Chapter 2: Learning Theories
... Repression: The ejection of anxiety-evoking ideas from awareness Regression: The return, under stress, to a form of behavior characteristic of an earlier stage of development Rationalization: The use of self-deceiving justifications for unacceptable behavior Displacement: The transfer of ideas and i ...
... Repression: The ejection of anxiety-evoking ideas from awareness Regression: The return, under stress, to a form of behavior characteristic of an earlier stage of development Rationalization: The use of self-deceiving justifications for unacceptable behavior Displacement: The transfer of ideas and i ...
Factors of Persuasion
... when you sneeze) or maladaptive (such as engaging in risky behavior because “everyone is doing it.”) • Many like to think of themselves as nonconformists, but a classic study by Solomon Asch demonstrated that we are more likely to conform than we think. ...
... when you sneeze) or maladaptive (such as engaging in risky behavior because “everyone is doing it.”) • Many like to think of themselves as nonconformists, but a classic study by Solomon Asch demonstrated that we are more likely to conform than we think. ...
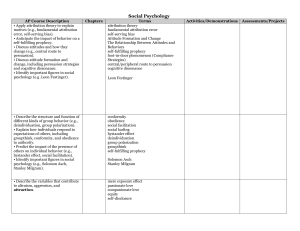
Social Psychology
... the scientific study of how we think about, influence, and relate to one another ...
... the scientific study of how we think about, influence, and relate to one another ...
Self-Concept - Homework Market
... “You can walk by and see someone's [MBTI type] posted up in their cube,” says Elizabeth Bryant, Southwest’s leadership ...
... “You can walk by and see someone's [MBTI type] posted up in their cube,” says Elizabeth Bryant, Southwest’s leadership ...
Individual Behavior, Personality, and Values
... “You can walk by and see someone's [MBTI type] posted up in their cube,” says Elizabeth Bryant, Southwest’s leadership ...
... “You can walk by and see someone's [MBTI type] posted up in their cube,” says Elizabeth Bryant, Southwest’s leadership ...
Chapter 11: Behaviorism (18921956) Glossary New Directions in
... Intervening Variable a hypothetical internal state that is used to explain relationships between observed variables, such as independent and dependent variables, in empirical research. Logical Positivism theory of knowledge. Only statements verifiable either logically or empirically would be c ...
... Intervening Variable a hypothetical internal state that is used to explain relationships between observed variables, such as independent and dependent variables, in empirical research. Logical Positivism theory of knowledge. Only statements verifiable either logically or empirically would be c ...
Social Psychology Chapter 16
... us to respond in a particular way to objects, people, and events (selffulfilling prophecy) Ex: A friend tells you that they believe Coach Stove is a mean teacher. You may feel dislike for Coach Stove, and act unfriendly. ...
... us to respond in a particular way to objects, people, and events (selffulfilling prophecy) Ex: A friend tells you that they believe Coach Stove is a mean teacher. You may feel dislike for Coach Stove, and act unfriendly. ...
Glossary of terms
... Passive: not showing respect for self. Passive communication styles are often used when someone is fearful of expressing their own needs and opinions. This communication style can lead to feelings of powerlessness and helplessness. ...
... Passive: not showing respect for self. Passive communication styles are often used when someone is fearful of expressing their own needs and opinions. This communication style can lead to feelings of powerlessness and helplessness. ...
Chapter 5: Managerial Ethics & Corporate Social Responsibility
... Learning to obtain positive outcomes and avoid negative ones by making the correct response in the presence of a stimulus (or cue or signal) Behavior is “Shaped” through ...
... Learning to obtain positive outcomes and avoid negative ones by making the correct response in the presence of a stimulus (or cue or signal) Behavior is “Shaped” through ...
Social and Cognitive-Behavioral Psychology
... Humans actively seek, select, and use information in order to construct a view of reality, meet their basic needs. ...
... Humans actively seek, select, and use information in order to construct a view of reality, meet their basic needs. ...
lecture 5 - cda college
... process by which people attempt to manage or control the perceptions others form of them. There is often a tendency that people present themselves so as to impress others in a desirable way. ...
... process by which people attempt to manage or control the perceptions others form of them. There is often a tendency that people present themselves so as to impress others in a desirable way. ...
Social Influences on Behavior
... • Control condition – less than 1% of participants ever made a mistake • Experimental condition – about 70% made at least one error by conforming to the group norm • Conformed on over 1/3 of all responses ...
... • Control condition – less than 1% of participants ever made a mistake • Experimental condition – about 70% made at least one error by conforming to the group norm • Conformed on over 1/3 of all responses ...
Social Learning Theory
... Freud’s Psychoanalytic Theory – The key is the process of identification. Social Learning Theory – Imitation, reinforcement. Cognitive Development Theory – Gender is an organizing scheme for the developing child. ...
... Freud’s Psychoanalytic Theory – The key is the process of identification. Social Learning Theory – Imitation, reinforcement. Cognitive Development Theory – Gender is an organizing scheme for the developing child. ...
psychology - nhsroom219
... (B) milieu therapy (C) primary prevention (D) secondary prevention (E) noncrisis intervention 51. Lawrence Kohlberg's theory of moral reasoning is best described by which of the following? (A) Personal conscience is innate and all human beings develop it at the same rate. (B) By adulthood, all peopl ...
... (B) milieu therapy (C) primary prevention (D) secondary prevention (E) noncrisis intervention 51. Lawrence Kohlberg's theory of moral reasoning is best described by which of the following? (A) Personal conscience is innate and all human beings develop it at the same rate. (B) By adulthood, all peopl ...
Marketing Management
... a) a phallic personality b) an Oedipus Complex c) an innovator d) someone who is neurotic 6. Why do marketing researchers most often use a trait theory? It is easy to measure. Attitudes 1. What is an attitude? 2. An attitude is the link between ___ and ___. a) knowledge, action b) perception, memory ...
... a) a phallic personality b) an Oedipus Complex c) an innovator d) someone who is neurotic 6. Why do marketing researchers most often use a trait theory? It is easy to measure. Attitudes 1. What is an attitude? 2. An attitude is the link between ___ and ___. a) knowledge, action b) perception, memory ...
Chapter 09 PowerPoint Presentation
... • Need for Power – Extent to which an individual desires to control or influence others ...
... • Need for Power – Extent to which an individual desires to control or influence others ...
History and Approaches
... bystander effect, social facilitation). • Identify important figures in social psychology (e.g., Solomon Asch, ...
... bystander effect, social facilitation). • Identify important figures in social psychology (e.g., Solomon Asch, ...
Social Psychology Flash Cards
... • Tendency to give too much weight to personality factors and not enough weight to situational factors when observing someone’s behavior. ...
... • Tendency to give too much weight to personality factors and not enough weight to situational factors when observing someone’s behavior. ...
Social Psychology
... Matching Hypothesis – The prediction that most people will find friends and mates that are perceived to be of about their same level of attractiveness. Expectancy-value Theory – A theory of social psychology that people decide whether to pursue a ...
... Matching Hypothesis – The prediction that most people will find friends and mates that are perceived to be of about their same level of attractiveness. Expectancy-value Theory – A theory of social psychology that people decide whether to pursue a ...
Values, Attitudes, Emotions, and Culture
... how managers think, feel, and behave • Explain what values and attitudes are and describe their impact on managerial action • Appreciate how moods and emotions influence all members of an organization • Describe the nature of emotional intelligence and its role in management • Define organizational ...
... how managers think, feel, and behave • Explain what values and attitudes are and describe their impact on managerial action • Appreciate how moods and emotions influence all members of an organization • Describe the nature of emotional intelligence and its role in management • Define organizational ...
Behavior modification
... Accomplishment of overall goal Target behavior defined in smaller operant units linked together in chain of activities Can focus on weakest links first divide it into smaller behavioral units Basic skills integrated whole avoid coaches’ trap salsa dancing ~ ...
... Accomplishment of overall goal Target behavior defined in smaller operant units linked together in chain of activities Can focus on weakest links first divide it into smaller behavioral units Basic skills integrated whole avoid coaches’ trap salsa dancing ~ ...
Potential Short Answer Questions
... According to Mischel and Shoda’s CAPS model, a person’s behavior in different settings/situations will be consistent if the _______________ are similar. Define and give an example of a schema. Explain Ellis’ A-B-C model of emotion. According to Ellis, why is it that people can often respond differen ...
... According to Mischel and Shoda’s CAPS model, a person’s behavior in different settings/situations will be consistent if the _______________ are similar. Define and give an example of a schema. Explain Ellis’ A-B-C model of emotion. According to Ellis, why is it that people can often respond differen ...