PPT
... – Math, Torque, Angular Momentum, Energy again, but more sophisticated – The material will not be on the 3rd exam, but will help with the exam. It will all be on the final ...
... – Math, Torque, Angular Momentum, Energy again, but more sophisticated – The material will not be on the 3rd exam, but will help with the exam. It will all be on the final ...
SPH4U: Lecture 14 Notes
... that the bat exerts on the ball? What is the average force Fav that the bat exerts on the ball? ...
... that the bat exerts on the ball? What is the average force Fav that the bat exerts on the ball? ...
Notes - UMD Physics
... and its top end tied to a fixed bar. Show that (a) the tension in the string is one-third the weight of the disk, (b) the magnitude of the acceleration of the CM is 2g/3, and (c) the speed of the CM is (4gh/3)1/2 after the disk has descended ...
... and its top end tied to a fixed bar. Show that (a) the tension in the string is one-third the weight of the disk, (b) the magnitude of the acceleration of the CM is 2g/3, and (c) the speed of the CM is (4gh/3)1/2 after the disk has descended ...
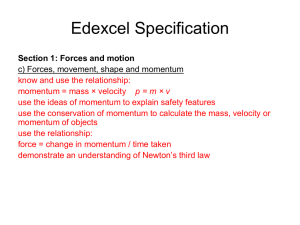
Momentum - WebPhysics
... • You have probably used the word momentum tossed out in everyday life – but not necessarily 100% correctly. • With a neighbor discuss where you have heard momentum talked about, and try to figure out from that what the average person probably thinks momentum means. ...
... • You have probably used the word momentum tossed out in everyday life – but not necessarily 100% correctly. • With a neighbor discuss where you have heard momentum talked about, and try to figure out from that what the average person probably thinks momentum means. ...
Velocity and Acceleration PowerPoint
... of motion involve similar changes. In fact, rarely does any object’s motion stay the same for very long. ...
... of motion involve similar changes. In fact, rarely does any object’s motion stay the same for very long. ...
File - Mr. Graham`s AP Physics 1 & AP Physics C
... from your free body diagram, write an equations for both the x and y axes; if the object is in equilibrium, then F=0; if the object is accelerating, then F=ma Be able to calculate the normal force (not necessarily equal to mg) Be able to solve force problems involving friction (fN) Be able to so ...
... from your free body diagram, write an equations for both the x and y axes; if the object is in equilibrium, then F=0; if the object is accelerating, then F=ma Be able to calculate the normal force (not necessarily equal to mg) Be able to solve force problems involving friction (fN) Be able to so ...
Energy and Power
... • as wave passes, the “particles” in the medium oscillate • medium has both inertia (KE) and elasticity (PE) • dimensional argument: v= length/time LT-1 • inertia is the mass of an element =mass/length ML-1 • tension F is the elastic character (a force) MLT-2 • how can we combine tension and mass d ...
... • as wave passes, the “particles” in the medium oscillate • medium has both inertia (KE) and elasticity (PE) • dimensional argument: v= length/time LT-1 • inertia is the mass of an element =mass/length ML-1 • tension F is the elastic character (a force) MLT-2 • how can we combine tension and mass d ...
Friction
... the only force acting upon an object is gravity. Objects which are said to be undergoing free-fall, are not encountering a significant force of air resistance; they are falling under the sole influence of gravity. Under such conditions, all objects will fall with the same rate of acceleration, regar ...
... the only force acting upon an object is gravity. Objects which are said to be undergoing free-fall, are not encountering a significant force of air resistance; they are falling under the sole influence of gravity. Under such conditions, all objects will fall with the same rate of acceleration, regar ...