Cell-Theory-and-Structure-reduced-photos-for
... Cells are the smallest living things Cells arise only from pre-existing cells All cells today represent a continuous line of descent from the first living cells ...
... Cells are the smallest living things Cells arise only from pre-existing cells All cells today represent a continuous line of descent from the first living cells ...
Chapter 3: Cells
... is made primarily from the carbohydrate cellulose and it surrounds the plasma membrane of a plant cell. ...
... is made primarily from the carbohydrate cellulose and it surrounds the plasma membrane of a plant cell. ...
Requirements for microbial growth are divided into two categories
... physical and chemical. Physical aspects include temperature, pH, and osmotic pressure. Chemical requirements include water, sources of carbon and nitrogen, minerals, oxygen, and organic growth factors. A. Temperature: most microbes live within restricted ranges of temperature with a Range of Toleran ...
... physical and chemical. Physical aspects include temperature, pH, and osmotic pressure. Chemical requirements include water, sources of carbon and nitrogen, minerals, oxygen, and organic growth factors. A. Temperature: most microbes live within restricted ranges of temperature with a Range of Toleran ...
SHRIMATI INDIRA GANDHI COLLEGE
... Isolation of fungi; Soil sample is collected Serial dilution is performed It is plated on rose Bengal agar or potato dextrose agar. Then it is incubated on 37ºc for 4 days The colonies are formed. 5. What is carboxysomes&PHB & capsules? These are present in autotrophic bacteria.these are polyhedrica ...
... Isolation of fungi; Soil sample is collected Serial dilution is performed It is plated on rose Bengal agar or potato dextrose agar. Then it is incubated on 37ºc for 4 days The colonies are formed. 5. What is carboxysomes&PHB & capsules? These are present in autotrophic bacteria.these are polyhedrica ...
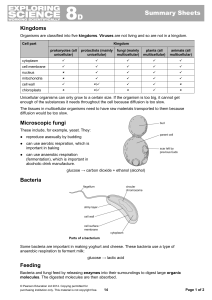
8D Unicellular Organisms
... Unicellular organisms can only grow to a certain size. If the organism is too big, it cannot get enough of the substances it needs throughout the cell because diffusion is too slow. The tissues in multicellular organisms need to have raw materials transported to them because diffusion would be too s ...
... Unicellular organisms can only grow to a certain size. If the organism is too big, it cannot get enough of the substances it needs throughout the cell because diffusion is too slow. The tissues in multicellular organisms need to have raw materials transported to them because diffusion would be too s ...
Differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
... DNA-related functions of the large cell in a smaller enclosure to ensure close proximity of materials and increased efficiency for cellular communication and functions. In contrast, the smaller prokaryotic cells have no nucleus. The materials are already fairly close to each other and there is only ...
... DNA-related functions of the large cell in a smaller enclosure to ensure close proximity of materials and increased efficiency for cellular communication and functions. In contrast, the smaller prokaryotic cells have no nucleus. The materials are already fairly close to each other and there is only ...
Lymphatic System and Immunity Levels of Organization
... Your exploration of immunity in the following modules will extend from the simplest to the most complex. Although the levels of organization are introduced in modules, the functional interconnections between the organizational levels will build throughout the development of modules within this unit. ...
... Your exploration of immunity in the following modules will extend from the simplest to the most complex. Although the levels of organization are introduced in modules, the functional interconnections between the organizational levels will build throughout the development of modules within this unit. ...
Helpful Bacteria - Dr. Annette M. Parrott
... • The bacterial cells are first stained with crystal violet. then treated with alcohol or acetone, whichwashes the stain out of gram-negative cells and then counterstained. • Bacteria that are not decolorized by the alcohol/acetone wash are ...
... • The bacterial cells are first stained with crystal violet. then treated with alcohol or acetone, whichwashes the stain out of gram-negative cells and then counterstained. • Bacteria that are not decolorized by the alcohol/acetone wash are ...
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM:
... A form of reproduction when a single celled organism splits into two single celled organisms. Steps of Binary Fission: 1. Cell Grows 2. DNA Copies 3. DNA Separates 4. Cell Separates ...
... A form of reproduction when a single celled organism splits into two single celled organisms. Steps of Binary Fission: 1. Cell Grows 2. DNA Copies 3. DNA Separates 4. Cell Separates ...
Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote Worksheet
... Read the passage below. Then answer the questions that follow. ...
... Read the passage below. Then answer the questions that follow. ...
prokaryote vs eukaryote worksheet
... Read the passage below. Then answer the questions that follow. ...
... Read the passage below. Then answer the questions that follow. ...
Chapter 5 Sanitation Hazards
... aerobic bacteria. Bacteria that require oxygen. allergy. When the body interprets a normally harmless protein as a dangerous substance and the body’s immune system then reacts to fight it. anaerobic bacteria. Bacteria that thrive without oxygen. bacteria. Single-celled organisms that reproduce by di ...
... aerobic bacteria. Bacteria that require oxygen. allergy. When the body interprets a normally harmless protein as a dangerous substance and the body’s immune system then reacts to fight it. anaerobic bacteria. Bacteria that thrive without oxygen. bacteria. Single-celled organisms that reproduce by di ...
Active Reading Section: Introduction to Cells
... Read the passage below. Then answer the questions that follow. ...
... Read the passage below. Then answer the questions that follow. ...
Chapter 4
... The flagellum has 3 basic parts: filament is the long, outermost region; a hook attaches to the filament; the basal body, which anchors the flagellum to the cell wall and plasma membrane The basal body is a small central rod inserted into a series of rings In gram negative bacteria, there are two pa ...
... The flagellum has 3 basic parts: filament is the long, outermost region; a hook attaches to the filament; the basal body, which anchors the flagellum to the cell wall and plasma membrane The basal body is a small central rod inserted into a series of rings In gram negative bacteria, there are two pa ...
Cell Structure and Function
... Mitochondria • Two main stages of cellular respiration, the Kreb’s Cycle and the Electron Transport Chain, occur in the mitochondria in order to transform energy from the food that organisms eat into chemical energy in the bonds of ATP. ...
... Mitochondria • Two main stages of cellular respiration, the Kreb’s Cycle and the Electron Transport Chain, occur in the mitochondria in order to transform energy from the food that organisms eat into chemical energy in the bonds of ATP. ...
File
... rigid bodies. Another group of spirals are helical and flexible; they are called Spirochetes. Unlike the spirilla, which use external appendages called flagella to move, spirochetes move by means of axial filaments, which resemble flagella but are contained within a flexible external sheath. ...
... rigid bodies. Another group of spirals are helical and flexible; they are called Spirochetes. Unlike the spirilla, which use external appendages called flagella to move, spirochetes move by means of axial filaments, which resemble flagella but are contained within a flexible external sheath. ...
23.11.2012
... using the IgE to highafinity Fc receptor for IgE (FceRI) aggregation of several molecules FceRI initiate mast cell degranulation (cytoplasmic granules mergers with the surface membrane and release their contents) activation of arachidonic acid metabolism (leukotriene C4, prostaglandin PGD2) - am ...
... using the IgE to highafinity Fc receptor for IgE (FceRI) aggregation of several molecules FceRI initiate mast cell degranulation (cytoplasmic granules mergers with the surface membrane and release their contents) activation of arachidonic acid metabolism (leukotriene C4, prostaglandin PGD2) - am ...
Cell communication
... - cholesterol (animal cells) reduces membrane fluidity; helps stabilize the membrane ...
... - cholesterol (animal cells) reduces membrane fluidity; helps stabilize the membrane ...
AP Biology Study Guide Name____________________ Per
... 7. Describe the structure of cilia and flagella and how these structures allow for cell movement. 8. Describe the various types of cell junctions in both plant and animal cells. ...
... 7. Describe the structure of cilia and flagella and how these structures allow for cell movement. 8. Describe the various types of cell junctions in both plant and animal cells. ...
Psychology of Food Choice
... WAYS LIVING THINGS GET THEIR ENERGY (nutrition) • Some are photosynthetic • Make their own food by using the sun’s light • Examples? ...
... WAYS LIVING THINGS GET THEIR ENERGY (nutrition) • Some are photosynthetic • Make their own food by using the sun’s light • Examples? ...
int cells la - About Mrs. Telfort
... Read the questions below. Highlight the answers within the text of the reading passage below, hen answer the questions in your own words. ...
... Read the questions below. Highlight the answers within the text of the reading passage below, hen answer the questions in your own words. ...
Gabby Melanson
... presence of hair-like organelles called cilia. Another word/name for Ciliophora is Paramecium. ...
... presence of hair-like organelles called cilia. Another word/name for Ciliophora is Paramecium. ...
Chemotaxis

Chemotaxis (from chemo- + taxis) is the movement of an organism in response to a chemical stimulus. Somatic cells, bacteria, and other single-cell or multicellular organisms direct their movements according to certain chemicals in their environment. This is important for bacteria to find food (e.g., glucose) by swimming toward the highest concentration of food molecules, or to flee from poisons (e.g., phenol). In multicellular organisms, chemotaxis is critical to early development (e.g., movement of sperm towards the egg during fertilization) and subsequent phases of development (e.g., migration of neurons or lymphocytes) as well as in normal function. In addition, it has been recognized that mechanisms that allow chemotaxis in animals can be subverted during cancer metastasis.Positive chemotaxis occurs if the movement is toward a higher concentration of the chemical in question; negative chemotaxis if the movement is in the opposite direction. Chemically prompted kinesis (randomly directed or nondirectional) can be called chemokinesis.