V - USU Physics
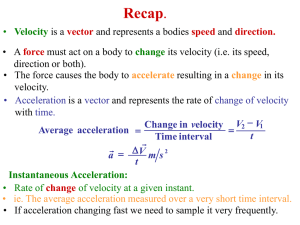
... • Car moved at a constant speed but its direction continuously changed – thus its velocity was changing. • But we now know that velocity changes are produced by an acceleration. • Thus when the car rounds the bend at a constant speed it is accelerating!! • Direction of acceleration is given by DV di ...
... • Car moved at a constant speed but its direction continuously changed – thus its velocity was changing. • But we now know that velocity changes are produced by an acceleration. • Thus when the car rounds the bend at a constant speed it is accelerating!! • Direction of acceleration is given by DV di ...
Chapter 5 Examples
... Example 8: Normal Force m = 10.0 kg mg = 98.0N Find: ax ≠ 0? FN? if ay = 0 FPy = FPsin(30) = 20.0N FPx = FPcos(30) = 34.6N ΣFx = FPx = m ax ax = 34.6N/10.0kg ax = 3.46m/s2 ΣFy = FN + FPy – mg = m ay FN + FPy – mg = 0 FN = mg – FPy= 98.0N – 20.0N FN = 78.0N ...
... Example 8: Normal Force m = 10.0 kg mg = 98.0N Find: ax ≠ 0? FN? if ay = 0 FPy = FPsin(30) = 20.0N FPx = FPcos(30) = 34.6N ΣFx = FPx = m ax ax = 34.6N/10.0kg ax = 3.46m/s2 ΣFy = FN + FPy – mg = m ay FN + FPy – mg = 0 FN = mg – FPy= 98.0N – 20.0N FN = 78.0N ...
Force Motion Pasco Lab
... Newton's Second Law – Constant Force (Force Sensor, Motion Sensor) PURPOSE The purpose of this laboratory activity is to investigate the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. THEORY Newton described the relationship between acceleration, force, and mass as follows: The acceleration of ...
... Newton's Second Law – Constant Force (Force Sensor, Motion Sensor) PURPOSE The purpose of this laboratory activity is to investigate the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration. THEORY Newton described the relationship between acceleration, force, and mass as follows: The acceleration of ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... Since the radius is 3.00m, the amplitude of oscillation in x direction is 3.00m. And the angular frequency is 8.00rad/s. Therefore the equation of motion in x direction is x A cosq 3.00mcos8.00t ...
... Since the radius is 3.00m, the amplitude of oscillation in x direction is 3.00m. And the angular frequency is 8.00rad/s. Therefore the equation of motion in x direction is x A cosq 3.00mcos8.00t ...
PIRA 200 - Mechanics
... Disc 03-07 Raise the mass to the desired height and let it fall freely. If the mass is raised twice as high, the nail will be driven twice as deep. The mass is 4kg. A 16d nail has a mass of about 7g and a 10f has a mass of about 5g. The maximum distance the mass can fall is about 86cm. Option: Calcu ...
... Disc 03-07 Raise the mass to the desired height and let it fall freely. If the mass is raised twice as high, the nail will be driven twice as deep. The mass is 4kg. A 16d nail has a mass of about 7g and a 10f has a mass of about 5g. The maximum distance the mass can fall is about 86cm. Option: Calcu ...
3.5 Application-Spring Mass Systems (Unforced Systems with Friction)
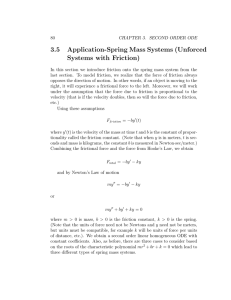
... Example 3.21 (English Units) A 16 pound weight is attached to a spring with friction constant 8lb · s/f t and spring constant 7lb/f t. Write the associated spring/mass ODE. Solution: In the English system, pounds are a unit of force and not mass. To convert, we use the formula from physics F = ma (o ...
... Example 3.21 (English Units) A 16 pound weight is attached to a spring with friction constant 8lb · s/f t and spring constant 7lb/f t. Write the associated spring/mass ODE. Solution: In the English system, pounds are a unit of force and not mass. To convert, we use the formula from physics F = ma (o ...
Roller coaster Activities
... The force of gravity acts between any two objects that have mass. Every mass on earth (large or small) feels the force of gravity pulling it towards the earth. This pull gives you your weight. ...
... The force of gravity acts between any two objects that have mass. Every mass on earth (large or small) feels the force of gravity pulling it towards the earth. This pull gives you your weight. ...
Physics 430
... An important issue is that x(t), being a actual position coordinate, has to be real. In general the first solution looks as if it is complex, while the second solution looks as if it is real. However, this depends on whether the coefficients are real or not. Both C1 and C2 can be complex, but if bot ...
... An important issue is that x(t), being a actual position coordinate, has to be real. In general the first solution looks as if it is complex, while the second solution looks as if it is real. However, this depends on whether the coefficients are real or not. Both C1 and C2 can be complex, but if bot ...