Chapter 11: From the Crusades to New Muslim Empires (Teacher
... A. You will learn about the Crusades, a series of religious wars launched against ________________________________________________________________________ B. The Crusades began in ____________________________________________ C. _________________ (The Holy Land) was the land between Egypt and Syria 1 ...
... A. You will learn about the Crusades, a series of religious wars launched against ________________________________________________________________________ B. The Crusades began in ____________________________________________ C. _________________ (The Holy Land) was the land between Egypt and Syria 1 ...
The Crusades Documents
... In the year of the Lord 1098, after the region all around Antioch had been wholly devastated by the multitude of our people, the strong as well as the weak were more and more harassed by famine. At that time, the famished ate the shoots of beansweeds growing in the fields and many kids of herbs and ...
... In the year of the Lord 1098, after the region all around Antioch had been wholly devastated by the multitude of our people, the strong as well as the weak were more and more harassed by famine. At that time, the famished ate the shoots of beansweeds growing in the fields and many kids of herbs and ...
1066 Battle of Hastings
... safe and to get it back while the Muslims fought to keep it. These wars lasted nearly 200 years. Pope Urban II called for Christians to fight in the war, stating that those who volunteered would go to heaven and be forgiven for their sins. Red crosses sewn on their tunics they entered a Holy War. It ...
... safe and to get it back while the Muslims fought to keep it. These wars lasted nearly 200 years. Pope Urban II called for Christians to fight in the war, stating that those who volunteered would go to heaven and be forgiven for their sins. Red crosses sewn on their tunics they entered a Holy War. It ...
The Crusades Theme: Mixed reasons for and mixed results of warfare
... • While the Crusades may have largely failed as military adventures, they helped encourage the reintegration of western Europe into the larger economy of the world ...
... • While the Crusades may have largely failed as military adventures, they helped encourage the reintegration of western Europe into the larger economy of the world ...
13-1 The Crusades screencast sheet
... Jerusalem had been ruled by the Roman Empire, then the Byzantine Empire before falling to the ___________ in the 600’s. In the late 1000's the ______________ took over and closed the city to Jewish and Christian pilgrims. The Seljuk Turks also threatened ____________________________________. Thus, t ...
... Jerusalem had been ruled by the Roman Empire, then the Byzantine Empire before falling to the ___________ in the 600’s. In the late 1000's the ______________ took over and closed the city to Jewish and Christian pilgrims. The Seljuk Turks also threatened ____________________________________. Thus, t ...
Crusades
... First Crusade • Crusaders in two groups, peasants and knights • Unskilled peasants answered Pope’s call – Eager to fight non-Christians in Holy Land – On the way attacked and slaughtered German Jews despite protests – Fell to Seljuk Turkish army at Jerusalem ...
... First Crusade • Crusaders in two groups, peasants and knights • Unskilled peasants answered Pope’s call – Eager to fight non-Christians in Holy Land – On the way attacked and slaughtered German Jews despite protests – Fell to Seljuk Turkish army at Jerusalem ...
High Middle Ages
... Alexus I in launching the first Crusade In his 1095 speech to the Council of Clermont in France, Pope Urban II urged Christian princes to embark on a crusade to save the Holy Land from the Turks. He combined the ideas of pilgrimage with waging a holy war against infidels (non believers) He granted C ...
... Alexus I in launching the first Crusade In his 1095 speech to the Council of Clermont in France, Pope Urban II urged Christian princes to embark on a crusade to save the Holy Land from the Turks. He combined the ideas of pilgrimage with waging a holy war against infidels (non believers) He granted C ...
Transcript of Lesson Audio
... The pope also had mixed motives for his support of the Crusades. Urban hoped to increase his power in Europe and perhaps heal to split between the Roman and Byzantine churches. He also hoped that the Crusades would set Christian knights to fighting Muslims instead of one another. The First Crusade – ...
... The pope also had mixed motives for his support of the Crusades. Urban hoped to increase his power in Europe and perhaps heal to split between the Roman and Byzantine churches. He also hoped that the Crusades would set Christian knights to fighting Muslims instead of one another. The First Crusade – ...
File
... Clermont in France Crusader armies marched to Jerusalem sacked several cities on their way. In 1099, they took Jerusalem back from the Muslims and massacred the population of ______________________ and __________________________ there. 2nd Crusade The __________________________ easily defeated ...
... Clermont in France Crusader armies marched to Jerusalem sacked several cities on their way. In 1099, they took Jerusalem back from the Muslims and massacred the population of ______________________ and __________________________ there. 2nd Crusade The __________________________ easily defeated ...
The Crusades and the Wider World
... The Soninke people from west Africa began trading with the Ghana empire The Mayans cleared forests and began to build cities in Central America The Seljuks Turks had taken over Jerusolem (the Holy Land) ...
... The Soninke people from west Africa began trading with the Ghana empire The Mayans cleared forests and began to build cities in Central America The Seljuks Turks had taken over Jerusolem (the Holy Land) ...
content - St George – Kearney
... remainder of 1095 and part of 1096 he traveled throughout France and Germany, preaching about crusade. This served to incite Europeans. Great famine in Europe served as a stimulating backdrop. 6. In 1096 Urban declared it “the will of God that the churches of the West and East be restored”. He appoi ...
... remainder of 1095 and part of 1096 he traveled throughout France and Germany, preaching about crusade. This served to incite Europeans. Great famine in Europe served as a stimulating backdrop. 6. In 1096 Urban declared it “the will of God that the churches of the West and East be restored”. He appoi ...
The Crusades - OnMyCalendar
... successful in capturing Jerusalem and establishing a foothold in Palestine Second Crusade 1147 – 1149 organized to recapture Jerusalem ended in defeat Third Crusade 1189 – 1191 three powerful monarchs, Philip II of France, Frederick I of Germany, and Richard the Lion-hearted of England participated ...
... successful in capturing Jerusalem and establishing a foothold in Palestine Second Crusade 1147 – 1149 organized to recapture Jerusalem ended in defeat Third Crusade 1189 – 1191 three powerful monarchs, Philip II of France, Frederick I of Germany, and Richard the Lion-hearted of England participated ...
The Crusades
... successful in capturing Jerusalem and establishing a foothold in Palestine Second Crusade 1147 – 1149 organized to recapture Jerusalem ended in defeat Third Crusade 1189 – 1191 three powerful monarchs, Philip II of France, Frederick I of Germany, and Richard the Lion-hearted of England participated ...
... successful in capturing Jerusalem and establishing a foothold in Palestine Second Crusade 1147 – 1149 organized to recapture Jerusalem ended in defeat Third Crusade 1189 – 1191 three powerful monarchs, Philip II of France, Frederick I of Germany, and Richard the Lion-hearted of England participated ...
The Crusades
... successful in capturing Jerusalem and establishing a foothold in Palestine Second Crusade 1147 – 1149 organized to recapture Jerusalem ended in defeat Third Crusade 1189 – 1191 three powerful monarchs, Philip II of France, Frederick I of Germany, and Richard the Lion-hearted of England participated ...
... successful in capturing Jerusalem and establishing a foothold in Palestine Second Crusade 1147 – 1149 organized to recapture Jerusalem ended in defeat Third Crusade 1189 – 1191 three powerful monarchs, Philip II of France, Frederick I of Germany, and Richard the Lion-hearted of England participated ...
The Crusades - Mr. Kelleher
... dislodge the Muslims from the Holy Land. • Also, it was during this time period that the Catholic Church, led by the pope, had tremendous political influence which was used to pressure various kings, etc., to seek the church’s favor. ...
... dislodge the Muslims from the Holy Land. • Also, it was during this time period that the Catholic Church, led by the pope, had tremendous political influence which was used to pressure various kings, etc., to seek the church’s favor. ...
Crusades overview
... Pope Urban II called upon the knights of Christendom to push back the conquests of Islam at the Council of Clermont in 1095. The response was tremendous. Many thousands of warriors took the vow of the cross and prepared for war. Why did they do it? During the past two decades, computer-assisted char ...
... Pope Urban II called upon the knights of Christendom to push back the conquests of Islam at the Council of Clermont in 1095. The response was tremendous. Many thousands of warriors took the vow of the cross and prepared for war. Why did they do it? During the past two decades, computer-assisted char ...
Was the Crusades a successful failure?
... Jerusalem was retaken by the Muslims led by Saladin • Third Crusade -1189, also known as the Kings Crusade, Frederick Barbarossa of Germany, Philip Augustus of France, and Richard the Lion Hearted of England • Other Crusades failed to establish the Christian rule in Palestine. The Muslim Turks contr ...
... Jerusalem was retaken by the Muslims led by Saladin • Third Crusade -1189, also known as the Kings Crusade, Frederick Barbarossa of Germany, Philip Augustus of France, and Richard the Lion Hearted of England • Other Crusades failed to establish the Christian rule in Palestine. The Muslim Turks contr ...
File
... Having experienced the luxuries of the East, many Europeans returned home with a desire to possess more of the rich goods they had seen. They brought back rugs, silks, spices, camphor, musk, ivory, and pearls. This desire made trade and commerce necessary. Hundreds of Italian merchants settled in As ...
... Having experienced the luxuries of the East, many Europeans returned home with a desire to possess more of the rich goods they had seen. They brought back rugs, silks, spices, camphor, musk, ivory, and pearls. This desire made trade and commerce necessary. Hundreds of Italian merchants settled in As ...
The Crusades - 8 Erin Online Classroom 2013
... the Crusades - a meeting of noble warriors on both sides who respected each other. 20th century writers, however, tended to condemn the Crusades as 'violent white colonialism' for which Christians needed to ask forgiveness. Some historians have compared the attempts to conquer kingdoms in the Holy L ...
... the Crusades - a meeting of noble warriors on both sides who respected each other. 20th century writers, however, tended to condemn the Crusades as 'violent white colonialism' for which Christians needed to ask forgiveness. Some historians have compared the attempts to conquer kingdoms in the Holy L ...
Crusades
... → Byzantine emperor, Alexius I, asks Pope Urban II for knights to help him fight Muslim Turks in 1095 …although they have been rivals (Great Schism), Urban agrees → Pope Urban II uses this as an opportunity to reclaim Jerusalem & the Holy Land …not to necessarily aid the Byzantines …calls for all Eu ...
... → Byzantine emperor, Alexius I, asks Pope Urban II for knights to help him fight Muslim Turks in 1095 …although they have been rivals (Great Schism), Urban agrees → Pope Urban II uses this as an opportunity to reclaim Jerusalem & the Holy Land …not to necessarily aid the Byzantines …calls for all Eu ...
The Crusades Pages 326-331
... back Asian goods, resulting in increased trade. These goods included spices, furs, cloth, cane sugar, rice, and different fruits. Increased trade across the Mediterranean helped European towns to grow and made the role of urban merchants more important. Another legacy of the Crusades was rising Chri ...
... back Asian goods, resulting in increased trade. These goods included spices, furs, cloth, cane sugar, rice, and different fruits. Increased trade across the Mediterranean helped European towns to grow and made the role of urban merchants more important. Another legacy of the Crusades was rising Chri ...
Crusades - Mr. L. Goldsack
... • Christ Burial Shroud (cloth that covered Christ in tomb) • Cross (Christ’s) Pieces scattered all throughout the world • and many others ...
... • Christ Burial Shroud (cloth that covered Christ in tomb) • Cross (Christ’s) Pieces scattered all throughout the world • and many others ...
CHAPTER 11: From the Crusades to New Muslim Empires
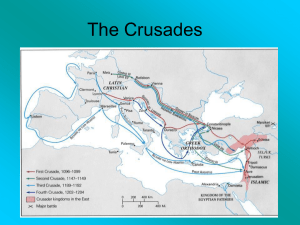
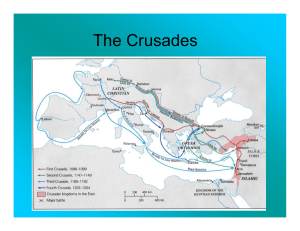
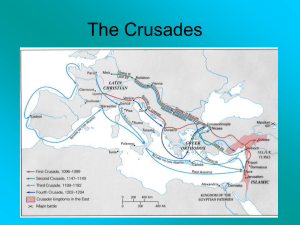
... Close to 30,000 crusaders fought their way through Anatolia and headed south toward Palestine The crusaders laid siege to the city of Antioch in Syria o After 9 months, a traitor let them through a opening in the city walls City fell to the Christians The next year, the crusaders surrounded Je ...
... Close to 30,000 crusaders fought their way through Anatolia and headed south toward Palestine The crusaders laid siege to the city of Antioch in Syria o After 9 months, a traitor let them through a opening in the city walls City fell to the Christians The next year, the crusaders surrounded Je ...
Document
... c. 1095 Pope Urban II calls for the crusades or holy wars d. Pope Urban II hoped to use this to reunite the eastern and western empires e. The main goal of the Crusades was to regain the Holy Land II. Why did people join? a. The Pope guaranteed them all salvation b. The promise of glory, land and ri ...
... c. 1095 Pope Urban II calls for the crusades or holy wars d. Pope Urban II hoped to use this to reunite the eastern and western empires e. The main goal of the Crusades was to regain the Holy Land II. Why did people join? a. The Pope guaranteed them all salvation b. The promise of glory, land and ri ...
First Crusade

The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a number of crusades that attempted to capture the Holy Lands, called by Pope Urban II in 1095. It started as a widespread pilgrimage in western christendom and ended as a military expedition by Roman Catholic Europe to regain the Holy Lands taken in the Muslim conquests of the Levant (632–661), ultimately resulting in the recapture of Jerusalem in 1099. It was launched on 27 November 1095 by Pope Urban II with the primary goal of responding to an appeal from Byzantine Emperor Alexios I Komnenos, who requested that western volunteers come to his aid and help to repel the invading Seljuq Turks from Anatolia. An additional goal soon became the principal objective—the Christian reconquest of the sacred city of Jerusalem and the Holy Land and the freeing of the Eastern Christians from Muslim rule.During the crusade, knights, peasants and serfs from many nations of Western Europe travelled over land and by sea, first to Constantinople and then on towards Jerusalem. The Crusaders arrived at Jerusalem, launched an assault on the city, and captured it in July 1099, massacring many of the city's Muslim, Christian, and Jewish inhabitants. They also established the crusader states of the Kingdom of Jerusalem, the County of Tripoli, the Principality of Antioch, and the County of Edessa.The First Crusade was followed by the Second to the Ninth Crusades. It was also the first major step towards reopening international trade in the West since the fall of the Western Roman Empire. Because the First Crusade was largely concerned with Jerusalem, a city which had not been under Christian dominion for 461 years, and the crusader army had refused to return the land to the control of the Byzantine Empire, the status of the First Crusade as defensive or as aggressive in nature remains controversial.