NEWSLETTER - Colonel EW Taylor Camp #1777
... John enlisted in 1863 and served the Confederacy as a private in Co. B, 37th Tennessee Infantry. He took part in most of the actions in which the Army of Tennessee fought after that. He was paroled in 1865. John died in 1895 and was buried not far from his home in a small hilltop family cemetery sta ...
... John enlisted in 1863 and served the Confederacy as a private in Co. B, 37th Tennessee Infantry. He took part in most of the actions in which the Army of Tennessee fought after that. He was paroled in 1865. John died in 1895 and was buried not far from his home in a small hilltop family cemetery sta ...
Fort Sumter
... Lincoln did not want to give the fort up. He had been told that there weren't enough supplies in the fort to defend it. Lincoln came up with a plan. He would send a supply ship to the fort and tell the South Carolina governor it was coming. If the ship got through, the fort would have enough supplie ...
... Lincoln did not want to give the fort up. He had been told that there weren't enough supplies in the fort to defend it. Lincoln came up with a plan. He would send a supply ship to the fort and tell the South Carolina governor it was coming. If the ship got through, the fort would have enough supplie ...
Fort Sumter
... Fort Sumter Abraham Lincoln won the election in 1860. He would be the country's next president. At this point, it was clear that the country could not avoid a war. Within weeks of the election, Southern states started to secede from the Union. Fort Sumter was a fort in South Carolina. It sat near th ...
... Fort Sumter Abraham Lincoln won the election in 1860. He would be the country's next president. At this point, it was clear that the country could not avoid a war. Within weeks of the election, Southern states started to secede from the Union. Fort Sumter was a fort in South Carolina. It sat near th ...
Civil War - Cherokee County Schools
... • Discord in government prevents Davis from governing effectively • North begins to question Lincoln continuing the War ...
... • Discord in government prevents Davis from governing effectively • North begins to question Lincoln continuing the War ...
chapter 8 powerpoint - Polk School District
... • Food, items for clothes, and basic items were in short supply, especially in the South • Staples like flour, coffee, and sugar were very expensive or hard to acquire • Women tried to keep their families fed and sheltered despite the difficulties • Many fought disguised as men; others served as spi ...
... • Food, items for clothes, and basic items were in short supply, especially in the South • Staples like flour, coffee, and sugar were very expensive or hard to acquire • Women tried to keep their families fed and sheltered despite the difficulties • Many fought disguised as men; others served as spi ...
KEY TERMS, IDEAS,
... *booster the North’s morale Border States had slaves (__________, Kentucky, Maryland, Delaware, West Virginia) *Border states supported UNION so Lincoln didn’t want them to ___________ or break away from the UNION) Camp in the South- more than 13,000 died from starvation, _________ + exposure. _____ ...
... *booster the North’s morale Border States had slaves (__________, Kentucky, Maryland, Delaware, West Virginia) *Border states supported UNION so Lincoln didn’t want them to ___________ or break away from the UNION) Camp in the South- more than 13,000 died from starvation, _________ + exposure. _____ ...
Civil War Notes doc
... Northern _______________ believe it will prolong the war by antagonizing the South. Confederates outraged: more determined to win o Both Sides Face Political Problems: North Dissent: In Maryland, _________________ suspends _______________: a court order that requires authorities to bring a p ...
... Northern _______________ believe it will prolong the war by antagonizing the South. Confederates outraged: more determined to win o Both Sides Face Political Problems: North Dissent: In Maryland, _________________ suspends _______________: a court order that requires authorities to bring a p ...
The Civil War in Indian Territory Divided Loyalties A Conflict Coming
... Opothleyahola, a large number of Creek followers, and about 6,500 from other tribes appealed to the “Great Father” in Washington for help. Aware of the Loyal Creek’s appeal to Washington, Cooper’s 2,000 man regiment attacked the “Loyal” on November 19th, 1861 just northwest of Tulsa); when the skirm ...
... Opothleyahola, a large number of Creek followers, and about 6,500 from other tribes appealed to the “Great Father” in Washington for help. Aware of the Loyal Creek’s appeal to Washington, Cooper’s 2,000 man regiment attacked the “Loyal” on November 19th, 1861 just northwest of Tulsa); when the skirm ...
Chapter 13 – Civil War
... • Confederates wanted to take control of the base since it was in the new CSA. • When Union forces refused to leave, the Confederacy opened fire and took back Fort Sumter and raised the Stars and Bars. • The Civil War officially began on April 12, 1861. ...
... • Confederates wanted to take control of the base since it was in the new CSA. • When Union forces refused to leave, the Confederacy opened fire and took back Fort Sumter and raised the Stars and Bars. • The Civil War officially began on April 12, 1861. ...
The Civil War: Key Battles & Turning Points
... The Confederate army was pushing further north. When they reached Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, the Union army was ready to stop them. Led by Robert E. Lee, the Confederate army fought the Union army for three days. As the Confederates continued to fight, more Union soldiers joined the battle against th ...
... The Confederate army was pushing further north. When they reached Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, the Union army was ready to stop them. Led by Robert E. Lee, the Confederate army fought the Union army for three days. As the Confederates continued to fight, more Union soldiers joined the battle against th ...
Election of 1860 Ppt - Taylor County Schools
... nominated Abraham Lincoln Democrats split • Northern Democrats – Stephen Douglas • Southern Democrats – John C. Breckenridge Constitutional ...
... nominated Abraham Lincoln Democrats split • Northern Democrats – Stephen Douglas • Southern Democrats – John C. Breckenridge Constitutional ...
The Civil War: Important Battles and Events
... ► Union General William Techumseh Sherman launched his Atlanta Campaign Several battles fought from Tennessee to Atlanta The Battle of Kennesaw Mtn. led to heavy Union losses, but did not deter the Union forces ...
... ► Union General William Techumseh Sherman launched his Atlanta Campaign Several battles fought from Tennessee to Atlanta The Battle of Kennesaw Mtn. led to heavy Union losses, but did not deter the Union forces ...
this page in PDF format
... Hoke’s division of 6,000 men had arrived in Wilmington and would soon be to his rear. Porter was incensed and blamed the failed attempt to take the fort on Butler’s lack of courage and mismanagement. Following the Christmas debacle, the Union high command replaced Butler with General Alfred Terry an ...
... Hoke’s division of 6,000 men had arrived in Wilmington and would soon be to his rear. Porter was incensed and blamed the failed attempt to take the fort on Butler’s lack of courage and mismanagement. Following the Christmas debacle, the Union high command replaced Butler with General Alfred Terry an ...
What was his role during the Civil War?
... The Civil War began at Fort Sumter. Fort Sumter was a US military fort behind Confederate lines. The Confederacy wanted Fort Sumter to surrender. Lincoln refused. Before he could resupply it, the South attacked. (p. 357) ...
... The Civil War began at Fort Sumter. Fort Sumter was a US military fort behind Confederate lines. The Confederacy wanted Fort Sumter to surrender. Lincoln refused. Before he could resupply it, the South attacked. (p. 357) ...
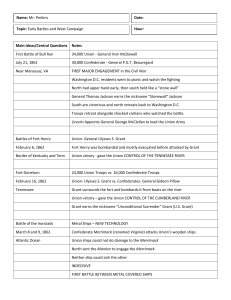
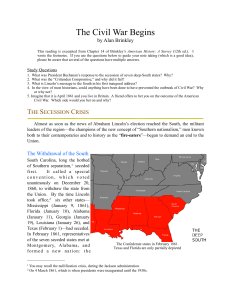
Secession Crisis-Brinkley - Scarsdale Public Schools
... was able by 1862 to manufacture almost all its own war materials. The South had almost no industry at all and, despite impressive efforts to increase its manufacturing capacity, had to rely on imports from Europe throughout the war. In addition, the North had a much better transportation system than ...
... was able by 1862 to manufacture almost all its own war materials. The South had almost no industry at all and, despite impressive efforts to increase its manufacturing capacity, had to rely on imports from Europe throughout the war. In addition, the North had a much better transportation system than ...
Lincoln`s Election and Fort Sumter PPT
... • The Confederate troops FIRED on the fort, Major Anderson and his men ran out of ammunition and had to give up. ...
... • The Confederate troops FIRED on the fort, Major Anderson and his men ran out of ammunition and had to give up. ...
Study Guide for SS8H6 The student will analyze the impact of the
... 17-18. Who were the Union and Confederate generals at the battle of Chickamauga? Rosecrans (U) v. Bragg (C) 19. What was the battle of Kennesaw Mountain? Between Johnston (C) and Sherman (U) – confederate victory 20. Who were the Confederate and Union generals at the above battle? See above 21. What ...
... 17-18. Who were the Union and Confederate generals at the battle of Chickamauga? Rosecrans (U) v. Bragg (C) 19. What was the battle of Kennesaw Mountain? Between Johnston (C) and Sherman (U) – confederate victory 20. Who were the Confederate and Union generals at the above battle? See above 21. What ...
Document
... Pictures in order across: Arsenal Incident, election 1860, Fort Sumter, Red River Campaign, Arkansas Secession, Pea ridge, battle of Helena Battle of Prairie Grove, battle of little Rock Appomattox courthouse ...
... Pictures in order across: Arsenal Incident, election 1860, Fort Sumter, Red River Campaign, Arkansas Secession, Pea ridge, battle of Helena Battle of Prairie Grove, battle of little Rock Appomattox courthouse ...
File
... -South’s goal was its own survival as a nation, thus its strategy was to “prepare and wait” on the enemy – to fight a defensive war • Southern army stayed in South, chose battlefields, waited on North to attack Early in the war, Confederate President Jefferson Davis imagined a struggle similar to th ...
... -South’s goal was its own survival as a nation, thus its strategy was to “prepare and wait” on the enemy – to fight a defensive war • Southern army stayed in South, chose battlefields, waited on North to attack Early in the war, Confederate President Jefferson Davis imagined a struggle similar to th ...
history of us book 6
... 57. After this Arkansas battle, Confederate soldiers massacred some 300 AfricanAmerican defenders of this fort. [106] ______________________ ...
... 57. After this Arkansas battle, Confederate soldiers massacred some 300 AfricanAmerican defenders of this fort. [106] ______________________ ...