MODELING OF NEMATIC ELECTROLYTES AND NONLINEAR ELECTROOSMOSIS
... externally applied electric field imposes a torque on the electric double layer and drives electrokinetic flows. The driving force, proportional to the product of charge and field, is balanced by the viscous drag; the resulting velocities grow linearly with the electric field. As a result, only a di ...
... externally applied electric field imposes a torque on the electric double layer and drives electrokinetic flows. The driving force, proportional to the product of charge and field, is balanced by the viscous drag; the resulting velocities grow linearly with the electric field. As a result, only a di ...
Chapter 18 clicker questions
... a) The area of the coil is changed. b) The orientation of the magnetic field relative to the coil is changed. c) The strength of the magnetic field in the vicinity of the coil is changed. d) All of the above. ...
... a) The area of the coil is changed. b) The orientation of the magnetic field relative to the coil is changed. c) The strength of the magnetic field in the vicinity of the coil is changed. d) All of the above. ...
Physics218_lecture_008
... – Friction, gravity – whatever force keeps it moving in a circle. – This force is often called the “centripetal force” ...
... – Friction, gravity – whatever force keeps it moving in a circle. – This force is often called the “centripetal force” ...
Mapping of steady-state electric fields and convective drifts in
... at the ionospheres and becomes much smaller in the equatorial plane. Visualizations such as this do not greatly improve our understanding when the field is approximately dipolar: it will be much more useful when the external fields have been incorporated in the model. The components and total electr ...
... at the ionospheres and becomes much smaller in the equatorial plane. Visualizations such as this do not greatly improve our understanding when the field is approximately dipolar: it will be much more useful when the external fields have been incorporated in the model. The components and total electr ...
25.7 The Photon Model of Electromagnetic Waves
... photo. Instead, it is a collection of dots. A few points on the detector have registered the presence of light, but most have not. As the illumination increases, the density of these dots increases until the dots form a full picture. This is not what we might expect. If light is a wave, reducing its ...
... photo. Instead, it is a collection of dots. A few points on the detector have registered the presence of light, but most have not. As the illumination increases, the density of these dots increases until the dots form a full picture. This is not what we might expect. If light is a wave, reducing its ...
textbook and other materials
... Course Withdrawal: The deadline to withdraw from a course shall not exceed 3/4 the duration of any class. Contact the Counseling Office at any TCC campus to initiate withdrawal from a course ('W' grade) or to change from Credit to Audit. Check the TCC Academic Calendar for deadlines. Students who s ...
... Course Withdrawal: The deadline to withdraw from a course shall not exceed 3/4 the duration of any class. Contact the Counseling Office at any TCC campus to initiate withdrawal from a course ('W' grade) or to change from Credit to Audit. Check the TCC Academic Calendar for deadlines. Students who s ...
photon - McMaster University > ECE
... A Scottish mathematical physicist who is widely regarded as the nineteenth century scientist who had the greatest influence on twentieth century physics. Maxwell demonstrated that electrical and magnetic forces are two complementary aspects of electromagnetism. He showed that electromagnetic fields ...
... A Scottish mathematical physicist who is widely regarded as the nineteenth century scientist who had the greatest influence on twentieth century physics. Maxwell demonstrated that electrical and magnetic forces are two complementary aspects of electromagnetism. He showed that electromagnetic fields ...
08-Electric Forces and Electric Fields
... ⊸ e is the smallest charge discovered ⊸Electricity is quantized comes in discreet numbers ⊶In nature atoms have no net charge ⊷# protons = # electrons ...
... ⊸ e is the smallest charge discovered ⊸Electricity is quantized comes in discreet numbers ⊶In nature atoms have no net charge ⊷# protons = # electrons ...
An Introduction to the New SI - IFSC-USP
... way that defining the value of c defines the meter. a. Frequency and time The frequency standard for the SI is established by assigning a value to the frequency of a particular atomic transition associated with the energy difference between two discrete atomic energy levels. That frequency is given ...
... way that defining the value of c defines the meter. a. Frequency and time The frequency standard for the SI is established by assigning a value to the frequency of a particular atomic transition associated with the energy difference between two discrete atomic energy levels. That frequency is given ...
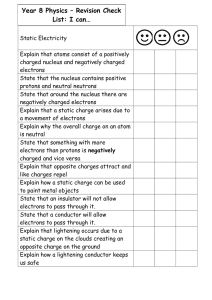
Year 8 Physics Revision Checklist1.02 MB
... Draw magnetic field lines round a magnet going from north to south: N S Explain that the magnetic field is strongest where the field lines are closest together Explain how the Earth’s magnetic field is similar to that of a large bar magnet Draw the Earth’s magnetic field, showing where it is stron ...
... Draw magnetic field lines round a magnet going from north to south: N S Explain that the magnetic field is strongest where the field lines are closest together Explain how the Earth’s magnetic field is similar to that of a large bar magnet Draw the Earth’s magnetic field, showing where it is stron ...
Chapter 23 Resource: Magnetism
... 5. The magnetic field is strongest near (the poles/the center) of a bar magnet. 6. Materials that can become magnetized include steel and (copper/iron). 7. The needle of a compass lines up with Earth’s magnetic field and points to (Earth’s poles/Earth’s equator). 8. Magnetic field lines that curve t ...
... 5. The magnetic field is strongest near (the poles/the center) of a bar magnet. 6. Materials that can become magnetized include steel and (copper/iron). 7. The needle of a compass lines up with Earth’s magnetic field and points to (Earth’s poles/Earth’s equator). 8. Magnetic field lines that curve t ...
Unit 5 - Mr. Abbott's Mathematics and Physics Page
... field, which in turn creates a changing electric field ...
... field, which in turn creates a changing electric field ...
Feb. 8 , `1927.
... adjacent the negative electrode. In the pre rectifier. ferred embodiment of the invention the tube . Referring to the illustrated embodiment is provided with concentric cylindrical elec of the invention it will be observed that the trodes and a space varying magnetic field bulb or tube 10 contains s ...
... adjacent the negative electrode. In the pre rectifier. ferred embodiment of the invention the tube . Referring to the illustrated embodiment is provided with concentric cylindrical elec of the invention it will be observed that the trodes and a space varying magnetic field bulb or tube 10 contains s ...
question bank
... 55. A straight conductor of circular x-section carries a current. Which one of the following statements is true in this regard? (a) No force acts on the conductor at any point. (b) An axial force acts on the conductor tending to increase its length. (c) A radial force acts towards the axis tending t ...
... 55. A straight conductor of circular x-section carries a current. Which one of the following statements is true in this regard? (a) No force acts on the conductor at any point. (b) An axial force acts on the conductor tending to increase its length. (c) A radial force acts towards the axis tending t ...
Charge of Object A
... Charge cannot be created nor destroyed. Objects become charged by transfer of charges. Electrons are rubbed off the hairs of a piece of fur, collecting and charging a plastic rod. Is the fur also charged? ...
... Charge cannot be created nor destroyed. Objects become charged by transfer of charges. Electrons are rubbed off the hairs of a piece of fur, collecting and charging a plastic rod. Is the fur also charged? ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.