AP BIO Lab 7: Genetics of Drosophila
... one or more mutations. They are the parental generation for your experiment. The offspring of this generation, which should already exist as eggs or larvae in the vial, are the F1 generation. 4. Record the letter written on the vial in Table 2 in the Analysis section of the lab. This will help you t ...
... one or more mutations. They are the parental generation for your experiment. The offspring of this generation, which should already exist as eggs or larvae in the vial, are the F1 generation. 4. Record the letter written on the vial in Table 2 in the Analysis section of the lab. This will help you t ...
Lab book: Title and date
... your lab notes, click on the Lab Notes button and move the cursor to the space above the dashed line and type a comment such as, "These are the results of the F1 generation for my first monohybrid cross." Click the Close button to close this panel and return to the Mate screen. To set up a cross bet ...
... your lab notes, click on the Lab Notes button and move the cursor to the space above the dashed line and type a comment such as, "These are the results of the F1 generation for my first monohybrid cross." Click the Close button to close this panel and return to the Mate screen. To set up a cross bet ...
Ch. 9 Presentation - Faculty Website Listing
... Incomplete dominance does not support the blending hypothesis because the original parental phenotypes reappear in the F2 generation. One example of incomplete dominance in humans is hypercholesterolemia, in which – dangerously high levels of cholesterol occur in the blood and ...
... Incomplete dominance does not support the blending hypothesis because the original parental phenotypes reappear in the F2 generation. One example of incomplete dominance in humans is hypercholesterolemia, in which – dangerously high levels of cholesterol occur in the blood and ...
Blueprint of life
... Use letters to represent the possible offspring in the second generation. _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ ...
... Use letters to represent the possible offspring in the second generation. _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ ...
Mendel Genetics 2015
... • When Mendel crossed contrasting, truebreeding white and purple flowered pea plants, all of the F1 hybrids were purple • When Mendel crossed the F1 hybrids, many of the F2 plants had purple flowers, but some had white • Mendel discovered a ratio of about three to one, purple to white flowers, in th ...
... • When Mendel crossed contrasting, truebreeding white and purple flowered pea plants, all of the F1 hybrids were purple • When Mendel crossed the F1 hybrids, many of the F2 plants had purple flowers, but some had white • Mendel discovered a ratio of about three to one, purple to white flowers, in th ...
Understanding Patterns of Inheritance Through Pedigree
... 1. Students are asked to examine their pedigree to determine how their trait is inherited. The focus is on identifying how the trait was passed from parent to offspring, not necessarily dominance or recessive characteristics, but who do you think gave you this trait, your mom or your dad? Who did th ...
... 1. Students are asked to examine their pedigree to determine how their trait is inherited. The focus is on identifying how the trait was passed from parent to offspring, not necessarily dominance or recessive characteristics, but who do you think gave you this trait, your mom or your dad? Who did th ...
public exam_basic genetics_R1
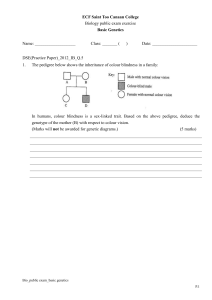
... 11. Red-green colour blindness is an X-linked recessive trait in humans. Peter is red-green colour blind while his daughter, Mary, is normal. (a) Deduce Mary’s genotype without using a genetic diagram. ...
... 11. Red-green colour blindness is an X-linked recessive trait in humans. Peter is red-green colour blind while his daughter, Mary, is normal. (a) Deduce Mary’s genotype without using a genetic diagram. ...
public exam_basic genetics_R1
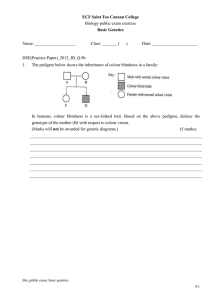
... 11. Red-green colour blindness is an X-linked recessive trait in humans. Peter is red-green colour blind while his daughter, Mary, is normal. (a) Deduce Mary’s genotype without using a genetic diagram. ...
... 11. Red-green colour blindness is an X-linked recessive trait in humans. Peter is red-green colour blind while his daughter, Mary, is normal. (a) Deduce Mary’s genotype without using a genetic diagram. ...
A. Outline: B. Reading assignment: C. Suggested practice questions
... dusting stigma with pollen from the desired parent (father) tying a bag over the flowers to keep out other pollen ...
... dusting stigma with pollen from the desired parent (father) tying a bag over the flowers to keep out other pollen ...
Gregor Mendal and Genetics
... because the role of these things in relation to inheritance & heredity had not been discovered yet. What makes Mendel's contributions so impressive is that he described the basic patterns of inheritance before the mechanism for inheritance (namely genes) was even discovered. There are a few importan ...
... because the role of these things in relation to inheritance & heredity had not been discovered yet. What makes Mendel's contributions so impressive is that he described the basic patterns of inheritance before the mechanism for inheritance (namely genes) was even discovered. There are a few importan ...
Probability and Punnett Square PPT
... What percentage of offspring would be expected to have short whiskers from the cross of two long-whiskered ...
... What percentage of offspring would be expected to have short whiskers from the cross of two long-whiskered ...
Early Concepts in Genetics
... A. A ____________________ is any characteristic that can be passed from parents to offspring. B. The scientific study of heredity is called genetics. Modern genetics began in the 1860’s with he work of an Austrian monk and scientist named _________________________________. He used pea plants to stud ...
... A. A ____________________ is any characteristic that can be passed from parents to offspring. B. The scientific study of heredity is called genetics. Modern genetics began in the 1860’s with he work of an Austrian monk and scientist named _________________________________. He used pea plants to stud ...
The Inheritance of Two Traits
... When Mendel performed his monohybrid crosses on pea plants, he was investigating one trait at a time. This method allowed him to determine the inheritance pattern of plant height, for instance, among generations. However, organisms are composed of many traits. The common pea, among other characteris ...
... When Mendel performed his monohybrid crosses on pea plants, he was investigating one trait at a time. This method allowed him to determine the inheritance pattern of plant height, for instance, among generations. However, organisms are composed of many traits. The common pea, among other characteris ...
When epigenetics meets alternative splicing: the roles of DNA
... in gene structure and to determine whether these changes are related to the splicing process. GC content architecture on the exon–intron structure has changed during evolution, especially during the transition from cold- to warmblooded organisms. The ancestral genome had short introns of low GC cont ...
... in gene structure and to determine whether these changes are related to the splicing process. GC content architecture on the exon–intron structure has changed during evolution, especially during the transition from cold- to warmblooded organisms. The ancestral genome had short introns of low GC cont ...
Natural selection
... the composition of a gene pool increases the probability favorable alleles will come together in the same individual. ...
... the composition of a gene pool increases the probability favorable alleles will come together in the same individual. ...
2014 Genetics Review
... _______________________ A characteristic that can be observed such as hair color, seed shape, flower color, etc _______________________ The joining of a sperm and egg to make a zygote _______________________ A gene choice that MASKS ANOTHER choice for a trait _______________________ A gene choice th ...
... _______________________ A characteristic that can be observed such as hair color, seed shape, flower color, etc _______________________ The joining of a sperm and egg to make a zygote _______________________ A gene choice that MASKS ANOTHER choice for a trait _______________________ A gene choice th ...
Introduction - HobbsAPBiology
... 5. The reappearance of white-flowered plants in the F2 generation indicated that the heritable factor for the white trait was not diluted or “blended” by coexisting with the purple-flower factor in F1 hybrids. 6. Mendel found similar 3 to 1 ratios of two traits among F2 offspring when he conducted c ...
... 5. The reappearance of white-flowered plants in the F2 generation indicated that the heritable factor for the white trait was not diluted or “blended” by coexisting with the purple-flower factor in F1 hybrids. 6. Mendel found similar 3 to 1 ratios of two traits among F2 offspring when he conducted c ...
DNA methylation involved in proline accumulation in - Funpec-RP
... regions of the world. Plant response to drought is a very complex network affecting almost all processes in plant metabolism and development, including water balance, nutrient uptake and metabolism, and photosynthetic assimilation. Plant survival and growth under drought conditions result via adapti ...
... regions of the world. Plant response to drought is a very complex network affecting almost all processes in plant metabolism and development, including water balance, nutrient uptake and metabolism, and photosynthetic assimilation. Plant survival and growth under drought conditions result via adapti ...
cancer_b
... Segregation analysis: discrete traits in families (con’t) Ascertainment bias and correction: sibship data • The way in which families are ascertained can have major effect on the interpretation we make of the data. Example: Ascertain affected children through the school system. Collect data on all ...
... Segregation analysis: discrete traits in families (con’t) Ascertainment bias and correction: sibship data • The way in which families are ascertained can have major effect on the interpretation we make of the data. Example: Ascertain affected children through the school system. Collect data on all ...
16 Simple Patterns of Inheritance
... characters was found in two discrete variants. For example, one character he followed was height, which had the variants known as tall and dwarf. Another was seed color, which had the variants yellow and green. A trait is an identifiable characteristic of an organism. The term trait usually refers t ...
... characters was found in two discrete variants. For example, one character he followed was height, which had the variants known as tall and dwarf. Another was seed color, which had the variants yellow and green. A trait is an identifiable characteristic of an organism. The term trait usually refers t ...
asdfs - Jefferson County Public Schools
... What are the 3 different kinds of inheritance you learned about? Dominant/recessive Incomplete dominance Co-dominance ...
... What are the 3 different kinds of inheritance you learned about? Dominant/recessive Incomplete dominance Co-dominance ...
"Experiments in Plant Hybridization" (1866), by Johann Gregor Mendel
... theory of blending between parental traits, as the offspring of a tall pea plant and a short pea plant yielded not a medium pea plant, but only tall pea plants. From 1856 to 1863, Mendel continued his experiments and noted that the trait of the parent that was missing in an organism from the first g ...
... theory of blending between parental traits, as the offspring of a tall pea plant and a short pea plant yielded not a medium pea plant, but only tall pea plants. From 1856 to 1863, Mendel continued his experiments and noted that the trait of the parent that was missing in an organism from the first g ...
Lecture 16 Notes CH.15
... The Chromosomal Basis for Inheritance: Some inheritance patterns are exceptions to the standard Mendelian inheritance 15.5 The phenotypic effects of some mammalian genes depend on whether they are inherited from the mother or the father Genomic Imprinting: • For a few mammalian traits, the phenotyp ...
... The Chromosomal Basis for Inheritance: Some inheritance patterns are exceptions to the standard Mendelian inheritance 15.5 The phenotypic effects of some mammalian genes depend on whether they are inherited from the mother or the father Genomic Imprinting: • For a few mammalian traits, the phenotyp ...
Mendelian genetics
... The important feature of Mendelian inheritance is that although a recessive allele is hidden in heterozygous individuals by the dominant allele, it is not lost to the population. The heterozygote Aa individual produces on average 1/2 A and 1/2 a gametes. Previous to this, blending inheritance was th ...
... The important feature of Mendelian inheritance is that although a recessive allele is hidden in heterozygous individuals by the dominant allele, it is not lost to the population. The heterozygote Aa individual produces on average 1/2 A and 1/2 a gametes. Previous to this, blending inheritance was th ...
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance

Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance is the transmittance of information from one generation of an organism to the next (e.g., human parent–child transmittance) that affects the traits of offspring without alteration of the primary structure of DNA (i.e., the sequence of nucleotides) or from environmental cues. The less precise term ""epigenetic inheritance"" may be used to describe both cell–cell and organism–organism information transfer. Although these two levels of epigenetic inheritance are equivalent in unicellular organisms, they may have distinct mechanisms and evolutionary distinctions in multicellular organisms.Four general categories of epigenetic modification are known: self-sustaining metabolic loops, in which a mRNA or protein product of a gene stimulates transcription of the gene; e.g. Wor1 gene in Candida albicans structural templating in which structures are replicated using a template or scaffold structure on the parent; e.g. the orientation and architecture of cytoskeletal structures, cilia and flagella, prions, proteins that replicate by changing the structure of normal proteins to match their own chromatin marks, in which methyl or acetyl groups bind to DNA nucleotides or histones thereby altering gene expression patterns; e.g. Lcyc gene in Linaria vulgaris described below RNA silencing, in which small RNA strands interfere (RNAi) with the transcription of DNA or translation of mRNA; known only from a few studies, mostly in Caenorhabditis elegansFor some epigenetically influenced traits, the epigenetic marks can be induced by the environment and some marks are heritable, leading some to view epigenetics as a relaxation of the rejection of soft inheritance of acquired characteristics.