Document
... 15- Find the real value of the carts acceleration using Newton’s second law which states that the force is proportional to the acceleration. F=ma where F could be found from the mass causing the motion of the cart. 16- Find the percentage error of the acceleration. PE ...
... 15- Find the real value of the carts acceleration using Newton’s second law which states that the force is proportional to the acceleration. F=ma where F could be found from the mass causing the motion of the cart. 16- Find the percentage error of the acceleration. PE ...
Wednesday, Sept. 18, 2013
... Relativistic Momentum • If we use the definition of momentum, the momentum of the ball thrown by Frank is entirely in the y direction pFy = mu0 • The change of momentum as observed by Frank is ΔpF = ΔpFy = −2mu0 • Mary measures the initial velocity of her own ball to be u’Mx = 0 and u’My = −u0. • I ...
... Relativistic Momentum • If we use the definition of momentum, the momentum of the ball thrown by Frank is entirely in the y direction pFy = mu0 • The change of momentum as observed by Frank is ΔpF = ΔpFy = −2mu0 • Mary measures the initial velocity of her own ball to be u’Mx = 0 and u’My = −u0. • I ...
Physics 132 Prof. Buehrle 4/01/14
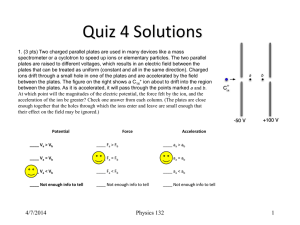
... 1. (3 pts) Two charged parallel plates are used in many devices like a mass spectrometer or a cyclotron to speed up ions or elementary particles. The two parallel plates are raised to different voltages, which results in an electric field between the plates that can be treated as uniform (constant a ...
... 1. (3 pts) Two charged parallel plates are used in many devices like a mass spectrometer or a cyclotron to speed up ions or elementary particles. The two parallel plates are raised to different voltages, which results in an electric field between the plates that can be treated as uniform (constant a ...
James M. Hill Physics 122 Problem Set
... 11. A 6.2 kg book is pressed against the wall. The coefficient of static friction between the book and wall is 0.16. Calculate the minimum applied force necessary to keep the book from slipping down. (380 N) 12. A 14.7 kg box is pressed up against the wall using an applied force of 600 N. For the bo ...
... 11. A 6.2 kg book is pressed against the wall. The coefficient of static friction between the book and wall is 0.16. Calculate the minimum applied force necessary to keep the book from slipping down. (380 N) 12. A 14.7 kg box is pressed up against the wall using an applied force of 600 N. For the bo ...
Taking Notes for Class - Teacher Resource Center
... he first understood the theory of gravitation and optics (white light is made up of the colors of the rainbow), and much mathematics. The three laws of motion were first compiled in his work Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy) commonly known a ...
... he first understood the theory of gravitation and optics (white light is made up of the colors of the rainbow), and much mathematics. The three laws of motion were first compiled in his work Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica (Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy) commonly known a ...
Momentum - GEOCITIES.ws
... The units for momentum would be mass units times velocity units. The standard metric unit of momentum is the kg*m/s. While the kg*m/s is the standard metric unit of momentum, there are a variety of other units which are acceptable (though not conventional) units of momentum; examples include kg*mi/h ...
... The units for momentum would be mass units times velocity units. The standard metric unit of momentum is the kg*m/s. While the kg*m/s is the standard metric unit of momentum, there are a variety of other units which are acceptable (though not conventional) units of momentum; examples include kg*mi/h ...
Ch 8 – Oscillation
... oscillator oscillates with large amplitude. • Damping or resistive forces limit the maximum amplitude. • For low velocity the damping force is proportional to the speed, but for high speed the damping force is proportional to speed square. • More energy needs to be provided by the driver to increase ...
... oscillator oscillates with large amplitude. • Damping or resistive forces limit the maximum amplitude. • For low velocity the damping force is proportional to the speed, but for high speed the damping force is proportional to speed square. • More energy needs to be provided by the driver to increase ...
Document
... 5.7.2. A ball on the end of a rope is moving in a vertical circle near the surface of the earth. Point A is at the top of the circle; C is at the bottom. Points B and D are exactly halfway between A and C. Which one of the following statements concerning the tension in the rope is true? a) The tens ...
... 5.7.2. A ball on the end of a rope is moving in a vertical circle near the surface of the earth. Point A is at the top of the circle; C is at the bottom. Points B and D are exactly halfway between A and C. Which one of the following statements concerning the tension in the rope is true? a) The tens ...
Chapter 11 Clickers
... 11.11.1. A star is rotating about an axis that passes through its center. When the star “dies,” the balance between the inward pressure due to the force of gravity and the outward pressure from nuclear processes is no longer present and the star collapses inward and its radius decreases with time. ...
... 11.11.1. A star is rotating about an axis that passes through its center. When the star “dies,” the balance between the inward pressure due to the force of gravity and the outward pressure from nuclear processes is no longer present and the star collapses inward and its radius decreases with time. ...
Aim: How do we explain Newton`s 3rd Law?
... 3. A traveler pulls a suitcase of mass 8.00 kg across a level surface by pulling on the handle 20.0 N at an angle of 50.0° relative to horizontal. Friction against the suitcase can be modeled by μk = 0.100. (a) Determine the acceleration of the suitcase. (b) What amount of force applied at the same ...
... 3. A traveler pulls a suitcase of mass 8.00 kg across a level surface by pulling on the handle 20.0 N at an angle of 50.0° relative to horizontal. Friction against the suitcase can be modeled by μk = 0.100. (a) Determine the acceleration of the suitcase. (b) What amount of force applied at the same ...
Chapter 11
... Given two vectors, A and B The vector (cross) product of A and B is defined as a third vector, C C is read as “A cross B” The magnitude of C is AB sin q ...
... Given two vectors, A and B The vector (cross) product of A and B is defined as a third vector, C C is read as “A cross B” The magnitude of C is AB sin q ...
Force and Motion II 1.1
... Physicists write this force law in the form F = kx , where the force constant k is k = 42m/T2 . The magnitude of the force F on the cart increases in direct proportion to the distance x that the cart is displaced from the equilibrium point (x=0). If you double x , then you double F. The constant ...
... Physicists write this force law in the form F = kx , where the force constant k is k = 42m/T2 . The magnitude of the force F on the cart increases in direct proportion to the distance x that the cart is displaced from the equilibrium point (x=0). If you double x , then you double F. The constant ...
Chapter #11 (Read Please)
... Given two vectors, A and B The vector (cross) product of A and B is defined as a third vector, C C is read as “A cross B” The magnitude of C is AB sin q ...
... Given two vectors, A and B The vector (cross) product of A and B is defined as a third vector, C C is read as “A cross B” The magnitude of C is AB sin q ...