Navigation Methods
... When people first started going out in boats they tended to stay close to shore so they could use landmarks to guide them. ...
... When people first started going out in boats they tended to stay close to shore so they could use landmarks to guide them. ...
Lab 1: The Celestial Sphere
... 2. The point where the rod holding the Earth hits the bottom of the outer globe is the south celestial pole. Opposite to this is the northern celestial pole. These are simply extensions of the poles of the Earth. 3. The place where the two outer hemispheres meet is known as the celestial equator. Th ...
... 2. The point where the rod holding the Earth hits the bottom of the outer globe is the south celestial pole. Opposite to this is the northern celestial pole. These are simply extensions of the poles of the Earth. 3. The place where the two outer hemispheres meet is known as the celestial equator. Th ...
Chapter2
... B. Astrology V. Astronomical Influences on Earth's Climate A. The Hypothesis B. The Evidence ...
... B. Astrology V. Astronomical Influences on Earth's Climate A. The Hypothesis B. The Evidence ...
Chap. 2: Known the Heavens
... • For convenience of people and making the time meaningful, the Earth is divided into 24 time zones, centered on 15° intervals of longitude around the globe • UT (universal time): for convenience of aviator and sailors, who regularly travel across time zones. – It is always the time in the zone that ...
... • For convenience of people and making the time meaningful, the Earth is divided into 24 time zones, centered on 15° intervals of longitude around the globe • UT (universal time): for convenience of aviator and sailors, who regularly travel across time zones. – It is always the time in the zone that ...
Astronomy vs. Astrology: Uptodate Zodiac Signs and Dates
... is with that of a spinning top, tilted at an angle, which slowly wobbles in a circle while rotating much faster on its axis. Similarly, the Earth’s axis completes the Circle of Precession in 26,000 years, while rotating on its axis in one day or about 24 hours (23h 56 m, to be precise). In addition ...
... is with that of a spinning top, tilted at an angle, which slowly wobbles in a circle while rotating much faster on its axis. Similarly, the Earth’s axis completes the Circle of Precession in 26,000 years, while rotating on its axis in one day or about 24 hours (23h 56 m, to be precise). In addition ...
AST 301 Introduction to Astronomy
... Apparent motion of Sun during the year The Earth orbits the Sun once a year. This makes the Sun appear to pass in front of different stars (the constellations of the zodiac) during a year. The zodiac does not lie on the celestial equator, but is on a circle tipped about 23o from the equator. This i ...
... Apparent motion of Sun during the year The Earth orbits the Sun once a year. This makes the Sun appear to pass in front of different stars (the constellations of the zodiac) during a year. The zodiac does not lie on the celestial equator, but is on a circle tipped about 23o from the equator. This i ...
ASTR 111 Lab Manual - Ohio Wesleyan University
... and the equator. Note that we must specify whether the point lies north or south of the equator, which we do by appending “N” or “S” to the angle. The north pole has latitude 90º N, while the south pole has latitude 90º S. Of course, the equator itself has latitude 0º. The meridian through a point, ...
... and the equator. Note that we must specify whether the point lies north or south of the equator, which we do by appending “N” or “S” to the angle. The north pole has latitude 90º N, while the south pole has latitude 90º S. Of course, the equator itself has latitude 0º. The meridian through a point, ...
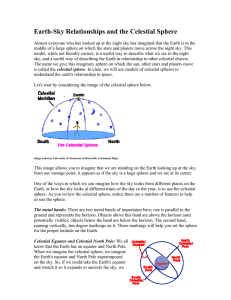
Earth-Sky Relationships and the Celestial Sphere
... would be able to divide the sky into a Northern and Southern Hemisphere. We call this dividing line on the sky the Celestial Equator, and it is represented on your celestial sphere as the “seam” between the bottom and top halves of the sphere. We know that the poles of the Earth are the points on t ...
... would be able to divide the sky into a Northern and Southern Hemisphere. We call this dividing line on the sky the Celestial Equator, and it is represented on your celestial sphere as the “seam” between the bottom and top halves of the sphere. We know that the poles of the Earth are the points on t ...
Study Guide for 1ST Astronomy Exam
... Draw and label the celestial sphere for an observer at any latitude, Draw the apparent motion of stars as seen by any observer looking North, East, South or West at any given latitude, Define a constellation and distinguish it from an asterism, Use celestial coordinates of Right Ascension an ...
... Draw and label the celestial sphere for an observer at any latitude, Draw the apparent motion of stars as seen by any observer looking North, East, South or West at any given latitude, Define a constellation and distinguish it from an asterism, Use celestial coordinates of Right Ascension an ...
Introduction to the Celestial Sphere
... If you watch the skies for a few hours, you will note the apparent motion of this fictitious celestial sphere and all things on it. This apparent motion is caused by the spinning motion (rotation) of the Earth on its axis. ...
... If you watch the skies for a few hours, you will note the apparent motion of this fictitious celestial sphere and all things on it. This apparent motion is caused by the spinning motion (rotation) of the Earth on its axis. ...
Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey (GOODS) Observation
... • Coordinate the space by means of static reference points in the sky. • Four such (quasi) static points are the equinoxes and solstices. • We use the Spring Solstice as the zero point of one coordinate. • CAUTION! The solstice actually precesses (50/yr), thus one MUST specify the year. • The 1950 ...
... • Coordinate the space by means of static reference points in the sky. • Four such (quasi) static points are the equinoxes and solstices. • We use the Spring Solstice as the zero point of one coordinate. • CAUTION! The solstice actually precesses (50/yr), thus one MUST specify the year. • The 1950 ...
North Celestial Pole
... Right ascension corresponds to longitude, but different units are used. Instead of 360°, a circle is broken into 24 hours of right ascension. So, 360° = 24 h R.A., 15° = 1 h R.A., and 1° = 4 min R.A. Note that hours of right ascension is a unit of angle, not time, although there is an obvious connec ...
... Right ascension corresponds to longitude, but different units are used. Instead of 360°, a circle is broken into 24 hours of right ascension. So, 360° = 24 h R.A., 15° = 1 h R.A., and 1° = 4 min R.A. Note that hours of right ascension is a unit of angle, not time, although there is an obvious connec ...
The View From Earth
... days; (3) accompanies the Sun (and other planets) as it moves relative to other stars in its immediate neighborhood; (4) orbits about the center of the Milky Way galaxy, with period 230 million years; (5) moves with the Milky Way galaxy as the Milky Way moves relative to other galaxies within the Lo ...
... days; (3) accompanies the Sun (and other planets) as it moves relative to other stars in its immediate neighborhood; (4) orbits about the center of the Milky Way galaxy, with period 230 million years; (5) moves with the Milky Way galaxy as the Milky Way moves relative to other galaxies within the Lo ...
Lecture notes on Coordinte systems
... angular distance, measured along the horizon, westwards from the S (in astronomy). In navigation, its eastwards from N. – 0 < h, 90◦ and 0 < α < 360◦ . – Celestial objects at a given location rise and set: this arises from the rotation of the Earth on its axisa Celestial objects appear to rise in th ...
... angular distance, measured along the horizon, westwards from the S (in astronomy). In navigation, its eastwards from N. – 0 < h, 90◦ and 0 < α < 360◦ . – Celestial objects at a given location rise and set: this arises from the rotation of the Earth on its axisa Celestial objects appear to rise in th ...
Universe 8/e Chapter 2 - Physics and Astronomy
... sphere with the Earth at its center. The surface of the celestial sphere is divided into 88 regions called constellations. Diurnal (Daily) Motion of the Celestial Sphere: The celestial sphere appears to rotate around the Earth once in each 24-hour period. In fact, it is actually the Earth that is ro ...
... sphere with the Earth at its center. The surface of the celestial sphere is divided into 88 regions called constellations. Diurnal (Daily) Motion of the Celestial Sphere: The celestial sphere appears to rotate around the Earth once in each 24-hour period. In fact, it is actually the Earth that is ro ...
constellation wars
... position of the stars and planets at a person's birth could determine that person’s destiny Helping them to “see” into the future ...
... position of the stars and planets at a person's birth could determine that person’s destiny Helping them to “see” into the future ...
Phys 1533 Descriptive Astronomy
... • Northern hemisphere: named after mythological heroes and animals. • Southern hemisphere: named by northern explorers when they traveled south. • There are 88 named constellations in all. ...
... • Northern hemisphere: named after mythological heroes and animals. • Southern hemisphere: named by northern explorers when they traveled south. • There are 88 named constellations in all. ...
Homework #2 Solutions Astronomy 10, Section 2 due: Monday
... 8) If the Earth did not rotate, could you define the celestial poles and equator? No, the celestial poles are the extension of the Earthʼs rotation axis out into space. If the Earth did not rotate, it would have no rotation axis. Likewise, the celestial equator is the Earthʼs equator projected out i ...
... 8) If the Earth did not rotate, could you define the celestial poles and equator? No, the celestial poles are the extension of the Earthʼs rotation axis out into space. If the Earth did not rotate, it would have no rotation axis. Likewise, the celestial equator is the Earthʼs equator projected out i ...
Paush – Indication of Weather Here I would like to
... definite positions on the celestial sphere in fig. 4. With reference to the stars, the plane of the ecliptic will have a definite position and, consequently, the ecliptic will be a particular great circle, which is found from observations to be inclined at an angle of about 23 ½o to the celestial e ...
... definite positions on the celestial sphere in fig. 4. With reference to the stars, the plane of the ecliptic will have a definite position and, consequently, the ecliptic will be a particular great circle, which is found from observations to be inclined at an angle of about 23 ½o to the celestial e ...
Celestial Sphere
... Declination (like latitude) is measured in degrees north or south of the Celestial equator. Right ascension (like longitude) is measured in units of hours, minutes, and seconds eastward from the position of the vernal equinox on the Celestial equator. The Vernal Equinox is the position of the Sun on ...
... Declination (like latitude) is measured in degrees north or south of the Celestial equator. Right ascension (like longitude) is measured in units of hours, minutes, and seconds eastward from the position of the vernal equinox on the Celestial equator. The Vernal Equinox is the position of the Sun on ...
RELATION BETWEEN LONGITUDE AND TIME
... Nadir – the corresponding point in the opposite hemisphere, directly below the observer Celestial equator – is the great circle formed by the intersection of the earth’s equatorial plane with the surface of the celestial sphere Declination of any celestial body – is the angular distance of the ...
... Nadir – the corresponding point in the opposite hemisphere, directly below the observer Celestial equator – is the great circle formed by the intersection of the earth’s equatorial plane with the surface of the celestial sphere Declination of any celestial body – is the angular distance of the ...
Life in the Universe
... International Astronomy Union (IAU) divided the entire night sky into 88 constellations. Helpers to find a way around the sky. Connection to the ancient astronomy, and good tool to naming stars (e.g., alpha Orioni the brightest star in Orion) stars in a constellation only appear to be clos ...
... International Astronomy Union (IAU) divided the entire night sky into 88 constellations. Helpers to find a way around the sky. Connection to the ancient astronomy, and good tool to naming stars (e.g., alpha Orioni the brightest star in Orion) stars in a constellation only appear to be clos ...
Armillary sphere

An armillary sphere (variations are known as spherical astrolabe, armilla, or armil) is a model of objects in the sky (in the celestial sphere), consisting of a spherical framework of rings, centred on Earth or the Sun, that represent lines of celestial longitude and latitude and other astronomically important features such as the ecliptic. As such, it differs from a celestial globe, which is a smooth sphere whose principal purpose is to map the constellations.With the Earth as center, an armillary sphere is known as Ptolemaic. With the sun as center, it is known as Copernican.