Conceptions3
... attract each other due to gravitational forces. How do the magnitudes of these attractive forces compare? ...
... attract each other due to gravitational forces. How do the magnitudes of these attractive forces compare? ...
Chapter 4 File
... Figure: A constant net external force F acts over a displacement s and does work on the plane. As a result of a work done, the plane’s kinetic energy changes. The net force is the vector sum of all the external forces acting on the plane, and it is assumed to have the same direction as the displac ...
... Figure: A constant net external force F acts over a displacement s and does work on the plane. As a result of a work done, the plane’s kinetic energy changes. The net force is the vector sum of all the external forces acting on the plane, and it is assumed to have the same direction as the displac ...
Rotational Dynamics
... Now move the coins so that they are only 1 or 2 cm apart. Wiggle the pencil as before. The torque that was required was much less this time. Thus, the amount of mass is not the only factor that determines how much torque is needed to change angular velocity; the location of that mass also is relevan ...
... Now move the coins so that they are only 1 or 2 cm apart. Wiggle the pencil as before. The torque that was required was much less this time. Thus, the amount of mass is not the only factor that determines how much torque is needed to change angular velocity; the location of that mass also is relevan ...
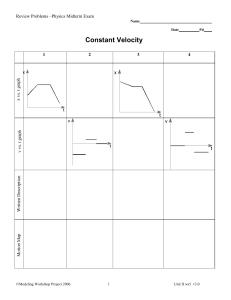
356 Linear Kinetics
... weight. Since W = mg then the acceleration they experience is SF = ma but SF = W = mg mg = ma ...
... weight. Since W = mg then the acceleration they experience is SF = ma but SF = W = mg mg = ma ...
vibrations and waves
... If the spring is hung vertically, the only change is in the equilibrium position, which is at the point where the spring force equals the gravitational force. ...
... If the spring is hung vertically, the only change is in the equilibrium position, which is at the point where the spring force equals the gravitational force. ...
schede di monitoraggio - Clil in Action
... Now we split the force F into its components on a convenient Cartesian plane that has the x axis parallel to the spring. The component F is directly proportional to the extension x of the spring from its equilibrium position, according to the linear relationship F = Kx, where K is the spring constan ...
... Now we split the force F into its components on a convenient Cartesian plane that has the x axis parallel to the spring. The component F is directly proportional to the extension x of the spring from its equilibrium position, according to the linear relationship F = Kx, where K is the spring constan ...
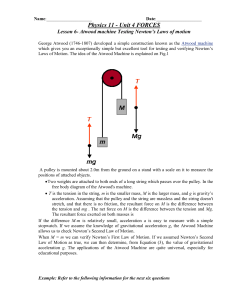
Physics 11 - BigEngine
... allows us to check Newton’s Second Law of Motion. When M = m we can verify Newton’s First Law of Motion. If we assumed Newton’s Second Law of Motion as true, we can then determine, from Equation (3), the value of gravitational acceleration g. The applications of the Atwood Machine are quite universa ...
... allows us to check Newton’s Second Law of Motion. When M = m we can verify Newton’s First Law of Motion. If we assumed Newton’s Second Law of Motion as true, we can then determine, from Equation (3), the value of gravitational acceleration g. The applications of the Atwood Machine are quite universa ...
Physics 207: Lecture 2 Notes
... Two particles, one positively charged and one negatively charged, are held apart. Since oppositely charged objects attract one another, the particles will accelerate towards each other when released. Let W+ be the work done on the positive charge by the negative charge. Let W– be the work done on th ...
... Two particles, one positively charged and one negatively charged, are held apart. Since oppositely charged objects attract one another, the particles will accelerate towards each other when released. Let W+ be the work done on the positive charge by the negative charge. Let W– be the work done on th ...
Slide 1
... • Finally applied these to find complete analog to rotational motion. • We can now describe the mechanical universe over an immense range of distances: a top, a hurricane, and a galaxy. A true achievement and always fun! • Next semester you’ll carry these tools into electromagnetism, in particular v ...
... • Finally applied these to find complete analog to rotational motion. • We can now describe the mechanical universe over an immense range of distances: a top, a hurricane, and a galaxy. A true achievement and always fun! • Next semester you’ll carry these tools into electromagnetism, in particular v ...
Fall 2013 Physics 172 – Recitation 4 Momentum
... Note that the average force is in the +y direction and is equal in magnitude to what the scale would register if the ball were just sitting on the scale, i.e., the weight of the ball or mg. Notice that the solution does not depend on h, the height from which the ball was released. Explain why! ...
... Note that the average force is in the +y direction and is equal in magnitude to what the scale would register if the ball were just sitting on the scale, i.e., the weight of the ball or mg. Notice that the solution does not depend on h, the height from which the ball was released. Explain why! ...