References
... candidates identified here and how their effects on parental and offspring traits are ...
... candidates identified here and how their effects on parental and offspring traits are ...
Biology Partnership - Gulf Coast State College
... Name _______________________________________ Date _____________________ Period _______ ...
... Name _______________________________________ Date _____________________ Period _______ ...
Mendel and his Peas Chapter 5 Lesson 1
... hybrid Science Use the offspring of two animals or plants with different forms of the same trait Common Use having two types of components that perform the same function, such as a vehicle powered by both a gas engine and an electric motor ...
... hybrid Science Use the offspring of two animals or plants with different forms of the same trait Common Use having two types of components that perform the same function, such as a vehicle powered by both a gas engine and an electric motor ...
Paper – III : Cell Biology,Genetics,Ecology and Biodiversity
... (xiii). A pure Rose combed chicken is mated with a pure Pea combed chicken. All the F1 are Walnuts. Cross F1Wulnut with Rose and Pea separately and how phenotypes and genotypes. (xiv). A cross between Rose combed chicken and Walnut combed chicken produced 15 Walnut, 14 Rose, 5 Pea and 6 Single comb ...
... (xiii). A pure Rose combed chicken is mated with a pure Pea combed chicken. All the F1 are Walnuts. Cross F1Wulnut with Rose and Pea separately and how phenotypes and genotypes. (xiv). A cross between Rose combed chicken and Walnut combed chicken produced 15 Walnut, 14 Rose, 5 Pea and 6 Single comb ...
Mendelian Genetics Review
... In horses, one which runs best in water (or in wet conditions) is called (WATER), and one which runs best in dry conditions is called (DRY). (WATER) is recessive to (DRY). A horse can also be either a trotter, which we will designate (GAIT) or a pacer, which we will designate (PACE). (PACE) is reces ...
... In horses, one which runs best in water (or in wet conditions) is called (WATER), and one which runs best in dry conditions is called (DRY). (WATER) is recessive to (DRY). A horse can also be either a trotter, which we will designate (GAIT) or a pacer, which we will designate (PACE). (PACE) is reces ...
Polygenic Traits
... in between. Obviously, Mendel’s rules are too simple to explain the inheritance of human height. Polygenic Traits ...
... in between. Obviously, Mendel’s rules are too simple to explain the inheritance of human height. Polygenic Traits ...
(b). - sandsbiochem
... What are the 3 different kinds of inheritance you learned about? Dominant/recessive Incomplete dominance Co-dominance ...
... What are the 3 different kinds of inheritance you learned about? Dominant/recessive Incomplete dominance Co-dominance ...
(b). - Houston Independent School District
... Original Source: Brookings School District http://local.brookings.k12.sd.us/biology/reviewlink.htm ...
... Original Source: Brookings School District http://local.brookings.k12.sd.us/biology/reviewlink.htm ...
Genetics review
... What are the 3 different kinds of inheritance you learned about? Dominant/recessive Incomplete dominance Co-dominance ...
... What are the 3 different kinds of inheritance you learned about? Dominant/recessive Incomplete dominance Co-dominance ...
Chapter 11 Complex Inheritance and Human Heredity
... Mendel's work was ignored for more than 30 years. During the early 1900s, scientists began to take an interest in hered–ity, and Mendel's work was rediscovered. About this time, Dr. Archibald Garrod, an English physician, became interested in a disorder linked to an enzyme deficiency called alkapton ...
... Mendel's work was ignored for more than 30 years. During the early 1900s, scientists began to take an interest in hered–ity, and Mendel's work was rediscovered. About this time, Dr. Archibald Garrod, an English physician, became interested in a disorder linked to an enzyme deficiency called alkapton ...
Document
... gamete formation, does the segregation of one pair alleles have any affect on the segregation of a different pair of alleles? In other words, does the gene that determines if a pea plant is tall or dwarf have any affect on the gene for seed color? ...
... gamete formation, does the segregation of one pair alleles have any affect on the segregation of a different pair of alleles? In other words, does the gene that determines if a pea plant is tall or dwarf have any affect on the gene for seed color? ...
Chapter 11 Section 11_1 The Work of Gregor Mendel
... • Every living thing has a set of characteristics inherited from its parent or ...
... • Every living thing has a set of characteristics inherited from its parent or ...
Preferential X-chromosome inactivation, DNA
... X chromosome, methylation and imprinting the availability and activity of the methylase. This in turn will depend on the amount of enzyme inherited in the egg cytoplasm, the stability of the maternallyinherited enzyme and the time of onset of activity of the embryonic gene coding for the methylase. ...
... X chromosome, methylation and imprinting the availability and activity of the methylase. This in turn will depend on the amount of enzyme inherited in the egg cytoplasm, the stability of the maternallyinherited enzyme and the time of onset of activity of the embryonic gene coding for the methylase. ...
chapter fourteen
... Every day we observe heritable variations (such as brown, green, or blue eyes) among individuals in a population. ...
... Every day we observe heritable variations (such as brown, green, or blue eyes) among individuals in a population. ...
asdfs
... color, R, is completely dominant to white flower color, r. If the plant is heterozygous for flower color, which alleles will be carried by the gametes it produces? ...
... color, R, is completely dominant to white flower color, r. If the plant is heterozygous for flower color, which alleles will be carried by the gametes it produces? ...
Genetics Part I - Napa Valley College
... If you cross pollinated homozygous purple plants with homozygous white plants (P generation) and the result was offspring that were all purple (F1). Which allele is dominant? ...
... If you cross pollinated homozygous purple plants with homozygous white plants (P generation) and the result was offspring that were all purple (F1). Which allele is dominant? ...
Type of Leopard Gecko Picture Gene
... Looks like Normal, but bigger. Giant Male: 90-109g in first year of life Female: 80-89g in first year of life Supergiant Looks like Normal, but bigger. Male: More than 110g at 1 year old Female: More than 90g at 1 year old Weights for all geckos other than Giant and Supergiant: Male: 70-90g (as adul ...
... Looks like Normal, but bigger. Giant Male: 90-109g in first year of life Female: 80-89g in first year of life Supergiant Looks like Normal, but bigger. Male: More than 110g at 1 year old Female: More than 90g at 1 year old Weights for all geckos other than Giant and Supergiant: Male: 70-90g (as adul ...
Ch 11 Mendelian Patterns of Inheritance
... In 1865, Mendel published his findings in a paper called Experiments on Plant Hybridization, which was mostly ignored at the time due to a number of reasons. First, Mendel was not well known in scientific community. Second, his theory ran against the popular model of blended inheritance. ...
... In 1865, Mendel published his findings in a paper called Experiments on Plant Hybridization, which was mostly ignored at the time due to a number of reasons. First, Mendel was not well known in scientific community. Second, his theory ran against the popular model of blended inheritance. ...
No Slide Title
... color of your skin, hair, and eyes, are the result of several genes acting together. ...
... color of your skin, hair, and eyes, are the result of several genes acting together. ...
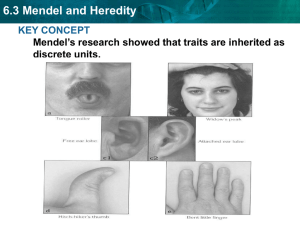
6.3 Mendel and Heredity
... Mendel laid the groundwork for genetics. • Traits are distinguishing characteristics that are inherited. • Genetics is the study of biological inheritance patterns and variation. • Gregor Mendel showed that traits are inherited as discrete units. • Many in Mendel’s day thought traits were blended. ...
... Mendel laid the groundwork for genetics. • Traits are distinguishing characteristics that are inherited. • Genetics is the study of biological inheritance patterns and variation. • Gregor Mendel showed that traits are inherited as discrete units. • Many in Mendel’s day thought traits were blended. ...
Waddington`s Legacy in Development and
... to provide a realistic model of how genes development in relation to evolution. Othreally operate in development and evolu- ers, such as epigenotype, individuation, tion. The dual concepts of canalization and chreod, evocation and homeorhesis, have genetic assimilation were the platform from lasted ...
... to provide a realistic model of how genes development in relation to evolution. Othreally operate in development and evolu- ers, such as epigenotype, individuation, tion. The dual concepts of canalization and chreod, evocation and homeorhesis, have genetic assimilation were the platform from lasted ...
Epigenetic chromatin states uniquely define the developmental
... process that arises from a small pool of self-renewing hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). Upon induction of differentiation, HSCs lose self-renewal ability and develop through a series of specialized progenitor cell types that possess restricted differentiation potential.1 Although several cell-intrin ...
... process that arises from a small pool of self-renewing hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). Upon induction of differentiation, HSCs lose self-renewal ability and develop through a series of specialized progenitor cell types that possess restricted differentiation potential.1 Although several cell-intrin ...
6.3 Mendel and Heredity
... Traits: are distinguishing characteristics that are inherited. Ex: eye color, leaf shape, tail length ...
... Traits: are distinguishing characteristics that are inherited. Ex: eye color, leaf shape, tail length ...
Darwin`s big problem and Mendelian genetics
... − it only works if individuals vary in ways that affect their survival and reproduction − offspring must be similar to their parents, but not exactly the same − if offspring were identical to their parents, they would be identical to each other, and there would be no “more successful” and “less succ ...
... − it only works if individuals vary in ways that affect their survival and reproduction − offspring must be similar to their parents, but not exactly the same − if offspring were identical to their parents, they would be identical to each other, and there would be no “more successful” and “less succ ...
punnett square
... certain traits in offspring that shows the different ways alleles can combine • A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result when certain genes are crossed ...
... certain traits in offspring that shows the different ways alleles can combine • A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result when certain genes are crossed ...
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance

Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance is the transmittance of information from one generation of an organism to the next (e.g., human parent–child transmittance) that affects the traits of offspring without alteration of the primary structure of DNA (i.e., the sequence of nucleotides) or from environmental cues. The less precise term ""epigenetic inheritance"" may be used to describe both cell–cell and organism–organism information transfer. Although these two levels of epigenetic inheritance are equivalent in unicellular organisms, they may have distinct mechanisms and evolutionary distinctions in multicellular organisms.Four general categories of epigenetic modification are known: self-sustaining metabolic loops, in which a mRNA or protein product of a gene stimulates transcription of the gene; e.g. Wor1 gene in Candida albicans structural templating in which structures are replicated using a template or scaffold structure on the parent; e.g. the orientation and architecture of cytoskeletal structures, cilia and flagella, prions, proteins that replicate by changing the structure of normal proteins to match their own chromatin marks, in which methyl or acetyl groups bind to DNA nucleotides or histones thereby altering gene expression patterns; e.g. Lcyc gene in Linaria vulgaris described below RNA silencing, in which small RNA strands interfere (RNAi) with the transcription of DNA or translation of mRNA; known only from a few studies, mostly in Caenorhabditis elegansFor some epigenetically influenced traits, the epigenetic marks can be induced by the environment and some marks are heritable, leading some to view epigenetics as a relaxation of the rejection of soft inheritance of acquired characteristics.