lists of federal prisoners of war who enlisted in the confederate army
... 10TH TENNESSEE REGIMENT was recruited from prisoners in Georgia, beginning with about 250 men in October and November 1864. Initially, recruitment was limited to Irish and other foreign immigrants, but when few agreed, native-born Union soldiers were enlisted. The 10th Tennessee recruited about 150 ...
... 10TH TENNESSEE REGIMENT was recruited from prisoners in Georgia, beginning with about 250 men in October and November 1864. Initially, recruitment was limited to Irish and other foreign immigrants, but when few agreed, native-born Union soldiers were enlisted. The 10th Tennessee recruited about 150 ...
The Cultural Landscape of the Colony of Virginia
... The fort had been cut off from its supply line, and surrendered next day. The Second Battle of Fort Sumter (8 September 1863) was a failed attempt by the Union to re-take the fort. Although the fort was reduced to rubble, it remained in Confederate hands until it was evacuated. ...
... The fort had been cut off from its supply line, and surrendered next day. The Second Battle of Fort Sumter (8 September 1863) was a failed attempt by the Union to re-take the fort. Although the fort was reduced to rubble, it remained in Confederate hands until it was evacuated. ...
The Civil War
... 1850s – Friends started to pick sides 1860, December 20 – South moves-out of D.C. to new home {Capitol of South, Richmond, VA} by February 1861, South had taken 7 friends to the new town 1861, April 12, 4:30am, the 1st mortar round was fired at Fort Sumter, SC 1861 – The 1st major battle of the war ...
... 1850s – Friends started to pick sides 1860, December 20 – South moves-out of D.C. to new home {Capitol of South, Richmond, VA} by February 1861, South had taken 7 friends to the new town 1861, April 12, 4:30am, the 1st mortar round was fired at Fort Sumter, SC 1861 – The 1st major battle of the war ...
File unit 7 vocabulary word wall
... emancipation of African-American slaves throughout the Confederate South. Celebrated on June 19 and recognized as a state holiday or special day of observance in most states. ...
... emancipation of African-American slaves throughout the Confederate South. Celebrated on June 19 and recognized as a state holiday or special day of observance in most states. ...
Anaconda - Civil War Rumblings
... chokehold on that portion of the Mississippi River. April 27, 1862 -- After Admiral Farragut's fleet sails past Forts Jackson and St Philip on its way to New Orleans, these forts surrender, totally removing any Confederate resistance to Northern action on the Mississippi River as far up to New Orlea ...
... chokehold on that portion of the Mississippi River. April 27, 1862 -- After Admiral Farragut's fleet sails past Forts Jackson and St Philip on its way to New Orleans, these forts surrender, totally removing any Confederate resistance to Northern action on the Mississippi River as far up to New Orlea ...
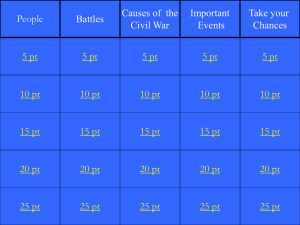
Civil War Jeopardy Review
... A document that declared an end to slavery in the states that were rebelling from the Union; and gave the Union a new cause for which to fight. ...
... A document that declared an end to slavery in the states that were rebelling from the Union; and gave the Union a new cause for which to fight. ...
Civil War Leaders and Battles part 1
... • South Carolina ceded December 20, 1860 By February 1, 1861 seven states had seceded from the United States. (South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana and Texas) ...
... • South Carolina ceded December 20, 1860 By February 1, 1861 seven states had seceded from the United States. (South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana and Texas) ...
Chapter 12 Review
... Chapter 12 Review 1. Where did the Confederates set up their capital after Virginia, North Carolina, Tennessee, and Arkansas seceded? __________________________________________ 2. What was the name of the General who captured Fort Sumter? __________________________________________ 3. What stream did ...
... Chapter 12 Review 1. Where did the Confederates set up their capital after Virginia, North Carolina, Tennessee, and Arkansas seceded? __________________________________________ 2. What was the name of the General who captured Fort Sumter? __________________________________________ 3. What stream did ...
05 USH (06-09) (1848-1877) Period 5. Westward Growth
... Freed slaves in rebelling states NOT border states (1) D. Vicksburg (1) (2) (3) (May 1863) Union victory-completed part of the Anaconda Plan ...
... Freed slaves in rebelling states NOT border states (1) D. Vicksburg (1) (2) (3) (May 1863) Union victory-completed part of the Anaconda Plan ...
usnotesmarch23sumter.doc
... CQ: Describe the Battle of Fort Sumter? What was President Lincoln’s view on Secession? As the Civil War began, what was Lincoln’s goal for the Union? The First Battle of the Civil War Fort Sumter – was the first battle of the Civil War. It was not a significant battle, just in that at was the f ...
... CQ: Describe the Battle of Fort Sumter? What was President Lincoln’s view on Secession? As the Civil War began, what was Lincoln’s goal for the Union? The First Battle of the Civil War Fort Sumter – was the first battle of the Civil War. It was not a significant battle, just in that at was the f ...
Chapter
... his siege of Vicksburg. In the east, after the hardwon Union victory at Gettysburg, the South never again invaded the North. In 1864 and 1865, Union armies gradually closed in on Lee’s Confederate forces in Virginia. Leaving Atlanta in flames, Sherman marched to the Georgia coast, took Savannah, the ...
... his siege of Vicksburg. In the east, after the hardwon Union victory at Gettysburg, the South never again invaded the North. In 1864 and 1865, Union armies gradually closed in on Lee’s Confederate forces in Virginia. Leaving Atlanta in flames, Sherman marched to the Georgia coast, took Savannah, the ...
March 3, 1863 - Net Start Class
... Abraham Lincoln is elected President. November 1860 Abraham Lincoln, who had declared "Government cannot endure permanently half slave, half free..." is elected president, the first Republican, receiving 180 of 303 possible electoral votes and 40 percent of the popular vote. ...
... Abraham Lincoln is elected President. November 1860 Abraham Lincoln, who had declared "Government cannot endure permanently half slave, half free..." is elected president, the first Republican, receiving 180 of 303 possible electoral votes and 40 percent of the popular vote. ...
Civil War Erupts Vocabulary Copy the vocabulary and the definitions
... • States between the North and the South - Missouri, Kentucky, and Maryland ...
... • States between the North and the South - Missouri, Kentucky, and Maryland ...
17 The Civil War (1860 - 1865) 17.1 Politics Before The War In the
... General P. G. T. Beauregard demanded that Union Major Robert Anderson surrender Fort Sumter in Charleston, South Carolina, which was an important fort because of its strategic position, which was to defend Charleston's harbor. The supplies of the besieged forts would only last a few weeks. The Union ...
... General P. G. T. Beauregard demanded that Union Major Robert Anderson surrender Fort Sumter in Charleston, South Carolina, which was an important fort because of its strategic position, which was to defend Charleston's harbor. The supplies of the besieged forts would only last a few weeks. The Union ...
Civil War - Appoquinimink High School
... Some tried to make changes: 1. Clara Barton – gave 1st aide to troops & started American Red ...
... Some tried to make changes: 1. Clara Barton – gave 1st aide to troops & started American Red ...
North and South
... Maryland, Delaware, W. Virginia – these had slaves At onset of war, Lincoln declared: he wasn’t fighting to free Blacks, but to save the Union. Maryland: Lincoln declared martial law - sent in Union troops to W. Virginia and Missouri. “Indian Territory” – Most of the 5 Civilized tribes (some owned s ...
... Maryland, Delaware, W. Virginia – these had slaves At onset of war, Lincoln declared: he wasn’t fighting to free Blacks, but to save the Union. Maryland: Lincoln declared martial law - sent in Union troops to W. Virginia and Missouri. “Indian Territory” – Most of the 5 Civilized tribes (some owned s ...
Civil War Battle begins
... were conscripted (drafted to serve in the armies) • Some men received bounties (money) to sign up; some signed up, received the bounty, then deserted (ran away) • Poorer men sometimes accepted money to fight in place of wealthier men who didn’t want to serve • Some 178,985 enlisted men served in bla ...
... were conscripted (drafted to serve in the armies) • Some men received bounties (money) to sign up; some signed up, received the bounty, then deserted (ran away) • Poorer men sometimes accepted money to fight in place of wealthier men who didn’t want to serve • Some 178,985 enlisted men served in bla ...
The Civil War - The Goals of War Change
... Bloody fighting made many Northerners want to hurt the South as much as possible (Especially following the Battle of Antietam - September 1862) ...
... Bloody fighting made many Northerners want to hurt the South as much as possible (Especially following the Battle of Antietam - September 1862) ...
CIVIL WAR BATTLES
... • Significance: Destroyed everything that could help the South in the war. ...
... • Significance: Destroyed everything that could help the South in the war. ...
Secession and Fort Sumter
... By February of 1861 ________________, ______________________, __________________, ______________________, __________________, and ____________________ (+ South Carolina) had seceded. On February 4th delegates from these states met to form a new ________________. The _________________________________ ...
... By February of 1861 ________________, ______________________, __________________, ______________________, __________________, and ____________________ (+ South Carolina) had seceded. On February 4th delegates from these states met to form a new ________________. The _________________________________ ...
Civil War - Cobb Learning
... Confederacy to death by capturing the Mississippi River and cutting off Louisiana, Texas, and Arkansas • Capturing Richmond, the capital, might have ended the war early, but General Robert E. Lee’s Confederate Army prevented that for years ...
... Confederacy to death by capturing the Mississippi River and cutting off Louisiana, Texas, and Arkansas • Capturing Richmond, the capital, might have ended the war early, but General Robert E. Lee’s Confederate Army prevented that for years ...
Bryan Price Audio Script When did the Battle take place? The Battle
... 4. Why did the South want to attack Fort Sumter? 1. South Carolina wanted Union soldiers to leave the fort because they believed that the Fort now belonged to them. They did not want the Union to continue to interfere with their affairs. 5. Who were the main people in charge? 1. Major Robert Anderso ...
... 4. Why did the South want to attack Fort Sumter? 1. South Carolina wanted Union soldiers to leave the fort because they believed that the Fort now belonged to them. They did not want the Union to continue to interfere with their affairs. 5. Who were the main people in charge? 1. Major Robert Anderso ...