FREE Sample Here
... force is applied, and that the force of expanding gases drives the ball out of the barrel when it is fired. But what keeps the cannonball moving when the gases no longer act on it? Galileo wondered about the same question when a ball gained speed in rolling down an incline but moved at constant spee ...
... force is applied, and that the force of expanding gases drives the ball out of the barrel when it is fired. But what keeps the cannonball moving when the gases no longer act on it? Galileo wondered about the same question when a ball gained speed in rolling down an incline but moved at constant spee ...
Momentum
... conceptually thought of as the tendency for an object to continue to move in its direction of travel. As such, it is a natural consequence of Newton's first law. •Momentum is a conserved quantity, meaning that the total momentum of any closed system (one not affected by external forces) cannot be ch ...
... conceptually thought of as the tendency for an object to continue to move in its direction of travel. As such, it is a natural consequence of Newton's first law. •Momentum is a conserved quantity, meaning that the total momentum of any closed system (one not affected by external forces) cannot be ch ...
Year 11 Biomechanics
... most common of all movements, as most human movement requires the rotation of body parts around joints (e.g. cycling, swimming and running). ...
... most common of all movements, as most human movement requires the rotation of body parts around joints (e.g. cycling, swimming and running). ...
David Walter
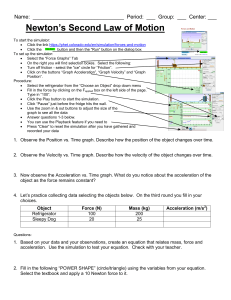
... 1. Observe the Position vs. Time graph. Describe how the position of the object changes over time. 2. Observe the Velocity vs. Time graph. Describe how the velocity of the object changes over time. ...
... 1. Observe the Position vs. Time graph. Describe how the position of the object changes over time. 2. Observe the Velocity vs. Time graph. Describe how the velocity of the object changes over time. ...
Chapter 5 - KFUPM Faculty List
... them in this chapter. Newton’s First Law If a body is a rest, it stays at rest. If it is in motion with constant velocity, it will continue with the same velocity (magnitude and direction) unless it is acted upon by a net external force. Remember that if the velocity is constant, then the object can ...
... them in this chapter. Newton’s First Law If a body is a rest, it stays at rest. If it is in motion with constant velocity, it will continue with the same velocity (magnitude and direction) unless it is acted upon by a net external force. Remember that if the velocity is constant, then the object can ...
Gravity and Orbits Lab Activity Fill in the blanks to complete
... That depends on how much mass the object has. Big heavy things (things with a lot of mass) have more inertia than light things. You have to push a bus harder than a scooter to get it to move. If something has a lot of mass, it's also hard to get it to stop moving. If the bus was moving fast, you'd n ...
... That depends on how much mass the object has. Big heavy things (things with a lot of mass) have more inertia than light things. You have to push a bus harder than a scooter to get it to move. If something has a lot of mass, it's also hard to get it to stop moving. If the bus was moving fast, you'd n ...
Phy 211: General Physics I
... reference frame and is therefore a fictitious force (i.e. it is not really a force it is only perceived as one) – is the perceived response of the object’s inertia resisting the circular motion (& its rotating environment) – has a magnitude equal to the centripetal force acting on the body ...
... reference frame and is therefore a fictitious force (i.e. it is not really a force it is only perceived as one) – is the perceived response of the object’s inertia resisting the circular motion (& its rotating environment) – has a magnitude equal to the centripetal force acting on the body ...
Chapter 4
... Fundamental (Field) Forces Types • Strong nuclear force • Electromagnetic force • Weak nuclear force • Gravity ...
... Fundamental (Field) Forces Types • Strong nuclear force • Electromagnetic force • Weak nuclear force • Gravity ...
Collision Prob PPT from class
... a flat surface, each with a speed of 1.0 meter per second relative to the surface. The objects collide head-on and are reported to rebound after the collision, each with a speed of 2.0 meters per second relative to the surface. Which of the following assessments of this report is most accurate? (A)M ...
... a flat surface, each with a speed of 1.0 meter per second relative to the surface. The objects collide head-on and are reported to rebound after the collision, each with a speed of 2.0 meters per second relative to the surface. Which of the following assessments of this report is most accurate? (A)M ...
SPH4U: Lecture 5 Notes
... More discussion of dynamics Recap Equivalence principle (inertial vs gravitational mass) The Free Body Diagram The tools we have for making & solving problems: Ropes & Pulleys (tension) Hooke’s Law (springs) ...
... More discussion of dynamics Recap Equivalence principle (inertial vs gravitational mass) The Free Body Diagram The tools we have for making & solving problems: Ropes & Pulleys (tension) Hooke’s Law (springs) ...