Punnett Square Practice Chapter 9
... dominant over white (r) throats in Goonie birds. Make a cross between a ...
... dominant over white (r) throats in Goonie birds. Make a cross between a ...
Document
... 1. Other research showed that pea hybrids could be produced 2. Many pea varieties were available 3. Peas are small plants and easy to grow 4. Peas can self-fertilize or be cross-fertilized 1.Self-fertilization – male and female parts on same flower so there will be self fertilization if flower not d ...
... 1. Other research showed that pea hybrids could be produced 2. Many pea varieties were available 3. Peas are small plants and easy to grow 4. Peas can self-fertilize or be cross-fertilized 1.Self-fertilization – male and female parts on same flower so there will be self fertilization if flower not d ...
mendelian genetics review questions
... T F 1. Certain acquired characteristics, such as mechanical or mathematical skill, may be inherited. T F 2. Identical twins are always of the same sex. T F 3. Fraternal twins are more closely related to each other than to other children in a family. T F 4. The father determines the sex of a child. T ...
... T F 1. Certain acquired characteristics, such as mechanical or mathematical skill, may be inherited. T F 2. Identical twins are always of the same sex. T F 3. Fraternal twins are more closely related to each other than to other children in a family. T F 4. The father determines the sex of a child. T ...
Heredity
... offspring. Traits like plant height, blossom color, color of peas, and whether the peas were wrinkled or smooth appeared to be passed down from the parent plant to the offspring. Mendel did not know about DNA or chromosomes, and he could not explain how these (8) _______________________ were passed ...
... offspring. Traits like plant height, blossom color, color of peas, and whether the peas were wrinkled or smooth appeared to be passed down from the parent plant to the offspring. Mendel did not know about DNA or chromosomes, and he could not explain how these (8) _______________________ were passed ...
Genetics Notes
... • Mendel would then allow the F1 hybrids to selfpollinate to produce an F2 generation. • It was mainly Mendel’s quantitative analysis of F2 plants that revealed the two fundamental principles of heredity: • the law of segregation ...
... • Mendel would then allow the F1 hybrids to selfpollinate to produce an F2 generation. • It was mainly Mendel’s quantitative analysis of F2 plants that revealed the two fundamental principles of heredity: • the law of segregation ...
sect10.1mendel - MissDavisNHSScience
... Mendel’s Interests and Experiments w/ Pea Plants *Gregor Mendel carried out the first important studies of heredity A. General Terms ...
... Mendel’s Interests and Experiments w/ Pea Plants *Gregor Mendel carried out the first important studies of heredity A. General Terms ...
Chapter 5: Heredity
... a pair of chromosomes separates during meiosis (mi OH sus), alleles for each trait also separate into different sex cells. As a result, every sex cell has one allele for each trait, as shown in Figure 2. The allele in one sex cell may control one form of the trait, such as having facial dimples. The ...
... a pair of chromosomes separates during meiosis (mi OH sus), alleles for each trait also separate into different sex cells. As a result, every sex cell has one allele for each trait, as shown in Figure 2. The allele in one sex cell may control one form of the trait, such as having facial dimples. The ...
A: Chapter 5: Heredity
... a pair of chromosomes separates during meiosis (mi OH sus), alleles for each trait also separate into different sex cells. As a result, every sex cell has one allele for each trait, as shown in Figure 2. The allele in one sex cell may control one form of the trait, such as having facial dimples. The ...
... a pair of chromosomes separates during meiosis (mi OH sus), alleles for each trait also separate into different sex cells. As a result, every sex cell has one allele for each trait, as shown in Figure 2. The allele in one sex cell may control one form of the trait, such as having facial dimples. The ...
A: Chapter 5: Heredity
... a pair of chromosomes separates during meiosis (mi OH sus), alleles for each trait also separate into different sex cells. As a result, every sex cell has one allele for each trait, as shown in Figure 2. The allele in one sex cell may control one form of the trait, such as having facial dimples. The ...
... a pair of chromosomes separates during meiosis (mi OH sus), alleles for each trait also separate into different sex cells. As a result, every sex cell has one allele for each trait, as shown in Figure 2. The allele in one sex cell may control one form of the trait, such as having facial dimples. The ...
PowerPoint Notes
... VI. The Principle of Independent Assortment A. Mendel needed to answer one more question: When alleles are being segregated during gamete formation, does the segregation of one pair alleles have any affect on the segregation of a different pair of alleles? In other words, does the gene that determin ...
... VI. The Principle of Independent Assortment A. Mendel needed to answer one more question: When alleles are being segregated during gamete formation, does the segregation of one pair alleles have any affect on the segregation of a different pair of alleles? In other words, does the gene that determin ...
Biology 1/e
... According to Mendel’s law of segregation, only one of the two alleles for a gene is put into a gamete. At fertilization, offspring receive from each parent one allele for each gene. Heterozygous pea plant ...
... According to Mendel’s law of segregation, only one of the two alleles for a gene is put into a gamete. At fertilization, offspring receive from each parent one allele for each gene. Heterozygous pea plant ...
Chapter 15
... phenotype, there is a 50% chance that each daughter will be a carrier like her mother, and a 50% chance that each son will have the disorder. ...
... phenotype, there is a 50% chance that each daughter will be a carrier like her mother, and a 50% chance that each son will have the disorder. ...
Genetic concepts lab
... Living things contain many genetic characteristics and it is therefore logical to want to design experiments which involve more than one at a time. However, the problem with studying multiple variables is tracing causal factors. In the future, computers may simplify the problem and allow experiments ...
... Living things contain many genetic characteristics and it is therefore logical to want to design experiments which involve more than one at a time. However, the problem with studying multiple variables is tracing causal factors. In the future, computers may simplify the problem and allow experiments ...
Virtual Lab Activity
... parent and selecting parents to cross. The alleles of the selected parents appear next to each box of the Punnett square. Determine the genotype and phenotype of the offspring that result from the genetic cross. Fill in the Punnett square by clicking and dragging the appropriate boxes in the Punnett ...
... parent and selecting parents to cross. The alleles of the selected parents appear next to each box of the Punnett square. Determine the genotype and phenotype of the offspring that result from the genetic cross. Fill in the Punnett square by clicking and dragging the appropriate boxes in the Punnett ...
Exploring Human Traits - University of Hawaii at Hilo
... were able to discover the basic facts of cell division and sexual reproduction. With these new discoveries, scientists began to focus genetics research to understanding how hereditary traits are passed on from parents to their children. Genetics is the branch of science that deals with inheritance o ...
... were able to discover the basic facts of cell division and sexual reproduction. With these new discoveries, scientists began to focus genetics research to understanding how hereditary traits are passed on from parents to their children. Genetics is the branch of science that deals with inheritance o ...
Document
... 7. Mendel used pea plants, because they reproduce quickly / slowly, and he could control how they grow / mate. 8. Mendel bred flowers resulting in F1 generation with dominant / recessive phenotype. He then allowed the F1 generation offspring to self-pollinate. This resulted in an F2 generation with ...
... 7. Mendel used pea plants, because they reproduce quickly / slowly, and he could control how they grow / mate. 8. Mendel bred flowers resulting in F1 generation with dominant / recessive phenotype. He then allowed the F1 generation offspring to self-pollinate. This resulted in an F2 generation with ...
Alien Alleles - Spring Lake Park Schools
... possible phenotypes and genotypes of offspring. Remember, each organism carries two sets of genes (one from each parent). When they reproduce, they pass down one of these two alleles to their offspring. ...
... possible phenotypes and genotypes of offspring. Remember, each organism carries two sets of genes (one from each parent). When they reproduce, they pass down one of these two alleles to their offspring. ...
Complex Inheritance and Human Heredity
... fatal/lethal. It does not occur until between the ages of ...
... fatal/lethal. It does not occur until between the ages of ...
4.11 Repro Biol 053 Reik NEW
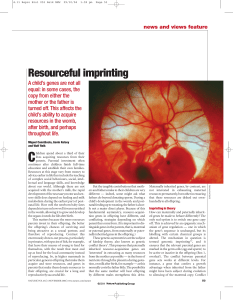
... Figure 2 Effects of imprinted genes on resource acquisition by offspring6. Imprinted genes that are expressed from the maternally derived copy are in purple; those expressed from the paternally derived copy are in blue. a, Growth of the fetus — promoted by, for example, Igf 2, a paternally expressed ...
... Figure 2 Effects of imprinted genes on resource acquisition by offspring6. Imprinted genes that are expressed from the maternally derived copy are in purple; those expressed from the paternally derived copy are in blue. a, Growth of the fetus — promoted by, for example, Igf 2, a paternally expressed ...
Chromosomes, Genes, DNA, Genes Inheritance, Selective Breeding,
... Read the passage below. Use the information in the passage and your own knowledge to answer the questions that follow. ...
... Read the passage below. Use the information in the passage and your own knowledge to answer the questions that follow. ...
X r Y
... controlled by environmental influences. • There are several examples of multifactorial traits. ...
... controlled by environmental influences. • There are several examples of multifactorial traits. ...
Genes are - GZ @ Science Class Online
... the relationship between DNA, alleles, genes, and chromosomes the way in which genotype determines phenotype the way chromosomes exist as pairs so that individuals inherit two copies of each gene. Biological concepts and processes relating to variation in phenotype will be selected from: the ...
... the relationship between DNA, alleles, genes, and chromosomes the way in which genotype determines phenotype the way chromosomes exist as pairs so that individuals inherit two copies of each gene. Biological concepts and processes relating to variation in phenotype will be selected from: the ...
Chapter 10 and 13
... How to Solve Genetics Problems Sample Problem: Mom and dad are heterozygous for tongue rolling where tongue rolling is dominant to non-rolling. What is the chance that the couple will produce a girl that is a non-roller? Use the following steps as a general guide to solve this and other problems: 1. ...
... How to Solve Genetics Problems Sample Problem: Mom and dad are heterozygous for tongue rolling where tongue rolling is dominant to non-rolling. What is the chance that the couple will produce a girl that is a non-roller? Use the following steps as a general guide to solve this and other problems: 1. ...
BSG_Genetics_Notes
... Use the internet to research the following questions. Once everyone on your team has completed each answer, compare and contrast your answers. After your team has compared and contrasted your answers, we will discuss this as a class. 1. Heredity explains a lot about who we are. What is heredity? Her ...
... Use the internet to research the following questions. Once everyone on your team has completed each answer, compare and contrast your answers. After your team has compared and contrasted your answers, we will discuss this as a class. 1. Heredity explains a lot about who we are. What is heredity? Her ...
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance

Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance is the transmittance of information from one generation of an organism to the next (e.g., human parent–child transmittance) that affects the traits of offspring without alteration of the primary structure of DNA (i.e., the sequence of nucleotides) or from environmental cues. The less precise term ""epigenetic inheritance"" may be used to describe both cell–cell and organism–organism information transfer. Although these two levels of epigenetic inheritance are equivalent in unicellular organisms, they may have distinct mechanisms and evolutionary distinctions in multicellular organisms.Four general categories of epigenetic modification are known: self-sustaining metabolic loops, in which a mRNA or protein product of a gene stimulates transcription of the gene; e.g. Wor1 gene in Candida albicans structural templating in which structures are replicated using a template or scaffold structure on the parent; e.g. the orientation and architecture of cytoskeletal structures, cilia and flagella, prions, proteins that replicate by changing the structure of normal proteins to match their own chromatin marks, in which methyl or acetyl groups bind to DNA nucleotides or histones thereby altering gene expression patterns; e.g. Lcyc gene in Linaria vulgaris described below RNA silencing, in which small RNA strands interfere (RNAi) with the transcription of DNA or translation of mRNA; known only from a few studies, mostly in Caenorhabditis elegansFor some epigenetically influenced traits, the epigenetic marks can be induced by the environment and some marks are heritable, leading some to view epigenetics as a relaxation of the rejection of soft inheritance of acquired characteristics.