Volcano Stations Answers
... ◦ Layers of lava form repeated non-explosive eruptions build up ◦ Lava is runny creating a volcano with gently sloping sides ◦ Hawaii’s Mauna Kea volcano is the tallest mountain on earth if you measure it from the sea floor to the top (taller than Everest) ...
... ◦ Layers of lava form repeated non-explosive eruptions build up ◦ Lava is runny creating a volcano with gently sloping sides ◦ Hawaii’s Mauna Kea volcano is the tallest mountain on earth if you measure it from the sea floor to the top (taller than Everest) ...
Warm up question What hypothesis is Alfred Wegener known for
... ash – materials less than 2mm; worldwide Volcanic dust – materials less than 0.25mm; same Lapilli – materials less than 64mm – fall near vent Volcanic bombs – red hot lava that cools in the air Volcanic blocks – solid rock blasted from the fissure, can be as big as a house ...
... ash – materials less than 2mm; worldwide Volcanic dust – materials less than 0.25mm; same Lapilli – materials less than 64mm – fall near vent Volcanic bombs – red hot lava that cools in the air Volcanic blocks – solid rock blasted from the fissure, can be as big as a house ...
Lab 5 Lecture
... Crater Lake was formed after Mt Mazama (a stratovolcano) erupted and collapsed back in on itself. ...
... Crater Lake was formed after Mt Mazama (a stratovolcano) erupted and collapsed back in on itself. ...
Shapes of igneous bodies
... Feeder dikes (regional extension - MOR) Flood basalts Extrusive bodies – Pyroclastic Landforms Pyroclastic Deposits include – volcaniclastic – formed by volcano (process irrelevant) - pyroclastic – formed from magma/lava aerially expelled from vent - lahar – volcanic debris mixed with water/melting ...
... Feeder dikes (regional extension - MOR) Flood basalts Extrusive bodies – Pyroclastic Landforms Pyroclastic Deposits include – volcaniclastic – formed by volcano (process irrelevant) - pyroclastic – formed from magma/lava aerially expelled from vent - lahar – volcanic debris mixed with water/melting ...
Unit 4 Chapter 13
... Cinder Cone A cinder cone happens when molten lava spewed from a vent piled up. It is the smallest of the volcanoes, formed by larger ones. It has a sloped angle that can be as much as 40o ...
... Cinder Cone A cinder cone happens when molten lava spewed from a vent piled up. It is the smallest of the volcanoes, formed by larger ones. It has a sloped angle that can be as much as 40o ...
Chapter 9 - Volcanoes
... • Crater – A funnel shaped pit at the top of many volcanoes. • Caldera – A large depression formed after the eruption and much larger than the crater. A crater with collapsed walls. • Lava Plateaus – Formed by repeated eruptions with massive outpourings of lava spreading out over a large area. These ...
... • Crater – A funnel shaped pit at the top of many volcanoes. • Caldera – A large depression formed after the eruption and much larger than the crater. A crater with collapsed walls. • Lava Plateaus – Formed by repeated eruptions with massive outpourings of lava spreading out over a large area. These ...
VOLCANOES
... • Eight main islands are exposed tips of the Hawaiian Ridge. • Age range is modern to ~6 million years old. • Volcanoes develop on the Pacific Plate as it moves across the Hawaiian Hotspot. ...
... • Eight main islands are exposed tips of the Hawaiian Ridge. • Age range is modern to ~6 million years old. • Volcanoes develop on the Pacific Plate as it moves across the Hawaiian Hotspot. ...
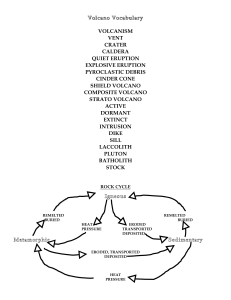
The Rock cycle: Initially proposed by James Hutton
... Describe the processes that change the composition of magma Bowen’s Reaction Series: Minerals crystallize at different temps. Mafic mineras crystalize at hotter temps. Felsic at cooler. So the mafic minerals crystallize and settle to the bottom of the magma chamber, leaving the rest of the magma mo ...
... Describe the processes that change the composition of magma Bowen’s Reaction Series: Minerals crystallize at different temps. Mafic mineras crystalize at hotter temps. Felsic at cooler. So the mafic minerals crystallize and settle to the bottom of the magma chamber, leaving the rest of the magma mo ...
Shield Volcano
... Cinder Cone Volcano • Cinder cones are the smallest volcanoes (< 500 ft), formed by explosive eruptions of explosive lava, and can form near other volcanoes (How does it form?) • Blown violently into the air, the erupting lava breaks apart into fragments called cinders that fall and accumulate arou ...
... Cinder Cone Volcano • Cinder cones are the smallest volcanoes (< 500 ft), formed by explosive eruptions of explosive lava, and can form near other volcanoes (How does it form?) • Blown violently into the air, the erupting lava breaks apart into fragments called cinders that fall and accumulate arou ...
Chapter 10
... Chapter 10 Section 1 1. Viscosity= A measure of fluid’s substance to flow 2. Vent= A opening in the surface of earth through which molten rock and gases are released 3. Pyroclastic Material= Volcanic rock during an eruption, including ash, bombs, and blocks 4. Volcano= A mountain formed of lava and/ ...
... Chapter 10 Section 1 1. Viscosity= A measure of fluid’s substance to flow 2. Vent= A opening in the surface of earth through which molten rock and gases are released 3. Pyroclastic Material= Volcanic rock during an eruption, including ash, bombs, and blocks 4. Volcano= A mountain formed of lava and/ ...
Directions: Read the information below. Use this information and
... volcanoes and shield volcanoes. Cinder cones are built from lava fragments called cinders. The lava fragments are ejected from a single vent and accumulate around the vent when they fall back to earth. Cinder cones grow rapidly and soon approach their maximum size. They rarely exceed 250m in height ...
... volcanoes and shield volcanoes. Cinder cones are built from lava fragments called cinders. The lava fragments are ejected from a single vent and accumulate around the vent when they fall back to earth. Cinder cones grow rapidly and soon approach their maximum size. They rarely exceed 250m in height ...
Chapter 6 study guide
... 18. If a volcano erupts quietly, what 2 types of lava flows will it have? 19. If a volcano erupts explosively, what will it produce in addition to (sometimes) lava flows? 20. What type of volcano forms from quiet eruptions? 21. What type of volcano forms from an explosive eruption without any lava f ...
... 18. If a volcano erupts quietly, what 2 types of lava flows will it have? 19. If a volcano erupts explosively, what will it produce in addition to (sometimes) lava flows? 20. What type of volcano forms from quiet eruptions? 21. What type of volcano forms from an explosive eruption without any lava f ...
Basalt has a high melting point and is very runny (like honey) – in
... and it flows like cold treacle. Because if flows more slowly than basalt, it forms volcanic cones with a much steeper shape, called cone volcanoes. Examples of cone volcanoes include Mt Taranaki and Mt Ruapehu. Rhyolite magma is the most viscous type of magma – it flows like tar. It is light in colo ...
... and it flows like cold treacle. Because if flows more slowly than basalt, it forms volcanic cones with a much steeper shape, called cone volcanoes. Examples of cone volcanoes include Mt Taranaki and Mt Ruapehu. Rhyolite magma is the most viscous type of magma – it flows like tar. It is light in colo ...
Volcano - watertown.k12.wi.us
... The height is usually less than ____________ feet (200 meters). The Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly and may bleed from the bottom or sides- called a "________________ eruption". These volcanoes ______________________often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava ...
... The height is usually less than ____________ feet (200 meters). The Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly and may bleed from the bottom or sides- called a "________________ eruption". These volcanoes ______________________often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava ...
clozevolcanonotes
... The height is usually less than ____________ feet (200 meters). The Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly and may bleed from the bottom or sides- called a "________________ eruption". These volcanoes ______________________often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava ...
... The height is usually less than ____________ feet (200 meters). The Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly and may bleed from the bottom or sides- called a "________________ eruption". These volcanoes ______________________often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava ...
Ch 3 Sec 4: Volcanic Landforms
... mountains and plateaus on Earth’s surface. Volcanic eruptions create landforms made of lava, ash, and other materials. Landforms formed when lava flows build up: 1. shield volcanoes- At some places on Earth’s surface, thin layers of lava pour out of a vent in a quiet eruption. More layers of such la ...
... mountains and plateaus on Earth’s surface. Volcanic eruptions create landforms made of lava, ash, and other materials. Landforms formed when lava flows build up: 1. shield volcanoes- At some places on Earth’s surface, thin layers of lava pour out of a vent in a quiet eruption. More layers of such la ...
Science Education Reform - American Geosciences Institute
... Understand that most volcanism occurs beneath the ocean. ...
... Understand that most volcanism occurs beneath the ocean. ...
Chapter 12
... That makes it 3 times the height of Mt. Everest. Unlike Everest, Olympus Mons has a very gentle slope. It is up to 550 km at its base. ...
... That makes it 3 times the height of Mt. Everest. Unlike Everest, Olympus Mons has a very gentle slope. It is up to 550 km at its base. ...
Volcanic Landforms
... Name__________________________________________ Date__________________ Period_________ ...
... Name__________________________________________ Date__________________ Period_________ ...
Itcha Range

The Itcha Range is a small isolated mountain range in the West-Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada. It is located 40 km (25 mi) northeast of Anahim Lake on the Chilcotin Plateau. With a maximum elevation of 2,375 m (7,792 ft), it is the lowest of three mountain ranges extending east from the Coast Mountains. Two mountains are named in the Itcha Range; Mount Downton and Itcha Mountain. A large provincial park surrounds the Itcha Range and other features in its vicinity. More than 15 animal species are known to exist in the Itcha Range area, as well as a grassland community that is limited only to this location of British Columbia. The Itcha Range resides in the territory of aboriginal peoples who have occupied this region for centuries. This area has a relatively dry environment compared to the Coast Mountains in the west.In contrast to most mountain ranges in British Columbia, the Itcha Range represents an inactive shield volcano. This highly dissected volcanic edifice consists of a variety of rock types, including basanite, hawaiite, trachyte, rhyolite, phonolite and alkali olivine basalt. They were deposited by different types of volcanic eruptions characterized by passive lava flows and explosivity. Two stages of eruptive activity have been identified at the volcano along with three sub-phases that are limited only to the first stage of development. The main body of the Itcha Range is between 3.8 and 3.0 million years old and thus over two million years ago it passed the most active shield stage of life. A long period of dormancy lasting for almost a million years followed, which was interrupted by the post-shield stage of volcanism 2.2 to 0.8 million years ago. More recent volcanic activity in and around the Itcha Range might have occurred in the last 340,000 years to produce cinder cones.The Itcha Range is part of an east-west trending volcanic zone called the Anahim Volcanic Belt. This consists of large shield volcanoes, small cinder cones, lava domes and lava flows that become progressively younger from west to east. Several explanations have been made regarding the creation of this feature, each citing a different geologic process. If volcanic activity were to resume at the Itcha Range, Canada's Interagency Volcanic Event Notification Plan (IVENP) is prepared to notify people threatened by eruptions.