LM1815
... allow a peak current of 3 mA in normal operation. Positive inputs are clamped by a 1 kΩ resistor and series diode, while an active clamp limits pin 3 to -350 mV for negative inputs (see R4, Q12, Q11 in internal schematic diagram). Operation of Zero Crossing Detector The LM1815 is designed to operate ...
... allow a peak current of 3 mA in normal operation. Positive inputs are clamped by a 1 kΩ resistor and series diode, while an active clamp limits pin 3 to -350 mV for negative inputs (see R4, Q12, Q11 in internal schematic diagram). Operation of Zero Crossing Detector The LM1815 is designed to operate ...
IDT23S09E - Integrated Device Technology
... All outputs should be uniformly loaded in order to achieve Zero I/O Delay. Since the CLKOUT pin is the internal feedback for the PLL, its relative loading can affect and adjust the input/output delay. For designs utilizing zero I/O Delay, all outputs including CLKOUT must be equally loaded. Even if ...
... All outputs should be uniformly loaded in order to achieve Zero I/O Delay. Since the CLKOUT pin is the internal feedback for the PLL, its relative loading can affect and adjust the input/output delay. For designs utilizing zero I/O Delay, all outputs including CLKOUT must be equally loaded. Even if ...
Basic Digital Logic 2 Review
... Textbooks on Digital Electronics (used is ok!) Electronics Workbench or other electronic simulation ...
... Textbooks on Digital Electronics (used is ok!) Electronics Workbench or other electronic simulation ...
An Ultra-Low-Voltage Ultra-Low-Power OTA With Improved Gain
... does not depend on the gate-source voltage, Consider that which is valid only for weak inversion and not for strong inversion [13]. In order that and are equal, and should be equal and constant. Therefore, the differential offset voltage of input transistors will reduce [13]. In order to avoid any s ...
... does not depend on the gate-source voltage, Consider that which is valid only for weak inversion and not for strong inversion [13]. In order that and are equal, and should be equal and constant. Therefore, the differential offset voltage of input transistors will reduce [13]. In order to avoid any s ...
Lab 2
... Prep question 3: Sketch a transistor diagram for a 2-input NOR gate. At this point, you may have noticed that all of the gates we are making are inverting. This is because the NFETs take a 1 input to generate a 0 output and the PFETs take a 0 input to make a 1 output. Any static CMOS gate you make a ...
... Prep question 3: Sketch a transistor diagram for a 2-input NOR gate. At this point, you may have noticed that all of the gates we are making are inverting. This is because the NFETs take a 1 input to generate a 0 output and the PFETs take a 0 input to make a 1 output. Any static CMOS gate you make a ...
AD835 250 MHz, Voltage Output 4-Quadrant Multiplier Data Sheet
... important in applying wideband circuits. The decoupling recommendations shown in Figure 2 should be followed closely. In remaining figures in this data sheet, these power supply decoupling components have been omitted for clarity but should be used wherever optimal performance with high speed inputs ...
... important in applying wideband circuits. The decoupling recommendations shown in Figure 2 should be followed closely. In remaining figures in this data sheet, these power supply decoupling components have been omitted for clarity but should be used wherever optimal performance with high speed inputs ...
Input/output devices in microcontrollers
... A peripheral is generally defined as any auxiliary device such as a computer mouse, keyboard, hard drive, etc. that connects to and works with the computer in some way. Other examples of peripherals are expansion cards, graphics cards, computer printers, image scanners, tape drives, microphones, lou ...
... A peripheral is generally defined as any auxiliary device such as a computer mouse, keyboard, hard drive, etc. that connects to and works with the computer in some way. Other examples of peripherals are expansion cards, graphics cards, computer printers, image scanners, tape drives, microphones, lou ...
Low Cost Pure Sine Wave Solar Inverter Circuit
... stage. Also referred to as a Johnson counter, this is a powerful IC which is able to count clock pulses and introduce a delay between them. The clock signal will feed into CPO of the counter, and the clock inhibit pin will simply be grounded since the 4017 circuit will remain active at all times. S ...
... stage. Also referred to as a Johnson counter, this is a powerful IC which is able to count clock pulses and introduce a delay between them. The clock signal will feed into CPO of the counter, and the clock inhibit pin will simply be grounded since the 4017 circuit will remain active at all times. S ...
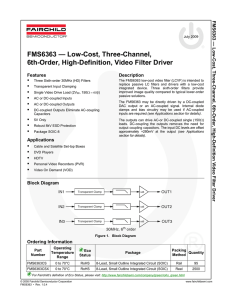
FMS6363 — Low-Cost, Three-Channel, 6th-Order, High-Definition, Video Filter Driver FM S6363 — Low-
... output driver and is held at the minimum value in order to decrease the standing DC current into the load. Since the FMS6363 has a 2x (6dB) gain, the output is typically connected via a 75Ω series back-matching resistor followed by the 75Ω video cable. Because of the inherent divide by two of this c ...
... output driver and is held at the minimum value in order to decrease the standing DC current into the load. Since the FMS6363 has a 2x (6dB) gain, the output is typically connected via a 75Ω series back-matching resistor followed by the 75Ω video cable. Because of the inherent divide by two of this c ...
AD9066 数据手册DataSheet下载
... The analog input range of the AD9066 is between 3.7 V and 4.2 V. Because the input is offset, the normal method of driving the analog input is to use a blocking capacitor between the analog source and the AD9066 analog input pins. In applications where DC coupling must be employed, the simple circui ...
... The analog input range of the AD9066 is between 3.7 V and 4.2 V. Because the input is offset, the normal method of driving the analog input is to use a blocking capacitor between the analog source and the AD9066 analog input pins. In applications where DC coupling must be employed, the simple circui ...
Alpha 1500 Series
... 150 - 264VAC, 47 - 63Hz (1500W). See power limitations for lower input ranges. 16A maximum Less than 50A 1.1mA @ 264VAC, 63Hz (low leakage current options available) 75% typical (configuration and input dependent) Compliant to EN61000-3-2 ( > 0.99 typical, reduced PFC > 255VAC) EN55022 level A 800W@ ...
... 150 - 264VAC, 47 - 63Hz (1500W). See power limitations for lower input ranges. 16A maximum Less than 50A 1.1mA @ 264VAC, 63Hz (low leakage current options available) 75% typical (configuration and input dependent) Compliant to EN61000-3-2 ( > 0.99 typical, reduced PFC > 255VAC) EN55022 level A 800W@ ...
UNR Series
... voltages with minimal ripple and noise. The distribution losses, unpredictable regulation and poor transient response of traditional centralized power systems are no longer acceptable. Power processing at the "point-of-use" is frequently the only way to achieve desired performance. DATEL’s new UNR S ...
... voltages with minimal ripple and noise. The distribution losses, unpredictable regulation and poor transient response of traditional centralized power systems are no longer acceptable. Power processing at the "point-of-use" is frequently the only way to achieve desired performance. DATEL’s new UNR S ...
LT1713/LT1714 - Single/Dual, 7ns, Low Power, 3V/5V/±5V Rail-to-Rail Comparators
... interval in which the input signal must remain stable prior to asserting the latch signal. Latch hold time (tH) is the interval after the latch is asserted in which the input signal must remain stable. Latch disable pulse width (tDPW) is the width of the negative pulse on the latch enable pin that l ...
... interval in which the input signal must remain stable prior to asserting the latch signal. Latch hold time (tH) is the interval after the latch is asserted in which the input signal must remain stable. Latch disable pulse width (tDPW) is the width of the negative pulse on the latch enable pin that l ...
DOC
... convert sensor information into pulses which can be easily counted by a computer. Background: the classic timer chip: the 555 The most popular timer or waveform-generator IC is the 555 (and its successors). It is also an easily misunderstood chip. The equivalent circuit of the 555 is shown in . Some ...
... convert sensor information into pulses which can be easily counted by a computer. Background: the classic timer chip: the 555 The most popular timer or waveform-generator IC is the 555 (and its successors). It is also an easily misunderstood chip. The equivalent circuit of the 555 is shown in . Some ...
Data Sheet
... logic interfacing. The HOLD and HOLD inputs may be used with both low and high level CMOS, TTL and ECL logic systems. Logic threshold programmability was achieved by using a differential amplifier as the input stage for the digital inputs. A predictable logic threshold may be programmed by referenci ...
... logic interfacing. The HOLD and HOLD inputs may be used with both low and high level CMOS, TTL and ECL logic systems. Logic threshold programmability was achieved by using a differential amplifier as the input stage for the digital inputs. A predictable logic threshold may be programmed by referenci ...
1E6 Electricity and Magnetism
... fabrication process give rise to large fluctuations in the amplifying properties of the devices used to construct the amplifier. This gives rise to varition in the amplifer gain, which can only be overcome by more advanced design techniques such as the use of feedback. ...
... fabrication process give rise to large fluctuations in the amplifying properties of the devices used to construct the amplifier. This gives rise to varition in the amplifer gain, which can only be overcome by more advanced design techniques such as the use of feedback. ...
The Typical Op-Amp
... need for coupling capacitors that are too large to be placed on an IC chip (please review D7 for a discussion on direct coupling). The level shifter stage may be one or more level shifters that are included to ensure that there is no dc offset in the output signal. In addition, these intermediate st ...
... need for coupling capacitors that are too large to be placed on an IC chip (please review D7 for a discussion on direct coupling). The level shifter stage may be one or more level shifters that are included to ensure that there is no dc offset in the output signal. In addition, these intermediate st ...
Action PAK AP7380 ® Frequency Input, Field Configurable
... output returns to the previous level. A couple more CCW turns will provide optimal noise rejection. 4. Run the input through the full frequency range to make sure that the pulses are sensed at both the low and high input frequencies. If the output drops out during this test, when the input freq. >0% ...
... output returns to the previous level. A couple more CCW turns will provide optimal noise rejection. 4. Run the input through the full frequency range to make sure that the pulses are sensed at both the low and high input frequencies. If the output drops out during this test, when the input freq. >0% ...
Pre-lab Exercise
... physical stops at the extreme positions (“single-turn” is misleading because the physical stops are usually such that the angle the potentiometer can turn is much less than 360°). However, the potentiometer mounted on the motor setup is a special potentiometer called a servo potentiometer. A servo p ...
... physical stops at the extreme positions (“single-turn” is misleading because the physical stops are usually such that the angle the potentiometer can turn is much less than 360°). However, the potentiometer mounted on the motor setup is a special potentiometer called a servo potentiometer. A servo p ...
Arduino and the Radio Amateur
... if(padState == 0){ //pin low if paddle pressed. If low, do this: digitalWrite(KeyOut,HIGH); //set Key down state delay(ditTime* 3); //stay that way for 3 dit times digitalWrite(KeyOut,LOW); // now have to be key up for 1 dit time delay(ditTime); ...
... if(padState == 0){ //pin low if paddle pressed. If low, do this: digitalWrite(KeyOut,HIGH); //set Key down state delay(ditTime* 3); //stay that way for 3 dit times digitalWrite(KeyOut,LOW); // now have to be key up for 1 dit time delay(ditTime); ...
CM8870/70C CMOS Integrated DTMF Receiver
... D elayed steering output. Presents a logic high when a received tone pair has been registered and the output latch is updated. Returns to logic low when the voltage on St/GT falls below VTSt. Early steering output. Presents a logic high immediately when the digital algorithm detects a recognizable t ...
... D elayed steering output. Presents a logic high when a received tone pair has been registered and the output latch is updated. Returns to logic low when the voltage on St/GT falls below VTSt. Early steering output. Presents a logic high immediately when the digital algorithm detects a recognizable t ...
advanced schottky (als and as) logic families
... version of relevant information to verify, before placing orders, that the information being relied on is current. TI warrants performance of its semiconductor products and related software to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in accordance with TI’s standard warranty. Testing and ot ...
... version of relevant information to verify, before placing orders, that the information being relied on is current. TI warrants performance of its semiconductor products and related software to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in accordance with TI’s standard warranty. Testing and ot ...
CA3162, CA3162A
... Inverters G1 and G2 are used as an astable multivibrator to provide the AC drive to the LCD backplane. Inverters G3, G4 and G5 are the digit-select inverters and require pull-up resistors to interface the open-collector outputs of the CA3162E to CMOS logic. The BCD outputs of the CA3162E may be conn ...
... Inverters G1 and G2 are used as an astable multivibrator to provide the AC drive to the LCD backplane. Inverters G3, G4 and G5 are the digit-select inverters and require pull-up resistors to interface the open-collector outputs of the CA3162E to CMOS logic. The BCD outputs of the CA3162E may be conn ...
Flip-flop (electronics)
In electronics, a flip-flop or latch is a circuit that has two stable states and can be used to store state information. A flip-flop is a bistable multivibrator. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will have one or two outputs. It is the basic storage element in sequential logic. Flip-flops and latches are a fundamental building block of digital electronics systems used in computers, communications, and many other types of systems.Flip-flops and latches are used as data storage elements. A flip-flop stores a single bit (binary digit) of data; one of its two states represents a ""one"" and the other represents a ""zero"". Such data storage can be used for storage of state, and such a circuit is described as sequential logic. When used in a finite-state machine, the output and next state depend not only on its current input, but also on its current state (and hence, previous inputs). It can also be used for counting of pulses, and for synchronizing variably-timed input signals to some reference timing signal.Flip-flops can be either simple (transparent or opaque) or clocked (synchronous or edge-triggered). Although the term flip-flop has historically referred generically to both simple and clocked circuits, in modern usage it is common to reserve the term flip-flop exclusively for discussing clocked circuits; the simple ones are commonly called latches.Using this terminology, a latch is level-sensitive, whereas a flip-flop is edge-sensitive. That is, when a latch is enabled it becomes transparent, while a flip flop's output only changes on a single type (positive going or negative going) of clock edge.