11.4 How Is The Information In A Gene
... • The ribosome joins the amino acids together with peptide bonds to form a protein. • When a stop codon is reached, the finished protein is released from the ribosome. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education Inc. ...
... • The ribosome joins the amino acids together with peptide bonds to form a protein. • When a stop codon is reached, the finished protein is released from the ribosome. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education Inc. ...
Practise Final exam
... Intrigued by the GEN polypeptide, you search for similar polypeptides in mice by looking for similar DNA sequences in mouse genomic DNA. You find a gene that matches bacterial GEN almost perfectly but it contains a 36 base pair insertion in the center. When you purify GEN polypeptide from mouse cell ...
... Intrigued by the GEN polypeptide, you search for similar polypeptides in mice by looking for similar DNA sequences in mouse genomic DNA. You find a gene that matches bacterial GEN almost perfectly but it contains a 36 base pair insertion in the center. When you purify GEN polypeptide from mouse cell ...
Regulatory Protein and Their Binding Sites
... heavy metal-protection genes turned on BEFORE you encounter trouble? ...
... heavy metal-protection genes turned on BEFORE you encounter trouble? ...
Document
... breaks off and is lost. • Duplication : when a segment of a chromosome is repeated • Inversion : when a segment of a chromosome is reversed. ...
... breaks off and is lost. • Duplication : when a segment of a chromosome is repeated • Inversion : when a segment of a chromosome is reversed. ...
FROM GENE TO PROTEIN - Scranton Prep Biology
... . Ambigully is absent,sincecodonscode for only one amino acid. The correct ordering and grouping of nucleotidesis important in the molecular languageof cells. This ordering is called the reading frame' Reading frame = The correct grouping of adjacentnucleotide triplets into codons that are in the co ...
... . Ambigully is absent,sincecodonscode for only one amino acid. The correct ordering and grouping of nucleotidesis important in the molecular languageof cells. This ordering is called the reading frame' Reading frame = The correct grouping of adjacentnucleotide triplets into codons that are in the co ...
Ch11_lecture - Dr Owen class material
... • The ribosome joins the amino acids together with peptide bonds to form a protein. • When a stop codon is reached, the finished protein is released from the ribosome. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education Inc. ...
... • The ribosome joins the amino acids together with peptide bonds to form a protein. • When a stop codon is reached, the finished protein is released from the ribosome. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education Inc. ...
SEMESTER II LSM4241 FUNCTIONAL GENOMICS
... SEMESTER II LSM4241 FUNCTIONAL GENOMICS Prerequisite: LSM3231 Workload: 30 lecture hours + 20 tutorial, self study and presentation hours This module aims to introduce selected topics on functional genomics. Areas covered include: the assignment of functions to novel genes following the genome-seque ...
... SEMESTER II LSM4241 FUNCTIONAL GENOMICS Prerequisite: LSM3231 Workload: 30 lecture hours + 20 tutorial, self study and presentation hours This module aims to introduce selected topics on functional genomics. Areas covered include: the assignment of functions to novel genes following the genome-seque ...
MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE
... A gene contains 999 nucleotides (including initiator codon & terminator codon). How many amino acids would be there in polypeptide chain ...
... A gene contains 999 nucleotides (including initiator codon & terminator codon). How many amino acids would be there in polypeptide chain ...
rna metabolism: how different bacteria reached the same
... of functional RNase Y. In these experiments, around 1600 mRNA transcripts are found in the RNase Y depleted strain, which are upregulated in comparison to when the enzyme in present, while several hundred non-coding RNA molecules are also found to be increased in its absence. Interestingly, across s ...
... of functional RNase Y. In these experiments, around 1600 mRNA transcripts are found in the RNase Y depleted strain, which are upregulated in comparison to when the enzyme in present, while several hundred non-coding RNA molecules are also found to be increased in its absence. Interestingly, across s ...
Transcription and Translation
... Each triplet code on a DNA molecule is transcribed into a triplet codon on the mRNA molecule. • If the DNA codes for a polypeptide is T-A-C—C-C-G—T-A-G—C-T-T—A-C-T • What would the codons on the complimentary strand of mRNA codons look like? A-U-G – G-G-C – A-U-C – G-A-A – U-G-A • DNA codes: T-A-C— ...
... Each triplet code on a DNA molecule is transcribed into a triplet codon on the mRNA molecule. • If the DNA codes for a polypeptide is T-A-C—C-C-G—T-A-G—C-T-T—A-C-T • What would the codons on the complimentary strand of mRNA codons look like? A-U-G – G-G-C – A-U-C – G-A-A – U-G-A • DNA codes: T-A-C— ...
B. Eukaryotic RNA polymerases
... 1. After about 8 ribonucleotides are added to the RNA molecule, RNA polymerase undergoes a conformation change and loses the sigma factor a) This marks the beginning of the elongation phase of transcription b) Elongation is catalyzed by the core enzyme (1) The holoenzyme lacking the sigma factor 2. ...
... 1. After about 8 ribonucleotides are added to the RNA molecule, RNA polymerase undergoes a conformation change and loses the sigma factor a) This marks the beginning of the elongation phase of transcription b) Elongation is catalyzed by the core enzyme (1) The holoenzyme lacking the sigma factor 2. ...
Gene Section MIRN21 (microRNA 21) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... is located near the transcription start site (+114). This potential peptide sequence shows homology to a 180-amino-acid human protein. However, it is not clear yet if pri-MIRN21 functions as an mRNA as well. Figure 1. B: Stem-loop structure of MIRN21. ...
... is located near the transcription start site (+114). This potential peptide sequence shows homology to a 180-amino-acid human protein. However, it is not clear yet if pri-MIRN21 functions as an mRNA as well. Figure 1. B: Stem-loop structure of MIRN21. ...
Biology 105: Introduction to Genetics
... Intrigued by the GEN polypeptide, you search for similar polypeptides in mice by looking for similar DNA sequences in mouse genomic DNA. You find a gene that matches bacterial GEN almost perfectly but it contains a 36 base pair insertion in the center. When you purify GEN polypeptide from mouse cell ...
... Intrigued by the GEN polypeptide, you search for similar polypeptides in mice by looking for similar DNA sequences in mouse genomic DNA. You find a gene that matches bacterial GEN almost perfectly but it contains a 36 base pair insertion in the center. When you purify GEN polypeptide from mouse cell ...
concept mapping challenge - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... b. If ribosomes stall during translation of the leader region because the appropriate charged aminoacyl-tRNA is absent, the terminator does not form and transcription will continue B. Riboswitches:effector molecule-mRNA interaction regulates transcription 1. Riboswitches (sensory RNAs) are a form of ...
... b. If ribosomes stall during translation of the leader region because the appropriate charged aminoacyl-tRNA is absent, the terminator does not form and transcription will continue B. Riboswitches:effector molecule-mRNA interaction regulates transcription 1. Riboswitches (sensory RNAs) are a form of ...
6 Protein_Synthesis - bloodhounds Incorporated
... There is no DNA template for this tail? Poly A tails are found on most mRNA molecules but not all (ex. histones mRNA have no poly A tail). In general, a eukaryotic mRNA molecule is longer than the required transcript. The enzyme RNA endonuclease cleaves the molecule at the poly(A) addition site to g ...
... There is no DNA template for this tail? Poly A tails are found on most mRNA molecules but not all (ex. histones mRNA have no poly A tail). In general, a eukaryotic mRNA molecule is longer than the required transcript. The enzyme RNA endonuclease cleaves the molecule at the poly(A) addition site to g ...
molecular biology review sheet
... Section 2 – The cell cycle multiples cells. Section 3 – Cells divide during the mitotic phase. Section 4 – Cancer cells grow and divide out of control. Chapter 11 Section 1 – Genes are made of DNA. Section 2 – Nucleic acids store information in their sequences of chemical units. Section 3 – DNA repl ...
... Section 2 – The cell cycle multiples cells. Section 3 – Cells divide during the mitotic phase. Section 4 – Cancer cells grow and divide out of control. Chapter 11 Section 1 – Genes are made of DNA. Section 2 – Nucleic acids store information in their sequences of chemical units. Section 3 – DNA repl ...
An in vitro RNA synthesis reaction was set up and allowed to
... inserted between positions 22 and 23 (position of insertion is indicated by an arrow on the figure above). Give the sequence of the new peptide produced by mutant B. Label the amino and carboxy termini of the peptide. d) One of these two mutants is fully functional, while the other is not. Which mut ...
... inserted between positions 22 and 23 (position of insertion is indicated by an arrow on the figure above). Give the sequence of the new peptide produced by mutant B. Label the amino and carboxy termini of the peptide. d) One of these two mutants is fully functional, while the other is not. Which mut ...
The Genetic Code: The most fundamental concept in all biology
... The Genetic Code: The most fundamental concept in all biology. Shortly after the discovery of the structure of DNA by Watson and Crick, scientists were faced with a significant problem: How does the information encoded in DNA get translated into a protein. In 1954, our old friend Francis Crick hypot ...
... The Genetic Code: The most fundamental concept in all biology. Shortly after the discovery of the structure of DNA by Watson and Crick, scientists were faced with a significant problem: How does the information encoded in DNA get translated into a protein. In 1954, our old friend Francis Crick hypot ...
Regulation
... A. Often is carried out by activators 1. Protein that _______________ transcription in response to environmental signal. B. These regulators also bind to specific operator sites: 1. Operator positions are usually upstream of the -35 element. 2. Some can be 100’s of bases upstream for promoter. These ...
... A. Often is carried out by activators 1. Protein that _______________ transcription in response to environmental signal. B. These regulators also bind to specific operator sites: 1. Operator positions are usually upstream of the -35 element. 2. Some can be 100’s of bases upstream for promoter. These ...
unit 4 study guide
... Know DNA Replication Know all about DNA, mRNA, and tRNA; Know diagrams of such molecules and be able to match parts to them. Know the monomers (building-blocks) for proteins and nucleic acids. Know how to transcribe and translate back and forth from DNA to mRNA to tRNA Know sequence of protein synth ...
... Know DNA Replication Know all about DNA, mRNA, and tRNA; Know diagrams of such molecules and be able to match parts to them. Know the monomers (building-blocks) for proteins and nucleic acids. Know how to transcribe and translate back and forth from DNA to mRNA to tRNA Know sequence of protein synth ...
Document
... • Be able to describe the components of DNA electrophoresis, and recognize patterns in a gel • Be able to describe the form and function of restriction enzymes (restriction endonucleases) • Be able to describe the process of DNA-mediated transformation of bacterial cells • Discuss the molecular basi ...
... • Be able to describe the components of DNA electrophoresis, and recognize patterns in a gel • Be able to describe the form and function of restriction enzymes (restriction endonucleases) • Be able to describe the process of DNA-mediated transformation of bacterial cells • Discuss the molecular basi ...
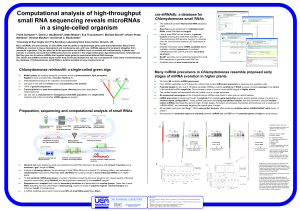
View Poster - Technology Networks
... Potential targets for four out of 18 tested candidate miRNAs could be verified by 5’ RACE analysis, showing cleavage in the centre of the predicted miRNA target site. This is similar to what is found in most miRNA targets of higher plants Two verified targets are associated with cell motility, one i ...
... Potential targets for four out of 18 tested candidate miRNAs could be verified by 5’ RACE analysis, showing cleavage in the centre of the predicted miRNA target site. This is similar to what is found in most miRNA targets of higher plants Two verified targets are associated with cell motility, one i ...
SURVEY AND SUMMARY Origins of tmRNA: the
... associated with Small protein B (SmpB). tmRNA is a hybrid molecule carrying out both transfer and messenger RNA activities, and its total length varies between about 260 and 430 nucleotides, depending on the cell species (Figure 4). It is always aminoacylated by alanine. As for SmpB, its topology ma ...
... associated with Small protein B (SmpB). tmRNA is a hybrid molecule carrying out both transfer and messenger RNA activities, and its total length varies between about 260 and 430 nucleotides, depending on the cell species (Figure 4). It is always aminoacylated by alanine. As for SmpB, its topology ma ...
pGLO Plasmid Map
... source of energy and a source of carbon. E. coli bacteria produce three enzymes (proteins) needed to digest arabinose as a food source. The genes that code for these enzymes are not expressed when arabinose is absent, but they are expressed when arabinose is present in their environment. How is this ...
... source of energy and a source of carbon. E. coli bacteria produce three enzymes (proteins) needed to digest arabinose as a food source. The genes that code for these enzymes are not expressed when arabinose is absent, but they are expressed when arabinose is present in their environment. How is this ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.