Objective: Identify and describe the three kinds of volcanic cones
... Both active and inactive volcanoes can be found in many places around the world. They are also found in space. Jupiter’s moon Io is the first moon or body other than Earth on which scientists have seen active volcanoes. The volcanoes on Io are so powerful that they shoot out many metric tons of mate ...
... Both active and inactive volcanoes can be found in many places around the world. They are also found in space. Jupiter’s moon Io is the first moon or body other than Earth on which scientists have seen active volcanoes. The volcanoes on Io are so powerful that they shoot out many metric tons of mate ...
Document
... 2. Magma temperature = hotter flows easier 3. Magma viscosity – determined by temp and ...
... 2. Magma temperature = hotter flows easier 3. Magma viscosity – determined by temp and ...
Chapter 5: Volcanoes
... from the magma chamber to the pipe until it flows or explodes out of the vent. ...
... from the magma chamber to the pipe until it flows or explodes out of the vent. ...
Force of Volcanoes
... Types of Eruptions and Volcanoes (video) ______________ volcanoes form from long, gradual lava flows, pouring out in all directions. The ___________ ______________ are short and built from these ejected materials, mainly ash and rocks that fall near the summit or crate of the volcano. ______________ ...
... Types of Eruptions and Volcanoes (video) ______________ volcanoes form from long, gradual lava flows, pouring out in all directions. The ___________ ______________ are short and built from these ejected materials, mainly ash and rocks that fall near the summit or crate of the volcano. ______________ ...
Volcanism 3
... Helicopter view, NW coast (btw, this cliff tends to collapse quite often on the road) ...
... Helicopter view, NW coast (btw, this cliff tends to collapse quite often on the road) ...
Click here for the "Dynamic Earth Vocabulary"
... A vent or hole where molten rock and other volcanic products have erupted onto the surface. It’s the Earth’s natural way to cool and release pressure. A body of air or liquid from which heat is collected. Heat can also be transferred from one object to another, or from one molecule to another throug ...
... A vent or hole where molten rock and other volcanic products have erupted onto the surface. It’s the Earth’s natural way to cool and release pressure. A body of air or liquid from which heat is collected. Heat can also be transferred from one object to another, or from one molecule to another throug ...
Volcanoes SHOW
... explosive volcanism where tephra is physically blown into the atmosphere tephra: any material that is blown out of a volcano (mostly ash) ...
... explosive volcanism where tephra is physically blown into the atmosphere tephra: any material that is blown out of a volcano (mostly ash) ...
What do we expect in a volcanic eruption?
... • Solids lofted into atm • Lava flows from from others (called some pyroclastics. Better • Range from mafic than fireworks? (e.g. basalt) to • You bet!!! felsic, like all ign rx • Rocks may form from ...
... • Solids lofted into atm • Lava flows from from others (called some pyroclastics. Better • Range from mafic than fireworks? (e.g. basalt) to • You bet!!! felsic, like all ign rx • Rocks may form from ...
Volcano types and projectiles
... The vent on the top of a volcano is called a crater. A caldera is the remnants of a volcano whose cone has collapsed. Krakatau is the most well-known caldera, sporting a diameter of 6 km. ...
... The vent on the top of a volcano is called a crater. A caldera is the remnants of a volcano whose cone has collapsed. Krakatau is the most well-known caldera, sporting a diameter of 6 km. ...
Powerpoint Presentation Physical Geology, 10/e
... • Cinder cones – Small – Steeply sloping – Composed of a pile of loose cinders ...
... • Cinder cones – Small – Steeply sloping – Composed of a pile of loose cinders ...
Volcano by jose angel garcia gomez and alejandro cuthy gomez
... • Volcanic activity is responsible for building up much of earths surface. lava from volcanoes cools and hardens into three types of mountains ...
... • Volcanic activity is responsible for building up much of earths surface. lava from volcanoes cools and hardens into three types of mountains ...
Shasta/Lava Beds/Lassen
... • Some lavas are silica rich – pasty, sticky, explosive (Mt. Shasta, Lassen Peak) • Some lavas are silica poor – runny, less ...
... • Some lavas are silica rich – pasty, sticky, explosive (Mt. Shasta, Lassen Peak) • Some lavas are silica poor – runny, less ...
Explosive Pyroclastic A volcano is a mountain formed beneath the
... Explosive Pyroclastic A volcano is a mountain formed beneath the ground when the Earth’s crust meets the mantle and magma collects there until it rises to the surface because magma is less dense than the surrounding rock is. Then the magma becomes liquid. Shield, cinder cone, and composite volcanoes ...
... Explosive Pyroclastic A volcano is a mountain formed beneath the ground when the Earth’s crust meets the mantle and magma collects there until it rises to the surface because magma is less dense than the surrounding rock is. Then the magma becomes liquid. Shield, cinder cone, and composite volcanoes ...
The Cascade Volcanoes - West Virginia University
... Strongly plagioclase porphyritic Andesite-dominated strato-volcanoes Wider variety of rock types (basalt-andesite-dacite-rhyolite suite) than in tholeiitic suites ...
... Strongly plagioclase porphyritic Andesite-dominated strato-volcanoes Wider variety of rock types (basalt-andesite-dacite-rhyolite suite) than in tholeiitic suites ...
Name - worldculturesblock9
... g. blasted lava that solidifies as it falls to the ground as ash/cinders/volcanic bombs ...
... g. blasted lava that solidifies as it falls to the ground as ash/cinders/volcanic bombs ...
VOLCANOES STUDY GUIDE Test 1/14/15 Key Words • Volcano
... Shield Volcano-built by thinner, fluid lava that spreads over a large area Cinder-Cone Volcanoes-built by thick lava, cone shape mountain, steep sides Composite Volcanoes-built by layers of ash and cinders sandwiched between layers of hardened lava Need to know Most of Earth’s volcanoes are loca ...
... Shield Volcano-built by thinner, fluid lava that spreads over a large area Cinder-Cone Volcanoes-built by thick lava, cone shape mountain, steep sides Composite Volcanoes-built by layers of ash and cinders sandwiched between layers of hardened lava Need to know Most of Earth’s volcanoes are loca ...
here
... Expanding gases pulverize rock, forming ash. Violent escape hurls ash, blocks of rock and blobs of magma into the air above the ...
... Expanding gases pulverize rock, forming ash. Violent escape hurls ash, blocks of rock and blobs of magma into the air above the ...
File
... Hot spot volcanoes • Can be EXPLOSIVE like convergent boundaries (yellowstone) • Or VERY mild like Hawaii • Hotspot is an area that has excess heat, the plate moves over it and creates volcano’s ...
... Hot spot volcanoes • Can be EXPLOSIVE like convergent boundaries (yellowstone) • Or VERY mild like Hawaii • Hotspot is an area that has excess heat, the plate moves over it and creates volcano’s ...
_____ 1. What happens to the atmosphere after large
... the left. Write the letter in the space provided. You may use the volcanoes listed on the right more than once. ...
... the left. Write the letter in the space provided. You may use the volcanoes listed on the right more than once. ...
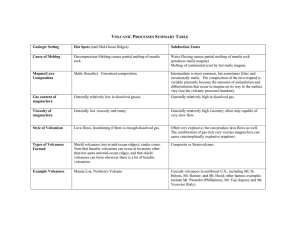
Geologic Setting Hot Spots (and Mid
... Intermediate is most common, but sometimes felsic and occasionally mafic. The composition of the lava erupted is variable primarily because the amounts of assimilation and differentiation that occur to magma on its way to the surface vary (see the volcanic processes handout). ...
... Intermediate is most common, but sometimes felsic and occasionally mafic. The composition of the lava erupted is variable primarily because the amounts of assimilation and differentiation that occur to magma on its way to the surface vary (see the volcanic processes handout). ...
Itcha Range

The Itcha Range is a small isolated mountain range in the West-Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada. It is located 40 km (25 mi) northeast of Anahim Lake on the Chilcotin Plateau. With a maximum elevation of 2,375 m (7,792 ft), it is the lowest of three mountain ranges extending east from the Coast Mountains. Two mountains are named in the Itcha Range; Mount Downton and Itcha Mountain. A large provincial park surrounds the Itcha Range and other features in its vicinity. More than 15 animal species are known to exist in the Itcha Range area, as well as a grassland community that is limited only to this location of British Columbia. The Itcha Range resides in the territory of aboriginal peoples who have occupied this region for centuries. This area has a relatively dry environment compared to the Coast Mountains in the west.In contrast to most mountain ranges in British Columbia, the Itcha Range represents an inactive shield volcano. This highly dissected volcanic edifice consists of a variety of rock types, including basanite, hawaiite, trachyte, rhyolite, phonolite and alkali olivine basalt. They were deposited by different types of volcanic eruptions characterized by passive lava flows and explosivity. Two stages of eruptive activity have been identified at the volcano along with three sub-phases that are limited only to the first stage of development. The main body of the Itcha Range is between 3.8 and 3.0 million years old and thus over two million years ago it passed the most active shield stage of life. A long period of dormancy lasting for almost a million years followed, which was interrupted by the post-shield stage of volcanism 2.2 to 0.8 million years ago. More recent volcanic activity in and around the Itcha Range might have occurred in the last 340,000 years to produce cinder cones.The Itcha Range is part of an east-west trending volcanic zone called the Anahim Volcanic Belt. This consists of large shield volcanoes, small cinder cones, lava domes and lava flows that become progressively younger from west to east. Several explanations have been made regarding the creation of this feature, each citing a different geologic process. If volcanic activity were to resume at the Itcha Range, Canada's Interagency Volcanic Event Notification Plan (IVENP) is prepared to notify people threatened by eruptions.