Bohr`s Complementarity and Kant`s Epistemology
... quantum symbolism from the measuring instrument, which is described in classical terms. Characteristically, in Bohr’s writings, this issue is often related to what he calls the ‘subject-object separation’ [Bohr1963, p.12]. Our analysis of the term ‘transcendental’ has thus far focused on the subject ...
... quantum symbolism from the measuring instrument, which is described in classical terms. Characteristically, in Bohr’s writings, this issue is often related to what he calls the ‘subject-object separation’ [Bohr1963, p.12]. Our analysis of the term ‘transcendental’ has thus far focused on the subject ...
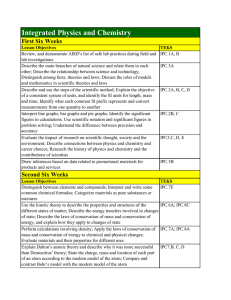
Integrated Physics and Chemistry
... different states of matter; Describe the energy transfers involved in changes of state; Describe the laws of conservation of mass and conservation of energy, and explain how they apply to changes of state Perform calculations involving density; Apply the laws of conservation of mass and conservation ...
... different states of matter; Describe the energy transfers involved in changes of state; Describe the laws of conservation of mass and conservation of energy, and explain how they apply to changes of state Perform calculations involving density; Apply the laws of conservation of mass and conservation ...
The Structure of the Proton more than eighty years. It also has been
... These are usually referred to as constituent quark masses. The most striking features of these quarks is that they carry fractional electric charges, 2/3 or -l/3 while all the particles that have been observed so far all carry integral charges. This implies from the charge conservation that one of t ...
... These are usually referred to as constituent quark masses. The most striking features of these quarks is that they carry fractional electric charges, 2/3 or -l/3 while all the particles that have been observed so far all carry integral charges. This implies from the charge conservation that one of t ...
11 Canonical quantization of classical fields
... fields, the basic entities in this case are anticommuting generators of abstract Grassmann (or Bieriezin) algebra which have no classical counterpart and can hardly be considered physical. The difference between bosonic and fermionic fields2 becomes particularly clear in the path integral approach t ...
... fields, the basic entities in this case are anticommuting generators of abstract Grassmann (or Bieriezin) algebra which have no classical counterpart and can hardly be considered physical. The difference between bosonic and fermionic fields2 becomes particularly clear in the path integral approach t ...
Level shifts of rubidium Rydberg states due to binary interactions
... limitation of the sum in Eq. 共3兲 does not change the calculated van der Waals shifts by more than about 1%. By restricting the sum in the described way, we find that typically of the order of hundreds of two-particle states 兩n⬘ , ᐉ⬘ , j⬘ , m⬘j 典 丢 兩n⬙ , ᐉ⬙ , j⬙ , m⬙j 典 still contribute, although the ...
... limitation of the sum in Eq. 共3兲 does not change the calculated van der Waals shifts by more than about 1%. By restricting the sum in the described way, we find that typically of the order of hundreds of two-particle states 兩n⬘ , ᐉ⬘ , j⬘ , m⬘j 典 丢 兩n⬙ , ᐉ⬙ , j⬙ , m⬙j 典 still contribute, although the ...
Flow of zero-point energy and exploration of phase space in
... tum tunneling which are not accessible to the classical system. On the other hand, the classical phase-space distribution may enter regions of phase space that correspond to a violation of the uncertainty principle. A famous example of the latter phenomena is the ZPE problem mentioned above. Stating ...
... tum tunneling which are not accessible to the classical system. On the other hand, the classical phase-space distribution may enter regions of phase space that correspond to a violation of the uncertainty principle. A famous example of the latter phenomena is the ZPE problem mentioned above. Stating ...
Document
... Consequently, von Neumann entropy is conserved, hence USELESS. However: vN entropy is constant if applied to closed systems, where all dof’s and their correlations are known. In practice: never the case! ...
... Consequently, von Neumann entropy is conserved, hence USELESS. However: vN entropy is constant if applied to closed systems, where all dof’s and their correlations are known. In practice: never the case! ...
Thermal noise and correlations in photon detection
... number n0 is detected by use of a noiseless singlemode detector with quantum efficiency and optical bandwidth ⌬. Here, the first term in the square root gives the usual 公N Poisson fluctuations, whereas the second term, important only when n0 is of the order of unity or larger, accounts for the p ...
... number n0 is detected by use of a noiseless singlemode detector with quantum efficiency and optical bandwidth ⌬. Here, the first term in the square root gives the usual 公N Poisson fluctuations, whereas the second term, important only when n0 is of the order of unity or larger, accounts for the p ...
Dynamical Realization of Coherent Structures in Condensed Matter
... water molecule (developed by G.Preparata and E.Del Giudice). Complete revision of theory and numerical calculations is presently under way (myself and E.Del ...
... water molecule (developed by G.Preparata and E.Del Giudice). Complete revision of theory and numerical calculations is presently under way (myself and E.Del ...
Strong quantum confinement effects in SnS nanocrystals produced
... to small particles and acceleration of reactions, which may be used for the preparation of new materials with desirable properties. During sonication, ultrasonic longitudinal waves are radiated through the solution causing alternating high and low pressure regions in the liquid medium. Millions of m ...
... to small particles and acceleration of reactions, which may be used for the preparation of new materials with desirable properties. During sonication, ultrasonic longitudinal waves are radiated through the solution causing alternating high and low pressure regions in the liquid medium. Millions of m ...
nature
... excitation spectrum. We can induce reversible changes between the two ground states of the system. A physical system that crosses the boundary between two phases changes its properties in a fundamental way. It may, for example, melt or freeze. This macroscopic change is driven by microscopic ¯uctuat ...
... excitation spectrum. We can induce reversible changes between the two ground states of the system. A physical system that crosses the boundary between two phases changes its properties in a fundamental way. It may, for example, melt or freeze. This macroscopic change is driven by microscopic ¯uctuat ...
Optical Properties of Semiconductor Quantum Dots
... dots and distilled in papers what we had learned. Things did not always work fine, far from that, but I am glad to see that we built something, that we, indeed, added a grain of sand to the mountain of human knowledge. There are many people that I must thank for this five-year adventure and I will s ...
... dots and distilled in papers what we had learned. Things did not always work fine, far from that, but I am glad to see that we built something, that we, indeed, added a grain of sand to the mountain of human knowledge. There are many people that I must thank for this five-year adventure and I will s ...
Pretest 1
... In interpreting the results of his "oil drop" experiment in 1909, Robert Millikan was able to determine ____. a. the charge on a proton b. that electrically neutral particles (neutrons) are present in the nuclei of atoms c. that the masses of protons and neutrons are nearly identical d. the charge o ...
... In interpreting the results of his "oil drop" experiment in 1909, Robert Millikan was able to determine ____. a. the charge on a proton b. that electrically neutral particles (neutrons) are present in the nuclei of atoms c. that the masses of protons and neutrons are nearly identical d. the charge o ...
1 Basics of Semiconductor and Spin Physics
... Thus the spin–orbit interaction can be written as A(LS), the constant A depending on the electron state in an atom. This interaction results in a splitting of atomic levels (the fine structure), which strongly increases for heavy atoms.3 In semiconductors, the spin–orbit interaction depends not only ...
... Thus the spin–orbit interaction can be written as A(LS), the constant A depending on the electron state in an atom. This interaction results in a splitting of atomic levels (the fine structure), which strongly increases for heavy atoms.3 In semiconductors, the spin–orbit interaction depends not only ...
A Dissertation entitled Quantum Theory of Ion
... exist for systems of mixed species of, e.g., atoms, ions, and electrons. These are important questions in physics, the answers to which will determine the degree we can understand the world around us, including phenomena as diverse as reactive processes in atomic collisions, chemical reactions, and ...
... exist for systems of mixed species of, e.g., atoms, ions, and electrons. These are important questions in physics, the answers to which will determine the degree we can understand the world around us, including phenomena as diverse as reactive processes in atomic collisions, chemical reactions, and ...