Newton`s Laws of Gravity and Orbits https://phet.colorado.edu/en
... b. The Gravity force vectors are (greater than, less than, equal to) the velocity vector. c. Adjust the velocity by sliding the arrow to be smaller and larger. Draw the path of the Earth with less velocity and with more velocity. ...
... b. The Gravity force vectors are (greater than, less than, equal to) the velocity vector. c. Adjust the velocity by sliding the arrow to be smaller and larger. Draw the path of the Earth with less velocity and with more velocity. ...
Chapter 9
... • SI unit of linear momentum is kg*m/s • Momentum is a vector, its direction coincides with the direction of velocity ...
... • SI unit of linear momentum is kg*m/s • Momentum is a vector, its direction coincides with the direction of velocity ...
Slides - Powerpoint - University of Toronto Physics
... • the greater its force of attraction toward the Earth. • the smaller its tendency to move i.e., the greater its inertia. So, the acceleration is the same. It is equal to the acceleration due to gravity: 10 m/s2 (precisely 9.8 m/s2). ...
... • the greater its force of attraction toward the Earth. • the smaller its tendency to move i.e., the greater its inertia. So, the acceleration is the same. It is equal to the acceleration due to gravity: 10 m/s2 (precisely 9.8 m/s2). ...
Inv 3
... strapped in with her seat belt. She knows that in the vertical direction, the gravitational force pulls her downward and the seat pushes her upward and that the net vertical force is zero, thus resulting in no upward or downward acceleration. In the horizontal direction, the back of the seat pushes ...
... strapped in with her seat belt. She knows that in the vertical direction, the gravitational force pulls her downward and the seat pushes her upward and that the net vertical force is zero, thus resulting in no upward or downward acceleration. In the horizontal direction, the back of the seat pushes ...
Explaining Motion
... Law 1 – if the resultant force acting on an object is zero, the momentum of the object does not change Law 2 – if there is a resultant force acting on an object, the momentum will change (c.o.m.=r.f x time) and is in the same direction ...
... Law 1 – if the resultant force acting on an object is zero, the momentum of the object does not change Law 2 – if there is a resultant force acting on an object, the momentum will change (c.o.m.=r.f x time) and is in the same direction ...
Chapter 3
... object transfers all of its momentum to the other object during the collision • If the collision involves a stationary object and a moving object, immediately after the collision, the previously stationary object will be moving, and the previously moving object will be stationary ...
... object transfers all of its momentum to the other object during the collision • If the collision involves a stationary object and a moving object, immediately after the collision, the previously stationary object will be moving, and the previously moving object will be stationary ...
Universal Gravitation
... It may seem reasonable to think that if weight = mg, since weight = 0, g = 0, but this is NOT true. If you stand on a scale in an elevator and then the cables are cut, you will also weigh nothing (ma = N – mg, but in free-fall a = g, so the normal force N = 0). This does not mean g = 0! Astronauts i ...
... It may seem reasonable to think that if weight = mg, since weight = 0, g = 0, but this is NOT true. If you stand on a scale in an elevator and then the cables are cut, you will also weigh nothing (ma = N – mg, but in free-fall a = g, so the normal force N = 0). This does not mean g = 0! Astronauts i ...
MP 2 Quarterly Review Sheet Answers
... B. between zero and Mg (although it is moving up it is accelerating DOWN) C. equal to Mg D. greater than Mg E. zero 9. A box is being pushed by a constant force along a horizontal surface. If the object’s velocity is constant, we can infer that there is _______ acting on the box A. a frictional forc ...
... B. between zero and Mg (although it is moving up it is accelerating DOWN) C. equal to Mg D. greater than Mg E. zero 9. A box is being pushed by a constant force along a horizontal surface. If the object’s velocity is constant, we can infer that there is _______ acting on the box A. a frictional forc ...
Centripetal Force
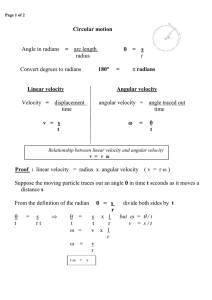
... In classical mechanics, the dynamics of a point particle are described by Newton’s 2nd law, F~ = m~a, where F~ is the net force, m is the mass, and ~a is the acceleration. This equation guarantees that F~ and ~a are parallel to each other. If ~v is the velocity, by definition ~v is always parallel t ...
... In classical mechanics, the dynamics of a point particle are described by Newton’s 2nd law, F~ = m~a, where F~ is the net force, m is the mass, and ~a is the acceleration. This equation guarantees that F~ and ~a are parallel to each other. If ~v is the velocity, by definition ~v is always parallel t ...
Simple Harmonic Motion
... The Total Energy of a Vibrating System is Constant KE + PE = constant If the maximum amplitude of the motion is x0 then the energy at any point x is given by: ½ mv2 + ½ kx2 = ½ kx02 From this we can solve for velocity: │v│= √ [(x02 –x2)(k/m)] From Hooke’s law, F = -kx and F =ma, therefore a = -(k/m ...
... The Total Energy of a Vibrating System is Constant KE + PE = constant If the maximum amplitude of the motion is x0 then the energy at any point x is given by: ½ mv2 + ½ kx2 = ½ kx02 From this we can solve for velocity: │v│= √ [(x02 –x2)(k/m)] From Hooke’s law, F = -kx and F =ma, therefore a = -(k/m ...
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that
... 1) Which of Newton's laws best explains why motorists should buckle-up? A) the second law ...
... 1) Which of Newton's laws best explains why motorists should buckle-up? A) the second law ...
TAP 407-1: Worked examples – Coulomb`s law
... Given the difference in magnitudes of gravitational and electrical forces you’ve just discovered, why do you feel gravitational attraction from the earth, but no electrical forces? ...
... Given the difference in magnitudes of gravitational and electrical forces you’ve just discovered, why do you feel gravitational attraction from the earth, but no electrical forces? ...
spirit 2 - CEENBoT / TekBot Site
... INSTRUCTING Concepts (Don’t Sit Under the Apple Tree) Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion Putting “Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion” in Recognizable terms: Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion states that the acceleration of an object is produced by a net force in the same direction as the acceleration, is directly proport ...
... INSTRUCTING Concepts (Don’t Sit Under the Apple Tree) Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion Putting “Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion” in Recognizable terms: Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion states that the acceleration of an object is produced by a net force in the same direction as the acceleration, is directly proport ...
Chapter 4 Motion, Energy, and Gravity
... Weight is the force that’s acting on your mass. Your weight depends on your mass AND the force that is acting on you. When you measure your weight, you actually measure the force acting on you, not just the mass. On the surface of Earth, the force that is acting on you is the gravitational for ...
... Weight is the force that’s acting on your mass. Your weight depends on your mass AND the force that is acting on you. When you measure your weight, you actually measure the force acting on you, not just the mass. On the surface of Earth, the force that is acting on you is the gravitational for ...
force
... – Vehicle restraints, such as seat belts, are the unbalanced force that stops you when a car stops suddenly so that you don’t go flying forward. – This applies to all vehicle restraints. ...
... – Vehicle restraints, such as seat belts, are the unbalanced force that stops you when a car stops suddenly so that you don’t go flying forward. – This applies to all vehicle restraints. ...
Ezio Fornero, Space and Motion as Problems of
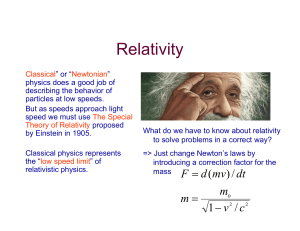
... theory laws of Physics are invariant with respect to all the possible different systems of reference, so special frames of references are not needed. This is an optimum method to discover the real, universal physical laws and leads to General Relativity. Let’s follow for now Classical Dynamics. Whil ...
... theory laws of Physics are invariant with respect to all the possible different systems of reference, so special frames of references are not needed. This is an optimum method to discover the real, universal physical laws and leads to General Relativity. Let’s follow for now Classical Dynamics. Whil ...