Lab 1: Introduction to Astronomy
... 11: Allows us to view celestial objects larger 13: “Father” whose only child is the Heliocentric model 15: The celestial equator’s latitude 16: Our Sun’s real name 19: Type of telescope that uses mirrors to direct light through reflection 21: Part of the telescope through which celestial objects are ...
... 11: Allows us to view celestial objects larger 13: “Father” whose only child is the Heliocentric model 15: The celestial equator’s latitude 16: Our Sun’s real name 19: Type of telescope that uses mirrors to direct light through reflection 21: Part of the telescope through which celestial objects are ...
astr221lect2x
... • Universal time (UT) is defined to be the mean solar time at 0° longitude. • It is also known as Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) because 0° longitude is defined to pass through Greenwich, England • It is the standard time used for astronomy and navigation around the world ...
... • Universal time (UT) is defined to be the mean solar time at 0° longitude. • It is also known as Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) because 0° longitude is defined to pass through Greenwich, England • It is the standard time used for astronomy and navigation around the world ...
The Science of Astronomy - Ohio Wesleyan University
... – The coordinates consist of latitude (angle between equator and geographical location) and longitude (angle, east or west, around the equator to point nearest to location) – The equator is an example of a great circle: a circle that divides a sphere into 2 equal parts (northern and southern hemisph ...
... – The coordinates consist of latitude (angle between equator and geographical location) and longitude (angle, east or west, around the equator to point nearest to location) – The equator is an example of a great circle: a circle that divides a sphere into 2 equal parts (northern and southern hemisph ...
BABYLON and SUMERIA 3000BC
... The Aztec calendar wheel is represented by 13 months of 20 days each, as determined by the movement of the Sun, Moon, and stars. ©Library of Congress ...
... The Aztec calendar wheel is represented by 13 months of 20 days each, as determined by the movement of the Sun, Moon, and stars. ©Library of Congress ...
29 Jan: Maps of the Sky
... for 2010: 221,600 miles or 356,600 km, 7 % less than its average distance. This will make the full Moon appear slightly larger than usual. “ ...
... for 2010: 221,600 miles or 356,600 km, 7 % less than its average distance. This will make the full Moon appear slightly larger than usual. “ ...
The Celestial Sphere
... We imagine a similar situation on the sky. The celestial sphere is an imaginary sphere of infinite radius with the earth located at its center. The north and south celestial poles of the celestial sphere are aligned with the N and S poles of the Earth. The celestial equator lies in the same plane as ...
... We imagine a similar situation on the sky. The celestial sphere is an imaginary sphere of infinite radius with the earth located at its center. The north and south celestial poles of the celestial sphere are aligned with the N and S poles of the Earth. The celestial equator lies in the same plane as ...
North Star
... Ecliptic: The path of our Sun across the celestial sphere is called the. It is inclined 23½° with respect to the celestial equator. ...
... Ecliptic: The path of our Sun across the celestial sphere is called the. It is inclined 23½° with respect to the celestial equator. ...
chapter 18
... The apparent path that the Sun traces annually along the celestial sphere is known as the ______________. a) parabolic b) elliptic c) ecliptic d) eclipse ...
... The apparent path that the Sun traces annually along the celestial sphere is known as the ______________. a) parabolic b) elliptic c) ecliptic d) eclipse ...
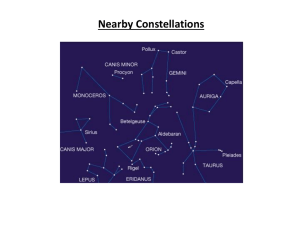
Nearby Constellations
... Stars/Constellations This several-hour-long time exposure, taken from tropical northern Australia, shows the clockwise motion of the southern stars around the South Celestial Pole. (Photo by David Miller/DMI.) ...
... Stars/Constellations This several-hour-long time exposure, taken from tropical northern Australia, shows the clockwise motion of the southern stars around the South Celestial Pole. (Photo by David Miller/DMI.) ...
CelestialSphere
... as big as it really is (9 orders of magnitude smaller) The Earth: Diameter = 13000 km = 1.3x107 m 1.3x107x10-9 ~ 10-2 = 1.3 cm (a marble) The Sun: Diameter = 1,400,000 km = 1.4x109 m (about 100 times the Earth’s) so it must be 1.4 m (about a foot less than my height) Earth-Sun Distance = 1.5x1011 m ...
... as big as it really is (9 orders of magnitude smaller) The Earth: Diameter = 13000 km = 1.3x107 m 1.3x107x10-9 ~ 10-2 = 1.3 cm (a marble) The Sun: Diameter = 1,400,000 km = 1.4x109 m (about 100 times the Earth’s) so it must be 1.4 m (about a foot less than my height) Earth-Sun Distance = 1.5x1011 m ...
CelestialSphere02
... as big as it really is (9 orders of magnitude smaller) The Earth: Diameter = 13000 km = 1.3x107 m 1.3x107x10-9 ~ 10-2 = 1.3 cm (a marble) The Sun: Diameter = 1,400,000 km = 1.4x109 m (about 100 times the Earth’s) so it must be 1.4 m (about a foot less than my height) Earth-Sun Distance = 1.5x1011 m ...
... as big as it really is (9 orders of magnitude smaller) The Earth: Diameter = 13000 km = 1.3x107 m 1.3x107x10-9 ~ 10-2 = 1.3 cm (a marble) The Sun: Diameter = 1,400,000 km = 1.4x109 m (about 100 times the Earth’s) so it must be 1.4 m (about a foot less than my height) Earth-Sun Distance = 1.5x1011 m ...
Document
... c) None of them has a measurable parallax since they are mostly within our own Solar System. d) They may have significantly different parallaxes. e) We cannot measure their parallaxes since they are all moving toward our Sun. ...
... c) None of them has a measurable parallax since they are mostly within our own Solar System. d) They may have significantly different parallaxes. e) We cannot measure their parallaxes since they are all moving toward our Sun. ...
chapter2 - Empyrean Quest Publishers
... The days there are long and the nights are short, and it is summer in the northern hemisphere and winter in the southern hemisphere The summer is hot not only because of the extended daylight hours but also because the Sun is high in the northern hemisphere’s sky As a result, sunlight strikes the gr ...
... The days there are long and the nights are short, and it is summer in the northern hemisphere and winter in the southern hemisphere The summer is hot not only because of the extended daylight hours but also because the Sun is high in the northern hemisphere’s sky As a result, sunlight strikes the gr ...
The sky
... • The whole pattern revolves around us • Constellations – patterns in star distribution • Constellations vary – related to mythology • Constellations not real • 1929 IUA – 88 official constellations • Every star belongs to a constellation ...
... • The whole pattern revolves around us • Constellations – patterns in star distribution • Constellations vary – related to mythology • Constellations not real • 1929 IUA – 88 official constellations • Every star belongs to a constellation ...
Astronomical Numbers
... 600 BC: The Greek philosopher Thales is sometimes called “the first scientist”. Thales: the universe is made of physical objects, which can be explained without mythology. Thales: the Earth is flat and stars are stuck to a rotating celestial sphere. ...
... 600 BC: The Greek philosopher Thales is sometimes called “the first scientist”. Thales: the universe is made of physical objects, which can be explained without mythology. Thales: the Earth is flat and stars are stuck to a rotating celestial sphere. ...
File
... The Ecliptic • The Sun’s apparent yearly path among the stars. • Tip the equatorial circle by 23.5° around a line passing through the Earth ...
... The Ecliptic • The Sun’s apparent yearly path among the stars. • Tip the equatorial circle by 23.5° around a line passing through the Earth ...
Session Two - A Sidewalk Astronomer in Charlottetown
... ◦ Mercury and Venus are always close to Sun. Outer planets are at various points on the ecliptic. Find out where a planet will be before going to try to observe it. ◦ If a planet is too close to or behind the Sun, it may not be visible at all for a long time. ◦ You may read that a planet is in a co ...
... ◦ Mercury and Venus are always close to Sun. Outer planets are at various points on the ecliptic. Find out where a planet will be before going to try to observe it. ◦ If a planet is too close to or behind the Sun, it may not be visible at all for a long time. ◦ You may read that a planet is in a co ...
Patterns in the Sky
... 3. Some celestial objects can be seen with the unaided eye and can be identified by their motion. 4. The Sun emits light and other forms of radiant energy that are necessary for life to exist on Earth. 5. Satellites have useful applications for technologies on Earth. 6. The study of the night sky ha ...
... 3. Some celestial objects can be seen with the unaided eye and can be identified by their motion. 4. The Sun emits light and other forms of radiant energy that are necessary for life to exist on Earth. 5. Satellites have useful applications for technologies on Earth. 6. The study of the night sky ha ...
File
... Daily East / West motion of the sky Due to the Earth’s rotation (15°/hour) [360°/24 hours = 15°/hour] [1° in 4 minutes] ...
... Daily East / West motion of the sky Due to the Earth’s rotation (15°/hour) [360°/24 hours = 15°/hour] [1° in 4 minutes] ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... sheet of paper • Let’s explore our turning star map! ...
... sheet of paper • Let’s explore our turning star map! ...
ASTRONOMICAL SURVEYING - I - IDC
... The millions of stars that we see in the sky on a clear cloudless night are all at varying distances from us. Since we are concerned with their relative distance rather than their actual distance from the observer. It is exceedingly convenient to picture the stars as distributed over the surface of ...
... The millions of stars that we see in the sky on a clear cloudless night are all at varying distances from us. Since we are concerned with their relative distance rather than their actual distance from the observer. It is exceedingly convenient to picture the stars as distributed over the surface of ...
Armillary sphere

An armillary sphere (variations are known as spherical astrolabe, armilla, or armil) is a model of objects in the sky (in the celestial sphere), consisting of a spherical framework of rings, centred on Earth or the Sun, that represent lines of celestial longitude and latitude and other astronomically important features such as the ecliptic. As such, it differs from a celestial globe, which is a smooth sphere whose principal purpose is to map the constellations.With the Earth as center, an armillary sphere is known as Ptolemaic. With the sun as center, it is known as Copernican.