Document
... – The tilt of the Earth’s axis brings the Northern Hemisphere is tilted Hemisphere closer to the Sun in Summer, and farther away from the Sun. from the Sun in Winter creating the seasons. • Geometry is true, but this accounts for only a minute fraction of the extra heating in summer. ...
... – The tilt of the Earth’s axis brings the Northern Hemisphere is tilted Hemisphere closer to the Sun in Summer, and farther away from the Sun. from the Sun in Winter creating the seasons. • Geometry is true, but this accounts for only a minute fraction of the extra heating in summer. ...
File
... Alexandria around 300 BCE. The main subjects of the work are geometry, proportion, and number theory. Euclid’s Elements (comprised of 13 books) form one of the most beautiful and influential works of science in the history of humankind. Its beauty lies in its logical development of geometry and othe ...
... Alexandria around 300 BCE. The main subjects of the work are geometry, proportion, and number theory. Euclid’s Elements (comprised of 13 books) form one of the most beautiful and influential works of science in the history of humankind. Its beauty lies in its logical development of geometry and othe ...
Navigation
... The Global Positioning System (GPS) • is a worldwide radio-navigation system formed from a constellation of 24 satellites and their ground stations. • GPS uses these "man-made stars" as reference points to calculate positions accurate to a matter of meters. In fact, with advanced forms of GPS you ...
... The Global Positioning System (GPS) • is a worldwide radio-navigation system formed from a constellation of 24 satellites and their ground stations. • GPS uses these "man-made stars" as reference points to calculate positions accurate to a matter of meters. In fact, with advanced forms of GPS you ...
The Quest Ahead - Mr. Catt`s Class
... the celestial equator where the Sun crosses it moving north). It is stated in hours, minutes, and seconds (with 24 hours encompassing the entire celestial equator). Figure 1.16b: Right ascension measures the angle around the celestial equator eastward from the vernal equinox. © 2007 Jones and Bartle ...
... the celestial equator where the Sun crosses it moving north). It is stated in hours, minutes, and seconds (with 24 hours encompassing the entire celestial equator). Figure 1.16b: Right ascension measures the angle around the celestial equator eastward from the vernal equinox. © 2007 Jones and Bartle ...
Introduction to Celestial Spheres (Professor Powerpoint)
... roughly east you’ll see them rise upward, go to highest point then start downward setting in the west. Looking toward the south you’ll see stars rise in the south east, go to the highest point and set in the southwest, a shorter arc across the sky. ...
... roughly east you’ll see them rise upward, go to highest point then start downward setting in the west. Looking toward the south you’ll see stars rise in the south east, go to the highest point and set in the southwest, a shorter arc across the sky. ...
Review: Quiz 1 Concepts Celestial sphere
... the horizon frame, and 1 degree per day, toward east, in the star frame. The stars move 361 degrees per day (west) in the horizon frame. Important circles: There are four circles that divide the celestial sphere in half. We use them in our frames of reference. Horizon: The horizontal circle. Divides ...
... the horizon frame, and 1 degree per day, toward east, in the star frame. The stars move 361 degrees per day (west) in the horizon frame. Important circles: There are four circles that divide the celestial sphere in half. We use them in our frames of reference. Horizon: The horizontal circle. Divides ...
The Celestial Sphere
... To precisely locate points on the earth's surface, degrees longitude and latitude have been divided into minutes (') and seconds (”) ...
... To precisely locate points on the earth's surface, degrees longitude and latitude have been divided into minutes (') and seconds (”) ...
The Sky and the Motions of the Earth
... of different constellations at different times of year. The path the Sun takes across heavens is called the ecliptic. The constellations which the Sun passes through are zodiac constellations. Because the Sun is bright, we can only see some constellations at certain times of year. ...
... of different constellations at different times of year. The path the Sun takes across heavens is called the ecliptic. The constellations which the Sun passes through are zodiac constellations. Because the Sun is bright, we can only see some constellations at certain times of year. ...
Observing the Sky - University of Northern Iowa
... course of the day. Seasons are caused by the Earth’s changing distance to the Sun. The Sun will be directly over your head at noon during the summer. The Sun will always rise/set due east/west as seen from Iowa. ...
... course of the day. Seasons are caused by the Earth’s changing distance to the Sun. The Sun will be directly over your head at noon during the summer. The Sun will always rise/set due east/west as seen from Iowa. ...
Chaper 1 part b
... first come into view moving upward, rising at some point along the eastern horizon. Then, they appear to arc across the sky. Finally, they disappear somewhere along the western horizon. ...
... first come into view moving upward, rising at some point along the eastern horizon. Then, they appear to arc across the sky. Finally, they disappear somewhere along the western horizon. ...
3. Celestial Sphere Mark
... – Therefore Polaris is 48 degrees above the horizon – This means you can always know your latitude in the northern hemisphere by knowing were Polaris is • Let’s look to the Northern Sky ...
... – Therefore Polaris is 48 degrees above the horizon – This means you can always know your latitude in the northern hemisphere by knowing were Polaris is • Let’s look to the Northern Sky ...
Chapter 2 PowerPoint
... • Concern about the progressive shift of the date of Easter • He arbitrarily dropped 10 days (October 5 to 14, 1582) • He modified the system of leap years – Only century years divisible by 400 are leap years – The year 2000 was therefore a leap year – The year 2100 will not be a leap year ...
... • Concern about the progressive shift of the date of Easter • He arbitrarily dropped 10 days (October 5 to 14, 1582) • He modified the system of leap years – Only century years divisible by 400 are leap years – The year 2000 was therefore a leap year – The year 2100 will not be a leap year ...
Friday, Sep. 5
... The west-to-east rotation makes stars appear to move east-to-west, generally rising in the east and setting in the west. The appearance is the same as if the stars were on a giant sphere surrounding the Earth, which rotates east-to-west about an axis running through the Earth’s poles. This imaginary ...
... The west-to-east rotation makes stars appear to move east-to-west, generally rising in the east and setting in the west. The appearance is the same as if the stars were on a giant sphere surrounding the Earth, which rotates east-to-west about an axis running through the Earth’s poles. This imaginary ...
P10293v3.0 Lab 1 Text
... From lecture, you should recall that the altitude of the North Celestial Pole above the Northern horizon is equal to your latitude. We can use this information to set up the Celestial Sphere model as shown on the next page. Go ahead and set up your Celestial Sphere as shown for a latitude of +33° (o ...
... From lecture, you should recall that the altitude of the North Celestial Pole above the Northern horizon is equal to your latitude. We can use this information to set up the Celestial Sphere model as shown on the next page. Go ahead and set up your Celestial Sphere as shown for a latitude of +33° (o ...
Ecliptic 1 2 3 Three tell tale visual characteristics a planet:
... front of the stars of Cancer, then towards Leo. ...
... front of the stars of Cancer, then towards Leo. ...
normal and two other geometries.
... attraction. The amount of this deflection computed by Einstein’s general theoy was double that figured from Newtonian theory. This cannot be checked ordinarily, since the sun’s brilliance makes it impossible to see the star rays passing near, but total eclipses furnish an opportunity. British expedi ...
... attraction. The amount of this deflection computed by Einstein’s general theoy was double that figured from Newtonian theory. This cannot be checked ordinarily, since the sun’s brilliance makes it impossible to see the star rays passing near, but total eclipses furnish an opportunity. British expedi ...
automatic astro-navigation
... ELESTIAL navigation has been brought into great prominence with the advent of modern high-speed jet aircraft, and the increased accuracy now required, coupled with space limitations and the greater work-load on the flight crew, have drastically changed the requirements for navigational equipment. Au ...
... ELESTIAL navigation has been brought into great prominence with the advent of modern high-speed jet aircraft, and the increased accuracy now required, coupled with space limitations and the greater work-load on the flight crew, have drastically changed the requirements for navigational equipment. Au ...
Ch2a
... Astronomers have thus adopted a specific location on the sky, known as the “First Point in Aries”, that is actually the intersection of the ecliptic and the celestial equator, (where the Sun is on the Spring equinox), to mark the zero point of the celestial longitude system, called Right Ascension. ...
... Astronomers have thus adopted a specific location on the sky, known as the “First Point in Aries”, that is actually the intersection of the ecliptic and the celestial equator, (where the Sun is on the Spring equinox), to mark the zero point of the celestial longitude system, called Right Ascension. ...
2 - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... A-6. The track of a star which rises directly in the east is shown with respect to an observer's horizon. The observer's location is (a) near but not at the north pole, (b) at an intermediate northern latitude, (c) near but slightly north of the equator, (d) on the equator, (e) near but slightly sou ...
... A-6. The track of a star which rises directly in the east is shown with respect to an observer's horizon. The observer's location is (a) near but not at the north pole, (b) at an intermediate northern latitude, (c) near but slightly north of the equator, (d) on the equator, (e) near but slightly sou ...
1000
... the same time and therefore realized the Earth was curved. He realized the distance between the cities was a 7 degree difference or about 1/50th of the earth’s total conference ...
... the same time and therefore realized the Earth was curved. He realized the distance between the cities was a 7 degree difference or about 1/50th of the earth’s total conference ...
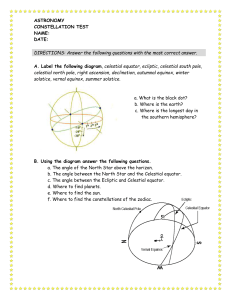
ASTRONOMY
... E. Fill in the blank. 1. There are about __________ stars you can see at night. 2. Latitudes on earth are like ____________ in space. 3. There are about ________ constellations. 4. The north-star has a magnitude of _____________. 5. The point directly overhead is called the ______________. 6. Polar ...
... E. Fill in the blank. 1. There are about __________ stars you can see at night. 2. Latitudes on earth are like ____________ in space. 3. There are about ________ constellations. 4. The north-star has a magnitude of _____________. 5. The point directly overhead is called the ______________. 6. Polar ...
The Celestial Sphere
... The diurnal path or the daily path of a star is a circle parallel to the celestial equator. Whether you can see a star or not depends on two things. First of all, the star must be above the horizon, and secondly it must be night. At any given place on the Earth, the celestial sphere consists of thr ...
... The diurnal path or the daily path of a star is a circle parallel to the celestial equator. Whether you can see a star or not depends on two things. First of all, the star must be above the horizon, and secondly it must be night. At any given place on the Earth, the celestial sphere consists of thr ...
Armillary sphere

An armillary sphere (variations are known as spherical astrolabe, armilla, or armil) is a model of objects in the sky (in the celestial sphere), consisting of a spherical framework of rings, centred on Earth or the Sun, that represent lines of celestial longitude and latitude and other astronomically important features such as the ecliptic. As such, it differs from a celestial globe, which is a smooth sphere whose principal purpose is to map the constellations.With the Earth as center, an armillary sphere is known as Ptolemaic. With the sun as center, it is known as Copernican.