1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 27 29 31 33 35 37 39 41
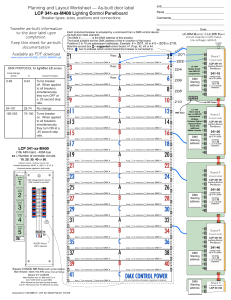
... LC-10M Master & LC-10S Slave As-built door label example: circuit boards in left-hand, The DMX # _______ is the DMX address of this breaker. low-voltage cabinet. The board jumpers set the DMX address of the #1 position of the board. 24 VAC Positions 2 to 10 are subsequent addresses. Example: #1= 201 ...
... LC-10M Master & LC-10S Slave As-built door label example: circuit boards in left-hand, The DMX # _______ is the DMX address of this breaker. low-voltage cabinet. The board jumpers set the DMX address of the #1 position of the board. 24 VAC Positions 2 to 10 are subsequent addresses. Example: #1= 201 ...
Installation, Wiring, and Specifications
... S Mechanical disconnect for output module power S Emergency stop switch for disconnecting system power It is recommended that emergency stop circuits be incorporated into the system for every machine controlled by a PLC. For maximum safety in a PLC system, these circuits must not be wired into the c ...
... S Mechanical disconnect for output module power S Emergency stop switch for disconnecting system power It is recommended that emergency stop circuits be incorporated into the system for every machine controlled by a PLC. For maximum safety in a PLC system, these circuits must not be wired into the c ...
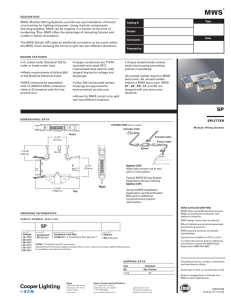
The MWS Splitter (SP)
... MWS, Modular Wiring Systems, provide low cost installation of branch circuit wiring for lighting and power. Using modular components that plug together, MWS can be installed in a fraction of the time of hardwiring. Plus, MWS offers the advantage of relocating fixtures and outlets in future renovatio ...
... MWS, Modular Wiring Systems, provide low cost installation of branch circuit wiring for lighting and power. Using modular components that plug together, MWS can be installed in a fraction of the time of hardwiring. Plus, MWS offers the advantage of relocating fixtures and outlets in future renovatio ...
impedance-based fault location methods for transmission line
... components of the voltage and current signals to calculate the impedance of the faulted line. The calculated impedance is considered to be a measure of the distance to fault. An IEEE guide [2] listed some notable definitions for fault location estimation in modern electric power system. Fault locati ...
... components of the voltage and current signals to calculate the impedance of the faulted line. The calculated impedance is considered to be a measure of the distance to fault. An IEEE guide [2] listed some notable definitions for fault location estimation in modern electric power system. Fault locati ...
Impact of Gate-Length Biasing on Threshold-Voltage Selection
... Triple-Vth can reduce leakage by ~8% more than is possible with dual-Vth Dual-Vth combined with biasing can achieve almost the same reduction ...
... Triple-Vth can reduce leakage by ~8% more than is possible with dual-Vth Dual-Vth combined with biasing can achieve almost the same reduction ...
Appendix D-4 Electrical Advanced-Level Training Issue Date: 12/29/11
... A standard may be defined as a document that applies collectively to codes, specifications, recommended practices, test methods, and guides, which have been prepared by a standards developing organization or group, and published in accordance with established procedures. Standards promote safety, re ...
... A standard may be defined as a document that applies collectively to codes, specifications, recommended practices, test methods, and guides, which have been prepared by a standards developing organization or group, and published in accordance with established procedures. Standards promote safety, re ...
A GUIDE TO LOW RESISTANCE TESTING - Test
... Mechanical stress from vibration during operation can also degrade connections, causing resistance to rise. These conditions result in excessive heating at the location when the component is carrying the rated current, based on the formula W=I2R. For example: 6000 A across a 100 µΩ bus = 3600 Watts. ...
... Mechanical stress from vibration during operation can also degrade connections, causing resistance to rise. These conditions result in excessive heating at the location when the component is carrying the rated current, based on the formula W=I2R. For example: 6000 A across a 100 µΩ bus = 3600 Watts. ...
soft start
... • Start Curves 1, 2, 3 – During acceleration, before reaching peak torque, the Pump Control Program automatically controls the voltage ramp-up, ...
... • Start Curves 1, 2, 3 – During acceleration, before reaching peak torque, the Pump Control Program automatically controls the voltage ramp-up, ...
The birth of the electric machines: a commentary on Faraday (1832
... Michael Faraday was born in 1791 in Newington Butts, now in South London, but then no more than a village in rural Surrey. He was the son of a blacksmith who had moved down from Cumbria in northwest England just before Michael was born. His family were not well off and Faraday received a typical wo ...
... Michael Faraday was born in 1791 in Newington Butts, now in South London, but then no more than a village in rural Surrey. He was the son of a blacksmith who had moved down from Cumbria in northwest England just before Michael was born. His family were not well off and Faraday received a typical wo ...