amino acid
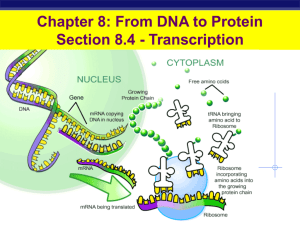
... information from the DNA in the nucleus to the cytoplasm where protein synthesis occurs. b) Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – rRNA makes up ribosomes. Ribosomes are the organelle responsible for assembling amino acids into proteins. c) Transfer RNA (tRNA) – transports specific amino acids to the ribosome for a ...
... information from the DNA in the nucleus to the cytoplasm where protein synthesis occurs. b) Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – rRNA makes up ribosomes. Ribosomes are the organelle responsible for assembling amino acids into proteins. c) Transfer RNA (tRNA) – transports specific amino acids to the ribosome for a ...
Solid Tumour Section t(6;22)(p21;q12) in hidradenoma of the skin
... Möller E, Stenman G, Mandahl N, Hamberg H, et al. POU5F1, encoding a key regulator of stem cell pluripotency, is fused to EWSR1 in hidradenoma of the skin and mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the salivary glands. J Pathol. 2008 ...
... Möller E, Stenman G, Mandahl N, Hamberg H, et al. POU5F1, encoding a key regulator of stem cell pluripotency, is fused to EWSR1 in hidradenoma of the skin and mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the salivary glands. J Pathol. 2008 ...
D.1 and D.2 Practice Test KEY
... 1. One process need for the spontaneous origin of life is the non-living synthesis of simple organic molecules/amino acids from inorganic molecules; 2. Another process needed for the spontaneous formation of life is the assembly of these simple organic molecules into polymers/polypeptides; 3. Anothe ...
... 1. One process need for the spontaneous origin of life is the non-living synthesis of simple organic molecules/amino acids from inorganic molecules; 2. Another process needed for the spontaneous formation of life is the assembly of these simple organic molecules into polymers/polypeptides; 3. Anothe ...
proteins - SharpSchool
... Even though a gene may have multiple alleles, a person can ONLY carry 2 of those alleles because chromosomes exist in PAIRS (not triples, quadruples etc.) Each chromosome in a pair only carries one allele for the trait. Example: Human Blood Type ...
... Even though a gene may have multiple alleles, a person can ONLY carry 2 of those alleles because chromosomes exist in PAIRS (not triples, quadruples etc.) Each chromosome in a pair only carries one allele for the trait. Example: Human Blood Type ...
workshop module 6: dna, rna and proteins - Peer
... 1. DNA is a polymer made of amino acids which is located in the nucleus. Each DNA nucleotide contains ribose, phosphate group, and nitrogenous bases. During DNA replication one strand of DNA acts as a template for mRNA replication. The nucleotide sequences can be divided into 3-base sequences called ...
... 1. DNA is a polymer made of amino acids which is located in the nucleus. Each DNA nucleotide contains ribose, phosphate group, and nitrogenous bases. During DNA replication one strand of DNA acts as a template for mRNA replication. The nucleotide sequences can be divided into 3-base sequences called ...
AP Lesson #50 After transcription, do prokaryotes need to modify
... – Protein coding gene is colinear with the mRNA – mRNA is ready to be translated into a protein ...
... – Protein coding gene is colinear with the mRNA – mRNA is ready to be translated into a protein ...
PDF file
... viruses, most all organisms on this planet store their cellular blueprints for life in double-stranded DNA molecules called chromosomes. In eukaryotic cells, chromosomes are copied during cell division, recombined and shuffled as a result of sexual reproduction, and transcribed into complementary RN ...
... viruses, most all organisms on this planet store their cellular blueprints for life in double-stranded DNA molecules called chromosomes. In eukaryotic cells, chromosomes are copied during cell division, recombined and shuffled as a result of sexual reproduction, and transcribed into complementary RN ...
Protocol
... into single stranded DNA) (2) annealing (raising the temperature to allow DNA primers to bind the specific DNA sequence they are complimentary to- forming Watson-Crick ...
... into single stranded DNA) (2) annealing (raising the temperature to allow DNA primers to bind the specific DNA sequence they are complimentary to- forming Watson-Crick ...
Transcription to Translation Scavenger Hunt
... They should have everything they need to get started now. Tell them that this is a “scavenger hunt” sort of activity and that the teams which come in first will “win”. 2. (2-5 min) Transcription: Instruct students that they will only be able to take their mRNA strip, their nucleotides and their stri ...
... They should have everything they need to get started now. Tell them that this is a “scavenger hunt” sort of activity and that the teams which come in first will “win”. 2. (2-5 min) Transcription: Instruct students that they will only be able to take their mRNA strip, their nucleotides and their stri ...
没有幻灯片标题
... 20.9 The basal apparatus assembles at the promoter 20.10 Initiation is followed by promoter clearance 20.11 A connection between transcription and repair 20.12 Promoters for RNA polymerase II have short sequence elements 20.13 Some promoter-binding proteins are repressors 20.14 Enhancers contain bid ...
... 20.9 The basal apparatus assembles at the promoter 20.10 Initiation is followed by promoter clearance 20.11 A connection between transcription and repair 20.12 Promoters for RNA polymerase II have short sequence elements 20.13 Some promoter-binding proteins are repressors 20.14 Enhancers contain bid ...
Do Complementary DNA Strands Code for Complementary Peptides?
... company on the basis of my experience in protein sequencing but I was tasked with the role of developing a peptide synthesiser. When I explained to the Managing Director that I had no experience in that area, he did not see a problem; “Putting peptides together amino acid by amino acid is simply the ...
... company on the basis of my experience in protein sequencing but I was tasked with the role of developing a peptide synthesiser. When I explained to the Managing Director that I had no experience in that area, he did not see a problem; “Putting peptides together amino acid by amino acid is simply the ...
Eukaryotic Gene Control
... Essential knowledge 3.B.1: Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to cell specialization. c. In eukaryotes, gene expression is complex and control involves regulatory genes, regulatory elements and transcription factors that act in concert. 1. Transcription factors bind to ...
... Essential knowledge 3.B.1: Gene regulation results in differential gene expression, leading to cell specialization. c. In eukaryotes, gene expression is complex and control involves regulatory genes, regulatory elements and transcription factors that act in concert. 1. Transcription factors bind to ...
Document
... nucleotides instead of the two strands found in DNA 2. RNA nucleotides contain the fivecarbon sugar ribose rather than the sugar deoxyribose, which is found in DNA nucleotides 3. In addition to the A, G, and C nitrogen bases found in DNA, RNA nucleotides can have a nitrogen base called uracil (U) ...
... nucleotides instead of the two strands found in DNA 2. RNA nucleotides contain the fivecarbon sugar ribose rather than the sugar deoxyribose, which is found in DNA nucleotides 3. In addition to the A, G, and C nitrogen bases found in DNA, RNA nucleotides can have a nitrogen base called uracil (U) ...
Hereditary Skin Disorders: Potential Targets for Gene
... • Untranslated (e.g. encodes an RNA, not a protein) • Mutation distribution: – Finnish mutation, nt70 AÆG • Arose ~4500 years ago • Detected in 1:120 Finnish controls • Contributes to 92% of mutations in Finnish patients • Accounts for 48% of CHH patients from elsewhere ...
... • Untranslated (e.g. encodes an RNA, not a protein) • Mutation distribution: – Finnish mutation, nt70 AÆG • Arose ~4500 years ago • Detected in 1:120 Finnish controls • Contributes to 92% of mutations in Finnish patients • Accounts for 48% of CHH patients from elsewhere ...
The rate of photosynthesis may vary with change that occur in
... Explain how an inducible operon regulates gene expression in prokaryotes. ...
... Explain how an inducible operon regulates gene expression in prokaryotes. ...
The Organization and Control of Eukaryotic Genomes
... tissues (seen in early insect development). ...
... tissues (seen in early insect development). ...
AnnotatorsInterface-GUS
... Using exons defined by curated gene 5' and 3' UTRs Automatic creation of RNA entry Merge existing RNA instances Tables affected: ...
... Using exons defined by curated gene 5' and 3' UTRs Automatic creation of RNA entry Merge existing RNA instances Tables affected: ...
Chapter 19: Viruses 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction What exactly is a Virus?
... that kill bacteria, fungi, etc, do NOT harm viruses** ...
... that kill bacteria, fungi, etc, do NOT harm viruses** ...
Measuring the Rates of Transcriptional Elongation in the Female
... numerous transposable element families, and contains few functional genes (Holmquist et al. 1998). Repetitive sequences account for the majority of all heterochromatic sequences in Drosophila melanogaster, whose genome is 30% heterochromatic, suggesting that they have a central role in heterochromat ...
... numerous transposable element families, and contains few functional genes (Holmquist et al. 1998). Repetitive sequences account for the majority of all heterochromatic sequences in Drosophila melanogaster, whose genome is 30% heterochromatic, suggesting that they have a central role in heterochromat ...
Activity
... together. As the code carried by mRNA is “read” on a ribosome, the proper tRNAs arrive in turn and give up the amino acids they carry to the growing polypeptide chain. The process by which the information from DNA is transferred into the language of proteins is known as translation. In this investig ...
... together. As the code carried by mRNA is “read” on a ribosome, the proper tRNAs arrive in turn and give up the amino acids they carry to the growing polypeptide chain. The process by which the information from DNA is transferred into the language of proteins is known as translation. In this investig ...
first of Chapter 11: Gene Regulation
... lac operon model • 2 kinds of genes: structural, regulatory elements. • Polycistronic structural genes, with promoter and operator constitute the lac operon. • Promoter mutants make no lac mRNA. • lacI gene makes a repressor, which binds to the operator. • When operator is ‘repressed’ no transcript ...
... lac operon model • 2 kinds of genes: structural, regulatory elements. • Polycistronic structural genes, with promoter and operator constitute the lac operon. • Promoter mutants make no lac mRNA. • lacI gene makes a repressor, which binds to the operator. • When operator is ‘repressed’ no transcript ...
Replication, Transcription, Translation
... Note: The binding of some inducer and repressor proteins to DNA is influenced through alteration of their three - dimensional structure by interactions with hormone molecules. ...
... Note: The binding of some inducer and repressor proteins to DNA is influenced through alteration of their three - dimensional structure by interactions with hormone molecules. ...
Gene Regulation and Pathological Studies Using Mouse models
... regions called the operator (o) and the promoter (p). Operator is the DNA sequence that repressor binds. The promoter is the site where RNA polymerase binds and starts transcription. Operator and promoter are “cis” or associated to lac operon. Lac repressor protein is “trans” to lac operon, since th ...
... regions called the operator (o) and the promoter (p). Operator is the DNA sequence that repressor binds. The promoter is the site where RNA polymerase binds and starts transcription. Operator and promoter are “cis” or associated to lac operon. Lac repressor protein is “trans” to lac operon, since th ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.