the idealized case of only 2 forces acting on the ...
Build an Electromagnet Problem: How can I make a stronger magnet
... F: Attitudes in Science Research: You have experimented with magnets in class, but scientist sometime need to use very powerful magnets. But a powerful magnet has a problem, how can the magnet be turned off and on? In 1820, a Danish physicist Hans Christian Oersted, discovered that there was a relat ...
... F: Attitudes in Science Research: You have experimented with magnets in class, but scientist sometime need to use very powerful magnets. But a powerful magnet has a problem, how can the magnet be turned off and on? In 1820, a Danish physicist Hans Christian Oersted, discovered that there was a relat ...
PHY140Y 7 Electrostatics and Coulomb`s Law
... charges, both static and flowing. Static charge distributions create electrostatic forces, whereas flowing charges (or “currents”) are responsible for both electric and magnetic forces. We will limit our focus to the basics of electrostatics, leaving the richer and more complex phenomena of electromag ...
... charges, both static and flowing. Static charge distributions create electrostatic forces, whereas flowing charges (or “currents”) are responsible for both electric and magnetic forces. We will limit our focus to the basics of electrostatics, leaving the richer and more complex phenomena of electromag ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.