v - Personal.psu.edu
... The effect of an external force is to change the momentum of the entire system. If the external force is zero the system maintains a zero or constant velocity and the total momentum of the system is conserved ...
... The effect of an external force is to change the momentum of the entire system. If the external force is zero the system maintains a zero or constant velocity and the total momentum of the system is conserved ...
Form B
... Which vehicle experiences the largest force? The largest magnitude of force is always experienced by the vehicle with the Newton's 3rd law: At the point of contact, the forces have equal magnitudes and opposite directions on the two objects. A) largest initial speed B) smallest initial speed C) larg ...
... Which vehicle experiences the largest force? The largest magnitude of force is always experienced by the vehicle with the Newton's 3rd law: At the point of contact, the forces have equal magnitudes and opposite directions on the two objects. A) largest initial speed B) smallest initial speed C) larg ...
Dynamics Review Sheet Solutions
... is zero, the object will A. slow down and stop B. change the direction of its motion C. accelerate uniformly D. continue moving with constant velocity 15. As a ball falls, the action force is the pull of the earth’s mass on the ball. The reaction force is the A. air resistance acting against the bal ...
... is zero, the object will A. slow down and stop B. change the direction of its motion C. accelerate uniformly D. continue moving with constant velocity 15. As a ball falls, the action force is the pull of the earth’s mass on the ball. The reaction force is the A. air resistance acting against the bal ...
CP PHYSICS
... 22. Draw the pathway of a projectile launched at an angle. Show vx and vy vectors as it moves up to its highest point and then falls back to the ground. 23. What is the only force acting on a projectile once it is released? 24. What is the relationship between the horizontal and vertical components ...
... 22. Draw the pathway of a projectile launched at an angle. Show vx and vy vectors as it moves up to its highest point and then falls back to the ground. 23. What is the only force acting on a projectile once it is released? 24. What is the relationship between the horizontal and vertical components ...
GRADE 11F: Physics 1
... collisions and apply the knowledge to collisions and explosions in one dimension. They determine the centre of gravity of a lamina and apply the principle of moments to real problems. ...
... collisions and apply the knowledge to collisions and explosions in one dimension. They determine the centre of gravity of a lamina and apply the principle of moments to real problems. ...
Lab #5 – Newton`s First Law
... orbiting the earth, astronauts are subject to a force of gravity that is only slightly less than what they would experience on the earth’s surface. Why, then, do they appear to be “weightless”? The answer is simple. While in orbit around the earth, they experience free fall motion in the same way th ...
... orbiting the earth, astronauts are subject to a force of gravity that is only slightly less than what they would experience on the earth’s surface. Why, then, do they appear to be “weightless”? The answer is simple. While in orbit around the earth, they experience free fall motion in the same way th ...
Physics Chapter 7
... elasticity of the body under gravitational influence. • If an orbiting body moves too close to a more massive body, the tidal force on the orbiting body may be large enough to break the body apart. • The distance at which tidal forces can become destructive is called Roche’s limit. ...
... elasticity of the body under gravitational influence. • If an orbiting body moves too close to a more massive body, the tidal force on the orbiting body may be large enough to break the body apart. • The distance at which tidal forces can become destructive is called Roche’s limit. ...
Document
... friction is 0.10 and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.03. a. what does the sled weigh? b. what force will be needed to start the sled moving? c. what force is needed to keep the sled moving at constant velocity? d. once moving, what total force must be applied to the sled to accelerate it at ...
... friction is 0.10 and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.03. a. what does the sled weigh? b. what force will be needed to start the sled moving? c. what force is needed to keep the sled moving at constant velocity? d. once moving, what total force must be applied to the sled to accelerate it at ...
Physics Definition
... An object’s mass is a measure of how difficult is to change its velocity. How much force must be applied to take/bring an object from/to rest. Also, how much effort is needed to change its direction. Mass is measured in Kg (kilograms). ...
... An object’s mass is a measure of how difficult is to change its velocity. How much force must be applied to take/bring an object from/to rest. Also, how much effort is needed to change its direction. Mass is measured in Kg (kilograms). ...
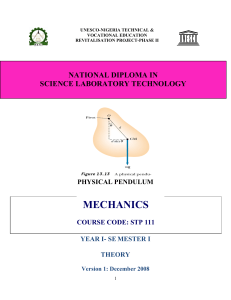
STP 111 THEOR - Unesco
... 2.4 Adhesion and cohesion Cohesion is the force of attraction between molecules of the same kind e.g the molecules of water Adhesion is the force of attraction between molecules of water and glass Cohesion and adhesion explain the different action of water and mercury when spilled on a clean glass s ...
... 2.4 Adhesion and cohesion Cohesion is the force of attraction between molecules of the same kind e.g the molecules of water Adhesion is the force of attraction between molecules of water and glass Cohesion and adhesion explain the different action of water and mercury when spilled on a clean glass s ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... When mass is in kilograms and acceleration is in m/s/s, the unit of force is in newtons (N). One newton is equal to the force required to accelerate one kilogram of mass at one ...
... When mass is in kilograms and acceleration is in m/s/s, the unit of force is in newtons (N). One newton is equal to the force required to accelerate one kilogram of mass at one ...
What are Forces?
... What are forces? • A force is a push or a pull. • We learned that Newton’s 2nd Law states that a Force is equal to the mass of a moving object times its acceleration. • We learned that Newton’s 3rd Law states that for every force there is an equal and opposite reaction force. ...
... What are forces? • A force is a push or a pull. • We learned that Newton’s 2nd Law states that a Force is equal to the mass of a moving object times its acceleration. • We learned that Newton’s 3rd Law states that for every force there is an equal and opposite reaction force. ...