Principal Types of Volcanoes
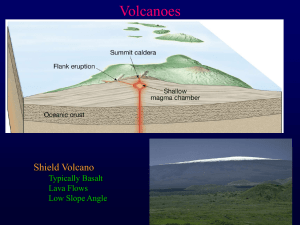
... of a warrior's shield. They are built up slowly by the accretion of thousands of highly fluid lava flows called basalt lava that spread widely over great distances, and then cool as thin, gently dipping sheets. Lavas also commonly erupt from vents along fractures (rift zones) that develop on the fla ...
... of a warrior's shield. They are built up slowly by the accretion of thousands of highly fluid lava flows called basalt lava that spread widely over great distances, and then cool as thin, gently dipping sheets. Lavas also commonly erupt from vents along fractures (rift zones) that develop on the fla ...
Classifying Volcanoes
... a. Plate tectonics; colliding plates produce excess magma which rises to the surface, after coming to the surface it cools and hardens forming the sides of the volcano 2. Parts of a volcano (draw diagram into notebooks) a. Magma Chamber- area where magma pools and builds up pressure before being rel ...
... a. Plate tectonics; colliding plates produce excess magma which rises to the surface, after coming to the surface it cools and hardens forming the sides of the volcano 2. Parts of a volcano (draw diagram into notebooks) a. Magma Chamber- area where magma pools and builds up pressure before being rel ...
Volcanoes Day 1 - NVHSEarthScienceOlsen
... Viscocity - _______ _______ _______ _______ _______ _______ _______ _______ ______. – This means that something that has a high viscosity does not flow easily. A substance with a high viscosity would be honey. A substance with a low viscosity would be water. – If the lava of a volcano has _______ __ ...
... Viscocity - _______ _______ _______ _______ _______ _______ _______ _______ ______. – This means that something that has a high viscosity does not flow easily. A substance with a high viscosity would be honey. A substance with a low viscosity would be water. – If the lava of a volcano has _______ __ ...
Hazards Chapter 3a
... destruction machines that we often make them out to be: (1) volcanoes frequently give us warning of their actions (2) many volcanoes are located in rural uninhabited places (3) if the eruption produces lava flows rather than poisonous gas or flaming particulates, it is more possible to evacuate and ...
... destruction machines that we often make them out to be: (1) volcanoes frequently give us warning of their actions (2) many volcanoes are located in rural uninhabited places (3) if the eruption produces lava flows rather than poisonous gas or flaming particulates, it is more possible to evacuate and ...
Volcanoes Week 2
... Lava blocks are often produced during violent volcanic eruptions when pieces of a volcano are blown away. The rock fragments are greater than 64 mm in size with no upward limit to their size. Lava blocks Lava blocks are large pieces of rock blown out of a volcano which have angular shapes and are so ...
... Lava blocks are often produced during violent volcanic eruptions when pieces of a volcano are blown away. The rock fragments are greater than 64 mm in size with no upward limit to their size. Lava blocks Lava blocks are large pieces of rock blown out of a volcano which have angular shapes and are so ...
1-10 levels at which an earthquake
... is measured on amount of damage caused; Above a 6 is very destructive ...
... is measured on amount of damage caused; Above a 6 is very destructive ...
Typical shield volcano Mauna Loa, Hawaii
... Plutonic igneous activity • Types of intrusive igneous features • Sill – a tabular, concordant pluton • - example in Ontario ...
... Plutonic igneous activity • Types of intrusive igneous features • Sill – a tabular, concordant pluton • - example in Ontario ...
Did a Massive Volcano Cause Massive Extinction?!
... explodes due to the high content of silica, does it have a high viscosity or low viscosity? ...
... explodes due to the high content of silica, does it have a high viscosity or low viscosity? ...
Volcanic Eruptions
... • Cool stiff lava that does not travel far from the erupting vent. • It cools and form sharp edged chunks. ...
... • Cool stiff lava that does not travel far from the erupting vent. • It cools and form sharp edged chunks. ...
VOLCANOES form where molten rock is vented at Earth`s surface.
... (also the largest volcano on earth) ...
... (also the largest volcano on earth) ...
VolcanicHazards2
... neighborhoods, such as the one shown here, can be evacuated. Buildings and other human-made structures are not so lucky! ...
... neighborhoods, such as the one shown here, can be evacuated. Buildings and other human-made structures are not so lucky! ...
Chapter 4 volcanoes powerpoint notes
... 3. Volcanoes create fertile soils which enhance agriculture. 4. Volcanoes, depending on number, frequency, and eruption size, could contribute to global cooling and the origin of ice ages, due to the blocking out of the sun. Plants failing to photosynthesize could result in total collapse of food we ...
... 3. Volcanoes create fertile soils which enhance agriculture. 4. Volcanoes, depending on number, frequency, and eruption size, could contribute to global cooling and the origin of ice ages, due to the blocking out of the sun. Plants failing to photosynthesize could result in total collapse of food we ...
volcanoes
... Volcanoes are classified as active or inactive. Inactive volcanoes are older and have usually erupted many times. A volcano is described as active if it is currently erupting or expected to erupt eventually. Eruption Stage A volcanic eruption occurs when lava, gasses, and other subterranean matter c ...
... Volcanoes are classified as active or inactive. Inactive volcanoes are older and have usually erupted many times. A volcano is described as active if it is currently erupting or expected to erupt eventually. Eruption Stage A volcanic eruption occurs when lava, gasses, and other subterranean matter c ...
File
... 4. Rocks are classified by what they are made of and how they form. Igneous rocks always begin as magma. What are the two main types of igneous rocks, and what is the main difference between them? How does each type form into solid rock? ...
... 4. Rocks are classified by what they are made of and how they form. Igneous rocks always begin as magma. What are the two main types of igneous rocks, and what is the main difference between them? How does each type form into solid rock? ...
Guidance for GEOGRAPHY End of Year
... The lava and ash deposited during an eruption breaks down to provide valuable nutrients for the soil. This creates very fertile soil which is good for agriculture ...
... The lava and ash deposited during an eruption breaks down to provide valuable nutrients for the soil. This creates very fertile soil which is good for agriculture ...
File
... gradually build a wide, gently sloping mountain called a shield volcano. Shield volcanoes rising from a hot spot on the ocean floor created the Hawaiian Islands. ...
... gradually build a wide, gently sloping mountain called a shield volcano. Shield volcanoes rising from a hot spot on the ocean floor created the Hawaiian Islands. ...
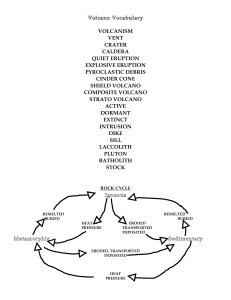
volcanism vent crater caldera quiet eruption explosive
... The height is usually less than 600 feet (200 meters). The Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly and may bleed from the bottom or sides- called a "flank eruption". These volcanoes do not often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava. Examples are Wizard Island (Crate ...
... The height is usually less than 600 feet (200 meters). The Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly and may bleed from the bottom or sides- called a "flank eruption". These volcanoes do not often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava. Examples are Wizard Island (Crate ...
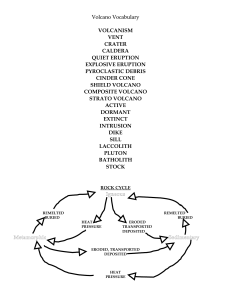
Volcano Vocabulary - watertown.k12.wi.us
... The height is usually less than 600 feet (200 meters). The Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly and may bleed from the bottom or sides- called a "flank eruption". These volcanoes do not often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava. Examples are Wizard Island (Crate ...
... The height is usually less than 600 feet (200 meters). The Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly and may bleed from the bottom or sides- called a "flank eruption". These volcanoes do not often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava. Examples are Wizard Island (Crate ...
Igneous Rocks - Occurrence and Classification
... Hawaiian – fluid basaltic lava is thrown into the air in jets from a vent or line of vents (a fissure) at the summit or on the flank of a volcano. Strombolian – distinct bursts of fluid lava (usually basalt or basaltic andesite) from the mouth of a magma-filled summit conduit. Vulcanian - short, vio ...
... Hawaiian – fluid basaltic lava is thrown into the air in jets from a vent or line of vents (a fissure) at the summit or on the flank of a volcano. Strombolian – distinct bursts of fluid lava (usually basalt or basaltic andesite) from the mouth of a magma-filled summit conduit. Vulcanian - short, vio ...
Itcha Range

The Itcha Range is a small isolated mountain range in the West-Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada. It is located 40 km (25 mi) northeast of Anahim Lake on the Chilcotin Plateau. With a maximum elevation of 2,375 m (7,792 ft), it is the lowest of three mountain ranges extending east from the Coast Mountains. Two mountains are named in the Itcha Range; Mount Downton and Itcha Mountain. A large provincial park surrounds the Itcha Range and other features in its vicinity. More than 15 animal species are known to exist in the Itcha Range area, as well as a grassland community that is limited only to this location of British Columbia. The Itcha Range resides in the territory of aboriginal peoples who have occupied this region for centuries. This area has a relatively dry environment compared to the Coast Mountains in the west.In contrast to most mountain ranges in British Columbia, the Itcha Range represents an inactive shield volcano. This highly dissected volcanic edifice consists of a variety of rock types, including basanite, hawaiite, trachyte, rhyolite, phonolite and alkali olivine basalt. They were deposited by different types of volcanic eruptions characterized by passive lava flows and explosivity. Two stages of eruptive activity have been identified at the volcano along with three sub-phases that are limited only to the first stage of development. The main body of the Itcha Range is between 3.8 and 3.0 million years old and thus over two million years ago it passed the most active shield stage of life. A long period of dormancy lasting for almost a million years followed, which was interrupted by the post-shield stage of volcanism 2.2 to 0.8 million years ago. More recent volcanic activity in and around the Itcha Range might have occurred in the last 340,000 years to produce cinder cones.The Itcha Range is part of an east-west trending volcanic zone called the Anahim Volcanic Belt. This consists of large shield volcanoes, small cinder cones, lava domes and lava flows that become progressively younger from west to east. Several explanations have been made regarding the creation of this feature, each citing a different geologic process. If volcanic activity were to resume at the Itcha Range, Canada's Interagency Volcanic Event Notification Plan (IVENP) is prepared to notify people threatened by eruptions.