Start of the Civil War
... South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Texas, Virginia, Arkansas, Tennessee, North Carolina Created “Confederate States of America” President = Jefferson Davis General = Robert E. Lee ...
... South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Texas, Virginia, Arkansas, Tennessee, North Carolina Created “Confederate States of America” President = Jefferson Davis General = Robert E. Lee ...
Part One: - HASANAPUSH
... Overall Strategy of the War MAP 16.1a Overall Strategy of the Civil War The initial Northern strategy for subduing the South, the so-called Anaconda Plan, entailed strangling it by a blockade at sea and obtaining control of the Mississippi River. But at the end of 1862, it was clear that the South’ ...
... Overall Strategy of the War MAP 16.1a Overall Strategy of the Civil War The initial Northern strategy for subduing the South, the so-called Anaconda Plan, entailed strangling it by a blockade at sea and obtaining control of the Mississippi River. But at the end of 1862, it was clear that the South’ ...
CivilWarTimeline
... Robert E. Lee invaded Pennsylvania in June 1863. He was hoping to threaten Washington and Philadelphia, to breed Northern morale, and to gain recognition and independence for the Southern Confederacy. At Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, Lee's Army of Northern Virginia met the Army of the Potomac unexpected ...
... Robert E. Lee invaded Pennsylvania in June 1863. He was hoping to threaten Washington and Philadelphia, to breed Northern morale, and to gain recognition and independence for the Southern Confederacy. At Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, Lee's Army of Northern Virginia met the Army of the Potomac unexpected ...
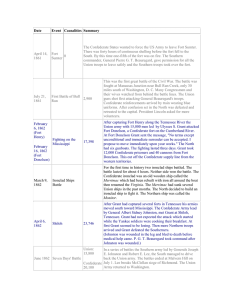
American Civil War: War Erupts Cornell Notes
... The Confederates attacked the fort before the supply ships arrived Anaconda Plan – three part plan to squeeze the life out of the Confederacy Naval blockade of Confederate coastline Take control of Mississippi River to split Confederacy in two Capture Richmond, VA – the Confederate capital Fig ...
... The Confederates attacked the fort before the supply ships arrived Anaconda Plan – three part plan to squeeze the life out of the Confederacy Naval blockade of Confederate coastline Take control of Mississippi River to split Confederacy in two Capture Richmond, VA – the Confederate capital Fig ...
File
... gunboats. The fighting lasted three days. Grant took 12,000 Confederate prisoners and 40 cannons from Fort Donelson. This cut off the Confederate supply line from the western territories. ...
... gunboats. The fighting lasted three days. Grant took 12,000 Confederate prisoners and 40 cannons from Fort Donelson. This cut off the Confederate supply line from the western territories. ...
Chapter 22 Girding for War: The North and the South, 1861-1865
... countries would try to gain access into the Americas again ...
... countries would try to gain access into the Americas again ...
THE AMERICAN CIVIL WAR
... April 3, 1865 - Grant took Richmond Va. - final blow to Lee's army Lee surrenders on April 9, 1865 at APPOMATTOX COURTHOUSE All Confederate troops forced to take an oath of loyalty to U.S. otherwise, terms of surrender were lenient ...
... April 3, 1865 - Grant took Richmond Va. - final blow to Lee's army Lee surrenders on April 9, 1865 at APPOMATTOX COURTHOUSE All Confederate troops forced to take an oath of loyalty to U.S. otherwise, terms of surrender were lenient ...
On July 17, 1862, Congress passed two acts
... Approximately 180,000 African Americans comprising 163 units served in the Union Army during the Civil War, and many more African Americans served in the Union Navy. Both free African-Americans and runaway slaves joined the fight. ...
... Approximately 180,000 African Americans comprising 163 units served in the Union Army during the Civil War, and many more African Americans served in the Union Navy. Both free African-Americans and runaway slaves joined the fight. ...
The Civil War
... USS Rattler, a small tinclad gunboat, led an active career on the Mississippi. ...
... USS Rattler, a small tinclad gunboat, led an active career on the Mississippi. ...
8thCivilWarPPTStudent
... • fought in and around the town of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, • The largest number of casualties in the American Civil War on BOTH sides • Is frequently cited as the war's turning point. • Union Maj. Gen. George Gordon Meade defeated attacks by Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee, ending Lee's invasion of ...
... • fought in and around the town of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, • The largest number of casualties in the American Civil War on BOTH sides • Is frequently cited as the war's turning point. • Union Maj. Gen. George Gordon Meade defeated attacks by Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee, ending Lee's invasion of ...
Notes Civil War
... settlement between the North and the South. • The Emancipation Proclamation caused an outcry to rise from the South who said that Lincoln was trying to stir up slave rebellion. • The North now had a much stronger moral cause. It had to preserve the Union and free the slaves. ...
... settlement between the North and the South. • The Emancipation Proclamation caused an outcry to rise from the South who said that Lincoln was trying to stir up slave rebellion. • The North now had a much stronger moral cause. It had to preserve the Union and free the slaves. ...
Chapter 20 Study Guide
... - Lincoln proclaimed a blockade without Congressional approval (they were not in session) - He increased the size of the army, something only Congress could do (they approved it later) - He ordered the Treasury dept. to transfer $ for military purpose to private citizens (in conflict with the Consti ...
... - Lincoln proclaimed a blockade without Congressional approval (they were not in session) - He increased the size of the army, something only Congress could do (they approved it later) - He ordered the Treasury dept. to transfer $ for military purpose to private citizens (in conflict with the Consti ...
Slide 1
... Protecting Washington, D.C. After Bull Run, Lincoln calls for 1 million additional soldiers Appoints General George McClellan to lead Army of the Potomac ...
... Protecting Washington, D.C. After Bull Run, Lincoln calls for 1 million additional soldiers Appoints General George McClellan to lead Army of the Potomac ...
Chapter 1
... A Federal brigade repulses a Confederate assault at Williamsburg, Virginia, in 1862, as the Peninsula Campaign presses toward Richmond. General Winfield Scott Hancock commanded the troops. For his success in this action, Hancock earned the nickname ...
... A Federal brigade repulses a Confederate assault at Williamsburg, Virginia, in 1862, as the Peninsula Campaign presses toward Richmond. General Winfield Scott Hancock commanded the troops. For his success in this action, Hancock earned the nickname ...
Civil War Notes 1 - Bibb County Schools
... _____________________ is the belief that states have the right to make decisions about issues that concern them. The __________________ states held this belief. ...
... _____________________ is the belief that states have the right to make decisions about issues that concern them. The __________________ states held this belief. ...
Notes
... the loss of Atlanta and Savannah, the Confederate war effort struggled to keep going ► The only Confederate troops left were Lee’s troops in Virginia, and a small group in North Carolina ► Most Confederate troops had given up and gone home ► They tried one more time to fight in March 1865, but faile ...
... the loss of Atlanta and Savannah, the Confederate war effort struggled to keep going ► The only Confederate troops left were Lee’s troops in Virginia, and a small group in North Carolina ► Most Confederate troops had given up and gone home ► They tried one more time to fight in March 1865, but faile ...
5.2 Sectionalism, 1850
... Secession & the Effects of Fort Sumter Civil War was not technically between slave states & free states (the “border states” of MO, KY, DE, MD did not secede) ...
... Secession & the Effects of Fort Sumter Civil War was not technically between slave states & free states (the “border states” of MO, KY, DE, MD did not secede) ...
The Civil War So Far*
... Hanover County, Virginia on May 31- June 12, 1864. Total casualties were more than 70,000. Winner: Confederates ...
... Hanover County, Virginia on May 31- June 12, 1864. Total casualties were more than 70,000. Winner: Confederates ...
The Battle of Bull Run (Manassas)
... •1st major battle of the Civil War ended in a victory for the Confederacy. •It became known as the First Battle of Bull Run because the following year a battle occurred at almost exactly the same site. •Approximately 35,000 troops were involved on each side. •The Union suffered about 2,900 casualtie ...
... •1st major battle of the Civil War ended in a victory for the Confederacy. •It became known as the First Battle of Bull Run because the following year a battle occurred at almost exactly the same site. •Approximately 35,000 troops were involved on each side. •The Union suffered about 2,900 casualtie ...
Civil War Study Guide
... and reforming prisons, Dix became the Superintendent of Nurses for the Union Army. In addition, she organized many women to serve as military nurses. Sally Louisa Tompkins- Southern woman who opened a hospital for the south in Richmond Virginia. Her hospital’s survival rate was at ...
... and reforming prisons, Dix became the Superintendent of Nurses for the Union Army. In addition, she organized many women to serve as military nurses. Sally Louisa Tompkins- Southern woman who opened a hospital for the south in Richmond Virginia. Her hospital’s survival rate was at ...
Glory Movie Guide and Assignment
... Federal Law of 1792 – Bans African-Americans from joining the Army even though many had fought bravely in the American Revolution Emancipation Proclamation – January 1, 1863, After the Union victory at Antietam, Lincoln issues the Emancipation Proclamation that frees the slaves in the Confederacy. W ...
... Federal Law of 1792 – Bans African-Americans from joining the Army even though many had fought bravely in the American Revolution Emancipation Proclamation – January 1, 1863, After the Union victory at Antietam, Lincoln issues the Emancipation Proclamation that frees the slaves in the Confederacy. W ...
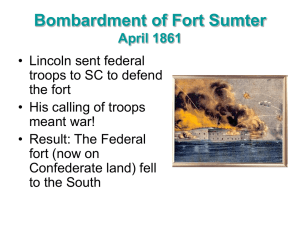
the attack on fort sumter
... should use force to dismiss the Union from remaining forts • Jefferson Davis, like Lincoln, preferred not to be seen as the aggressor – Would lose valuable political points ...
... should use force to dismiss the Union from remaining forts • Jefferson Davis, like Lincoln, preferred not to be seen as the aggressor – Would lose valuable political points ...
The Civil War
... Conscription in the Union 1863: 18-35 year old men $300 buyout Widespread public outcry Increased political corruption in the cities July 11, 1863: Riot in New York Irish Catholics Hatred of Blacks and the wealthy Massive violence ...
... Conscription in the Union 1863: 18-35 year old men $300 buyout Widespread public outcry Increased political corruption in the cities July 11, 1863: Riot in New York Irish Catholics Hatred of Blacks and the wealthy Massive violence ...
Love Story Notes part 2
... Union Victories in the West -- Lincoln’s New Hero – US Grant Union strategy for the West was to capture and control the Mississippi River General Ulysses S Grant was in charge for the Union February 1862, Grant attacked and captured Forts Henry and Donelson in Tennessee These Confederate for ...
... Union Victories in the West -- Lincoln’s New Hero – US Grant Union strategy for the West was to capture and control the Mississippi River General Ulysses S Grant was in charge for the Union February 1862, Grant attacked and captured Forts Henry and Donelson in Tennessee These Confederate for ...