Ecology: the study of interrelationships between organisms and their
... common ancestor • Analogy = similarity in function not due to a common ancestor • DNA comparison ...
... common ancestor • Analogy = similarity in function not due to a common ancestor • DNA comparison ...
Cell Wall
... Other bacteria in the mouth become trapped in the slime and form a biofilm & eventually a buildup of plaque. Staphylococcus The slime layer of Gram+ Staphylococcus allows it to thrive in the salty, hypertonic environment of the skin. Glycocalyces are not specific to Gram+ or Gram- bacteria, sometime ...
... Other bacteria in the mouth become trapped in the slime and form a biofilm & eventually a buildup of plaque. Staphylococcus The slime layer of Gram+ Staphylococcus allows it to thrive in the salty, hypertonic environment of the skin. Glycocalyces are not specific to Gram+ or Gram- bacteria, sometime ...
Name
... Cell wall – a rigid (stiff) structure on the outside of some cells that supports and protects the cell ...
... Cell wall – a rigid (stiff) structure on the outside of some cells that supports and protects the cell ...
Recitation 1 Solutions
... Classify each of the above organisms as unicellular or multi-cellular. Bacterial and yeast cells are unicellular whereas flies, mice and rabbits are multi-cellular. 2. You are given three different cell types, each stained with a dye that specifically binds to deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). You observ ...
... Classify each of the above organisms as unicellular or multi-cellular. Bacterial and yeast cells are unicellular whereas flies, mice and rabbits are multi-cellular. 2. You are given three different cell types, each stained with a dye that specifically binds to deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). You observ ...
Cell Transport
... 5. Understand that a CONCENTRATION GRADIENT exists whenever there is a difference in the quantity of liquid or gas molecules. Diffusion occurs down the concentration gradient. 6. Explain that USEFUL substances (glucose, oxygen, amino acids, fatty acids) ENTER the cell and WASTE substances (carbon di ...
... 5. Understand that a CONCENTRATION GRADIENT exists whenever there is a difference in the quantity of liquid or gas molecules. Diffusion occurs down the concentration gradient. 6. Explain that USEFUL substances (glucose, oxygen, amino acids, fatty acids) ENTER the cell and WASTE substances (carbon di ...
6 Active Transport 0809
... becomes a membrane bound organelle called a vesicle Vesicles can fuse with lysosomes to digests contents. Two kinds of Endocytosis: ...
... becomes a membrane bound organelle called a vesicle Vesicles can fuse with lysosomes to digests contents. Two kinds of Endocytosis: ...
A theory on the Origins of Eukaryotic Cells
... both she and the theory were ridiculed by mainstream biologists for a number of years. Thanks to her persistance, and the large volumes of data that support this hypothesis gathered by her and many other scientists over the last 30 years, biology can now offer a plausible explanation for the evoluti ...
... both she and the theory were ridiculed by mainstream biologists for a number of years. Thanks to her persistance, and the large volumes of data that support this hypothesis gathered by her and many other scientists over the last 30 years, biology can now offer a plausible explanation for the evoluti ...
Chapter 17: The History and Diversity of Life
... Called “true” bacteria because they have a thick, rigid cell wall made of the carbohydrate peptidoglycan Very diverse, some photosynthetic ...
... Called “true” bacteria because they have a thick, rigid cell wall made of the carbohydrate peptidoglycan Very diverse, some photosynthetic ...
2.3: Eukaryotic Evolution and Diversity pg. 67 For about 1.5 billion
... One cell engulfs a different type of cell. The engulf cell survives and becomes an internal part of the engulfing cell. Prokaryotes do not have membrane bond organelles, yet eukaryotes have membrane bond organelles. These organelles may have been ancestors of once free-living prokaryotes. There are ...
... One cell engulfs a different type of cell. The engulf cell survives and becomes an internal part of the engulfing cell. Prokaryotes do not have membrane bond organelles, yet eukaryotes have membrane bond organelles. These organelles may have been ancestors of once free-living prokaryotes. There are ...
Bacteria Notes - Sardis Secondary
... • Video clip 4. Transformation (sexual) • Bacteria cells that pick up DNA from dead bacteria cells Video clip ...
... • Video clip 4. Transformation (sexual) • Bacteria cells that pick up DNA from dead bacteria cells Video clip ...
Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
... There is a basic cell structure that is present in many but not all living cells: the nucleus. The nucleus of a cell is a structure in the cytoplasm that is surrounded by a membrane (the nuclear membrane) and contains DNA. Based on whether they have a nucleus, there are two basic types of cells: pro ...
... There is a basic cell structure that is present in many but not all living cells: the nucleus. The nucleus of a cell is a structure in the cytoplasm that is surrounded by a membrane (the nuclear membrane) and contains DNA. Based on whether they have a nucleus, there are two basic types of cells: pro ...
CELLS & the ORGANELLES
... – Usually smaller, simple – No membrane bound parts (organelles) – Ex: bacteria ...
... – Usually smaller, simple – No membrane bound parts (organelles) – Ex: bacteria ...
Section 3 - HCABIOLOGY
... 9. The difference in the concentration of dissolved particles from one location to another is called a. concentration gradient b. concentrated solution c. saline solution d. dynamic gradient 10. Diffusion results from a. the energy produced by the cell. b. the natural motion of particles c. transpor ...
... 9. The difference in the concentration of dissolved particles from one location to another is called a. concentration gradient b. concentrated solution c. saline solution d. dynamic gradient 10. Diffusion results from a. the energy produced by the cell. b. the natural motion of particles c. transpor ...
Cell Communication
... Cell Signaling Activity- 25 pts. • Each person selects one activity to complete: – Create a comic strip demonstrating either cell-to-cell contact OR an example of distance signaling. Comic must be informational. – Writing! Write about a time when one action triggered a chain of events. Describe the ...
... Cell Signaling Activity- 25 pts. • Each person selects one activity to complete: – Create a comic strip demonstrating either cell-to-cell contact OR an example of distance signaling. Comic must be informational. – Writing! Write about a time when one action triggered a chain of events. Describe the ...
Chapter 27: Bacteria and Archaea Reading Guide Overview The
... 17. You should now have some idea why there is so much potential for genetic diversity with bacterial populations. Although mutation is the major source of genetic variation in prokaryotes, explain each of the following three other sources of variation: (A) recombination, (B) transformation, and (C) ...
... 17. You should now have some idea why there is so much potential for genetic diversity with bacterial populations. Although mutation is the major source of genetic variation in prokaryotes, explain each of the following three other sources of variation: (A) recombination, (B) transformation, and (C) ...
Surrounded By Microbes
... Archaebacteria can be found everywhere even in extreme environments such as hot springs or waters with sulfur or high salinity. ...
... Archaebacteria can be found everywhere even in extreme environments such as hot springs or waters with sulfur or high salinity. ...
Slide ()
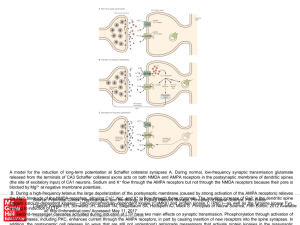
... A model for the induction of long-term potentiation at Schaffer collateral synapses A. During normal, low-frequency synaptic transmission glutamate released from the terminals of CA3 Schaffer collateral axons acts on both NMDA and AMPA receptors in the postsynaptic membrane of dendritic spines (the ...
... A model for the induction of long-term potentiation at Schaffer collateral synapses A. During normal, low-frequency synaptic transmission glutamate released from the terminals of CA3 Schaffer collateral axons acts on both NMDA and AMPA receptors in the postsynaptic membrane of dendritic spines (the ...
Chapter 3
... • Actin interacts with motor molecules such as myosin. • In the presence of ATP, myosin pulls actin along • Example: muscle cells ...
... • Actin interacts with motor molecules such as myosin. • In the presence of ATP, myosin pulls actin along • Example: muscle cells ...
Introduction to Microbiology
... undefined nuclear region in the cytoplasm is called nucleoid. A prokaryotic cell has three architectural regions: • On the outside, flagelig and pilli project from the cell’s surface. These are structures (not present in all prokaryotes) made of proteins that facilitate movement and communication be ...
... undefined nuclear region in the cytoplasm is called nucleoid. A prokaryotic cell has three architectural regions: • On the outside, flagelig and pilli project from the cell’s surface. These are structures (not present in all prokaryotes) made of proteins that facilitate movement and communication be ...
sol5_5
... • 1 It is easy to identify a bacteria cell under the microscope because it doesn’t haveA B C D ...
... • 1 It is easy to identify a bacteria cell under the microscope because it doesn’t haveA B C D ...
LS CH 9 SEC 2 PWR PT
... • KEY- THERE ARE TWO WAYS IN WHICH BACTERIA CAN REPRODUCE • 1. ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION- A PROCESS THAT INVOLVES ONLY ONE PARENT AND PRODUCES OFFSPRING THAT ARE IDENTICAL TO PARENT. • 2. SEXUAL REPRODUCTION- TWO PARENTS COMBINE THEIR GENETIC MATERIAL TO PRODUCE A NEW ORGANISM WHICH DIFFERS FROM BOTH PAR ...
... • KEY- THERE ARE TWO WAYS IN WHICH BACTERIA CAN REPRODUCE • 1. ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION- A PROCESS THAT INVOLVES ONLY ONE PARENT AND PRODUCES OFFSPRING THAT ARE IDENTICAL TO PARENT. • 2. SEXUAL REPRODUCTION- TWO PARENTS COMBINE THEIR GENETIC MATERIAL TO PRODUCE A NEW ORGANISM WHICH DIFFERS FROM BOTH PAR ...
“Endo-“ = “Symbiotic”
... Scientists think that protists are the oldest eukaryotes. If so, they must have evolved from prokaryotic cells. How did this happen? The endosymbiotic theory provides the most widely accepted explanation. That’s because it is well supported by evidence. The First Eukaryotic Cells According to the en ...
... Scientists think that protists are the oldest eukaryotes. If so, they must have evolved from prokaryotic cells. How did this happen? The endosymbiotic theory provides the most widely accepted explanation. That’s because it is well supported by evidence. The First Eukaryotic Cells According to the en ...
Ribbons of Life
... Organisms that have moved onto dry land have to maintain systems that keep all their cells surrounded by fluid. Plants and animals transport water through vascular systems and circulatory systems to ensure that the aquatic environment is ...
... Organisms that have moved onto dry land have to maintain systems that keep all their cells surrounded by fluid. Plants and animals transport water through vascular systems and circulatory systems to ensure that the aquatic environment is ...
Quiz5ch5new.doc
... molecules from __________. a. an area of higher concentration of that type of molecule to an area of lower concentration b. an area of lower concentration of that type of molecule to an area of higher concentration c. outside the cell to inside the cell ...
... molecules from __________. a. an area of higher concentration of that type of molecule to an area of lower concentration b. an area of lower concentration of that type of molecule to an area of higher concentration c. outside the cell to inside the cell ...
Chemotaxis

Chemotaxis (from chemo- + taxis) is the movement of an organism in response to a chemical stimulus. Somatic cells, bacteria, and other single-cell or multicellular organisms direct their movements according to certain chemicals in their environment. This is important for bacteria to find food (e.g., glucose) by swimming toward the highest concentration of food molecules, or to flee from poisons (e.g., phenol). In multicellular organisms, chemotaxis is critical to early development (e.g., movement of sperm towards the egg during fertilization) and subsequent phases of development (e.g., migration of neurons or lymphocytes) as well as in normal function. In addition, it has been recognized that mechanisms that allow chemotaxis in animals can be subverted during cancer metastasis.Positive chemotaxis occurs if the movement is toward a higher concentration of the chemical in question; negative chemotaxis if the movement is in the opposite direction. Chemically prompted kinesis (randomly directed or nondirectional) can be called chemokinesis.